Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (352.7 KB).
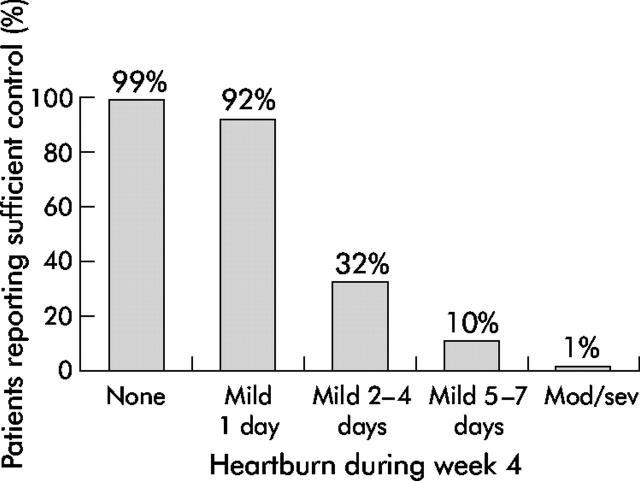
Figure 1 .
Most patients accept up to one day with mild heartburn per week during treatment. Few accept more frequent heartburn or moderate/severe heartburn.10
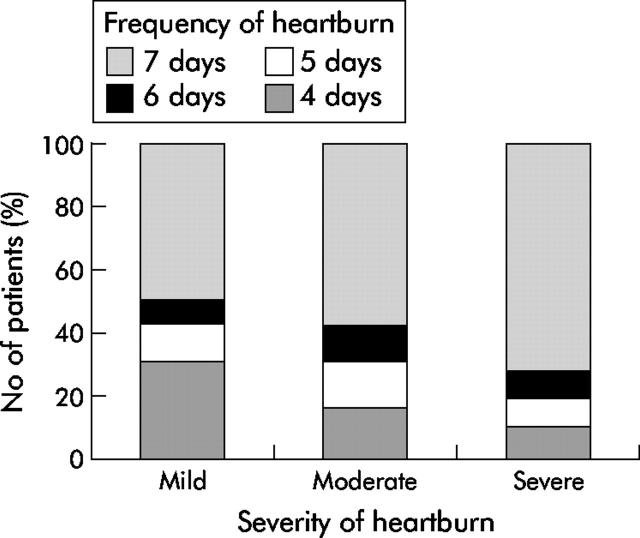
Figure 2 .
Patients with severe heartburn are likely to have more frequent heartburn than those with mild heartburn (AstraZeneca, data on file).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achem S. R., Kolts B. E., MacMath T., Richter J., Mohr D., Burton L., Castell D. O. Effects of omeprazole versus placebo in treatment of noncardiac chest pain and gastroesophageal reflux. Dig Dis Sci. 1997 Oct;42(10):2138–2145. doi: 10.1023/a:1018843223263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adang R. P., Vismans J. F., Talmon J. L., Hasman A., Ambergen A. W., Stockbrügger R. W. Appropriateness of indications for diagnostic upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: association with relevant endoscopic disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 1995 Nov;42(5):390–397. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(95)70037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allgood P. C., Bachmann M. Medical or surgical treatment for chronic gastrooesophageal reflux? A systematic review of published evidence of effectiveness. Eur J Surg. 2000 Sep;166(9):713–721. doi: 10.1080/110241500750008475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An evidence-based appraisal of reflux disease management--the Genval Workshop Report. Gut. 1999 Apr;44 (Suppl 2):S1–16. doi: 10.1136/gut.44.2008.s1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D., Paré P., Pericak D., Pyzyk M., Canadian Pantoprazole GERD Study Group Symptom relief in gastroesophageal reflux disease: a randomized, controlled comparison of pantoprazole and nizatidine in a mixed patient population with erosive esophagitis or endoscopy-negative reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001 Oct;96(10):2849–2857. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.4237_a.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bani-Hani K., Sue-Ling H., Johnston D., Axon A. T., Martin I. G. Barrett's oesophagus: results from a 13-year surveillance programme. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000 Jun;12(6):649–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate C. M., Green J. R., Axon A. T., Murray F. E., Tildesley G., Emmas C. E., Taylor M. D. Omeprazole is more effective than cimetidine for the relief of all grades of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease-associated heartburn, irrespective of the presence or absence of endoscopic oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1997 Aug;11(4):755–763. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1997.00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate C. M., Griffin S. M., Keeling P. W., Axon A. T., Dronfield M. W., Chapman R. W., O'Donoghue D., Calam J., Crowe J., Mountfords R. A. Reflux symptom relief with omeprazole in patients without unequivocal oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1996 Aug;10(4):547–555. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1996.44186000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belafsky P. C., Postma G. N., Koufman J. A. Laryngopharyngeal reflux symptoms improve before changes in physical findings. Laryngoscope. 2001 Jun;111(6):979–981. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200106000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blot W. J., Devesa S. S., Fraumeni J. F., Jr Continuing climb in rates of esophageal adenocarcinoma: an update. JAMA. 1993 Sep 15;270(11):1320–1320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blot W. J., Devesa S. S., Kneller R. W., Fraumeni J. F., Jr Rising incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and gastric cardia. JAMA. 1991 Mar 13;265(10):1287–1289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branski Ryan C., Bhattacharyya Neil, Shapiro Jo. The reliability of the assessment of endoscopic laryngeal findings associated with laryngopharyngeal reflux disease. Laryngoscope. 2002 Jun;112(6):1019–1024. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200206000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bytzer P., Christensen P. B., Damkier P., Vinding K., Seersholm N. Adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and Barrett's esophagus: a population-based study. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999 Jan;94(1):86–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.00776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron A. J., Lomboy C. T. Barrett's esophagus: age, prevalence, and extent of columnar epithelium. Gastroenterology. 1992 Oct;103(4):1241–1245. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91510-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson R., Dent J., Bolling-Sternevald E., Johnsson F., Junghard O., Lauritsen K., Riley S., Lundell L. The usefulness of a structured questionnaire in the assessment of symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998 Oct;33(10):1023–1029. doi: 10.1080/003655298750026697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson R., Dent J., Watts R., Riley S., Sheikh R., Hatlebakk J., Haug K., de Groot G., van Oudvorst A., Dalväg A. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in primary care: an international study of different treatment strategies with omeprazole. International GORD Study Group. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998 Feb;10(2):119–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson R., Galmiche J. P., Dent J., Lundell L., Frison L. Prognostic factors influencing relapse of oesophagitis during maintenance therapy with antisecretory drugs: a meta-analysis of long-term omeprazole trials. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1997 Jun;11(3):473–482. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1997.00167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell Donald O., Kahrilas Peter J., Richter Joel E., Vakil Nimish B., Johnson David A., Zuckerman Seth, Skammer Wendy, Levine Jeffrey G. Esomeprazole (40 mg) compared with lansoprazole (30 mg) in the treatment of erosive esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002 Mar;97(3):575–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05532.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers J., Cooke R., Anggiansah A., Owen W. Effect of omeprazole in patients with chest pain and normal coronary anatomy: initial experience. Int J Cardiol. 1998 Jun 1;65(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5273(98)00093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba N., De Gara C. J., Wilkinson J. M., Hunt R. H. Speed of healing and symptom relief in grade II to IV gastroesophageal reflux disease: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 1997 Jun;112(6):1798–1810. doi: 10.1053/gast.1997.v112.pm9178669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow W. H., Finkle W. D., McLaughlin J. K., Frankl H., Ziel H. K., Fraumeni J. F., Jr The relation of gastroesophageal reflux disease and its treatment to adenocarcinomas of the esophagus and gastric cardia. JAMA. 1995 Aug 9;274(6):474–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condra L. J., Morreale A. P., Stolley S. N., Marcus D. Assessment of patient satisfaction with a formulary switch from omeprazole to lansoprazole in gastroesophageal reflux disease maintenance therapy. Am J Manag Care. 1999 May;5(5):631–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conio M., Cameron A. J., Romero Y., Branch C. D., Schleck C. D., Burgart L. J., Zinsmeister A. R., Melton L. J., 3rd, Locke G. R., 3rd Secular trends in the epidemiology and outcome of Barrett's oesophagus in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Gut. 2001 Mar;48(3):304–309. doi: 10.1136/gut.48.3.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csendes A., Smok G., Burdiles P., Quesada F., Huertas C., Rojas J., Korn O. Prevalence of Barrett's esophagus by endoscopy and histologic studies: a prospective evaluation of 306 control subjects and 376 patients with symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux. Dis Esophagus. 2000;13(1):5–11. doi: 10.1046/j.1442-2050.2000.00065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaney B. C. Why do dyspeptic patients over the age of 50 consult their general practitioner? A qualitative investigation of health beliefs relating to dyspepsia. Br J Gen Pract. 1998 Aug;48(433):1481–1485. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earlam R. J. Production of epigastric pain in duodenal ulcer by lower oesophageal acid perfusion. Br Med J. 1970 Dec 19;4(5737):714–716. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5737.714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisendrath P., Tack J., Devière J. Diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease in general practice: a Belgian national survey. Endoscopy. 2002 Dec;34(12):998–1003. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-35831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elf M., Wikblad K. Satisfaction with information and quality of life in patients undergoing chemotherapy for cancer. The role of individual differences in information preference. Cancer Nurs. 2001 Oct;24(5):351–356. doi: 10.1097/00002820-200110000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow D. C., Vaughan T. L., Hansten P. D., Stanford J. L., Risch H. A., Gammon M. D., Chow W. H., Dubrow R., Ahsan H., Mayne S. T. Use of aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of esophageal and gastric cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1998 Feb;7(2):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow D. C., Vaughan T. L., Sweeney C., Gammon M. D., Chow W. H., Risch H. A., Stanford J. L., Hansten P. D., Mayne S. T., Schoenberg J. B. Gastroesophageal reflux disease, use of H2 receptor antagonists, and risk of esophageal and gastric cancer. Cancer Causes Control. 2000 Mar;11(3):231–238. doi: 10.1023/a:1008913828105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farup C., Kleinman L., Sloan S., Ganoczy D., Chee E., Lee C., Revicki D. The impact of nocturnal symptoms associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease on health-related quality of life. Arch Intern Med. 2001 Jan 8;161(1):45–52. doi: 10.1001/archinte.161.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farup P. G., Hovde O., Torp R., Wetterhus S. Patients with functional dyspepsia responding to omeprazole have a characteristic gastro-oesophageal reflux pattern. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1999 Jun;34(6):575–579. doi: 10.1080/003655299750026029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. Empirical trials in treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dig Dis. 2000;18(1):20–26. doi: 10.1159/000016930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R., Fennerty M. B., Ofman J. J., Gralnek I. M., Johnson C., Camargo E., Sampliner R. E. The clinical and economic value of a short course of omeprazole in patients with noncardiac chest pain. Gastroenterology. 1998 Jul;115(1):42–49. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R., Ofman J. J., Gralnek I. M., Johnson C., Camargo E., Sampliner R. E., Fennerty M. B. Clinical and economic assessment of the omeprazole test in patients with symptoms suggestive of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Arch Intern Med. 1999 Oct 11;159(18):2161–2168. doi: 10.1001/archinte.159.18.2161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R., Ofman J. J., Sampliner R. E., Camargo L., Wendel C., Fennerty M. B. The omeprazole test is as sensitive as 24-h oesophageal pH monitoring in diagnosing gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in symptomatic patients with erosive oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000 Apr;14(4):389–396. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2000.00733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraz M. B., Quaresma M. R., Aquino L. R., Atra E., Tugwell P., Goldsmith C. H. Reliability of pain scales in the assessment of literate and illiterate patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1990 Aug;17(8):1022–1024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. Surgery and medical treatment in persistent somatizing patients. J Psychosom Res. 1992 Jul;36(5):439–447. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(92)90004-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman David. Counting cancers at the junction - a problem of routine statistics. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002 Feb;14(2):99–101. doi: 10.1097/00042737-200202000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L., Kleinman L., Ganoczy D., McQuaid K., Sloan S., Eggleston A., Tougas G., Farup C. Upper gastrointestinal symptoms in North America: prevalence and relationship to healthcare utilization and quality of life. Dig Dis Sci. 2000 Apr;45(4):809–818. doi: 10.1023/a:1005468332122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerson Lauren B., Shetler Katerina, Triadafilopoulos George. Prevalence of Barrett's esophagus in asymptomatic individuals. Gastroenterology. 2002 Aug;123(2):461–467. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.34748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin F., Bombardier C., Beaton D. Cross-cultural adaptation of health-related quality of life measures: literature review and proposed guidelines. J Clin Epidemiol. 1993 Dec;46(12):1417–1432. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(93)90142-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyatt G. H., Townsend M., Berman L. B., Keller J. L. A comparison of Likert and visual analogue scales for measuring change in function. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(12):1129–1133. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(87)90080-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. M., Bytzer P., Schaffalitzky De Muckadell O. B. Management of dyspeptic patients in primary care. Value of the unaided clinical diagnosis and of dyspepsia subgrouping. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998 Aug;33(8):799–805. doi: 10.1080/00365529850171431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding S. M., Richter J. E., Guzzo M. R., Schan C. A., Alexander R. W., Bradley L. A. Asthma and gastroesophageal reflux: acid suppressive therapy improves asthma outcome. Am J Med. 1996 Apr;100(4):395–405. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9343(97)89514-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding S. M., Sontag S. J. Asthma and gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000 Aug;95(8 Suppl):S23–S32. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9270(00)01075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havelund T., Lind T., Wiklund I., Glise H., Hernqvist H., Lauritsen K., Lundell L., Pedersen S. A., Carlsson R., Junghard O. Quality of life in patients with heartburn but without esophagitis: effects of treatment with omeprazole. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999 Jul;94(7):1782–1789. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho K. Y., Ng W. L., Kang J. Y., Yeoh K. G. Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a common cause of noncardiac chest pain in a country with a low prevalence of reflux esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1998 Sep;43(9):1991–1997. doi: 10.1023/a:1018842811123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungin A. P., Thomas P. R., Bramble M. G., Corbett W. A., Idle N., Contractor B. R., Berridge D. C., Cann G. What happens to patients following open access gastroscopy? An outcome study from general practice. Br J Gen Pract. 1994 Nov;44(388):519–521. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huskisson E. C. Measurement of pain. Lancet. 1974 Nov 9;2(7889):1127–1131. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90884-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyland M. E., Kenyon C. A., Allen R., Howarth P. Diary keeping in asthma: comparison of written and electronic methods. BMJ. 1993 Feb 20;306(6876):487–489. doi: 10.1136/bmj.306.6876.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irwin R. S., Richter J. E. Gastroesophageal reflux and chronic cough. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000 Aug;95(8 Suppl):S9–14. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9270(00)01073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isolauri J., Laippala P. Prevalence of symptoms suggestive of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in an adult population. Ann Med. 1995 Feb;27(1):67–70. doi: 10.3109/07853899509031939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsen R., Bernersen B., Straume B., Førde O. H., Bostad L., Burhol P. G. Prevalences of endoscopic and histological findings in subjects with and without dyspepsia. BMJ. 1991 Mar 30;302(6779):749–752. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6779.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson F., Joelsson B., Gudmundsson K., Greiff L. Symptoms and endoscopic findings in the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1987 Aug;22(6):714–718. doi: 10.3109/00365528709011148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson F., Roth Y., Damgaard Pedersen N. E., Joelsson B. Cimetidine improves GERD symptoms in patients selected by a validated GERD questionnaire. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1993 Feb;7(1):81–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1993.tb00073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson F., Weywadt L., Solhaug J. H., Hernqvist H., Bengtsson L. One-week omeprazole treatment in the diagnosis of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998 Jan;33(1):15–20. doi: 10.1080/00365529850166149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahrilas P. J., Falk G. W., Johnson D. A., Schmitt C., Collins D. W., Whipple J., D'Amico D., Hamelin B., Joelsson B. Esomeprazole improves healing and symptom resolution as compared with omeprazole in reflux oesophagitis patients: a randomized controlled trial. The Esomeprazole Study Investigators. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000 Oct;14(10):1249–1258. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2000.00856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahrilas P. J., Quigley E. M. Clinical esophageal pH recording: a technical review for practice guideline development. Gastroenterology. 1996 Jun;110(6):1982–1996. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.1101982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay L., Jørgensen T., Jensen K. H. Epidemiology of abdominal symptoms in a random population: prevalence, incidence, and natural history. Eur J Epidemiol. 1994 Oct;10(5):559–566. doi: 10.1007/BF01719573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klauser A. G., Schindlbeck N. E., Müller-Lissner S. A. Symptoms in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Lancet. 1990 Jan 27;335(8683):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90287-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman Leah, McIntosh Emma, Ryan Mandy, Schmier Jordana, Crawley Joseph, Locke G. Richard, 3rd, De Lissovoy Gregory. Willingness to pay for complete symptom relief of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Arch Intern Med. 2002 Jun 24;162(12):1361–1366. doi: 10.1001/archinte.162.12.1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch T. Life quality vs the 'quality of life': assumptions underlying prospective quality of life instruments in health care planning. Soc Sci Med. 2000 Aug;51(3):419–427. doi: 10.1016/s0277-9536(99)00474-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagergren J., Bergström R., Lindgren A., Nyrén O. Symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux as a risk factor for esophageal adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1999 Mar 18;340(11):825–831. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199903183401101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassen A. T., Pedersen F. M., Bytzer P., Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O. B. Helicobacter pylori test-and-eradicate versus prompt endoscopy for management of dyspeptic patients: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2000 Aug 5;356(9228):455–460. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(00)02553-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman D. A., Oehlke M., Helfand M. Risk factors for Barrett's esophagus in community-based practice. GORGE consortium. Gastroenterology Outcomes Research Group in Endoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997 Aug;92(8):1293–1297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind T., Havelund T., Carlsson R., Anker-Hansen O., Glise H., Hernqvist H., Junghard O., Lauritsen K., Lundell L., Pedersen S. A. Heartburn without oesophagitis: efficacy of omeprazole therapy and features determining therapeutic response. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997 Oct;32(10):974–979. doi: 10.3109/00365529709011212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind T., Havelund T., Lundell L., Glise H., Lauritsen K., Pedersen S. A., Anker-Hansen O., Stubberöd A., Eriksson G., Carlsson R. On demand therapy with omeprazole for the long-term management of patients with heartburn without oesophagitis--a placebo-controlled randomized trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999 Jul;13(7):907–914. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1999.00564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren S., Janzon L. Prevalence of swallowing complaints and clinical findings among 50-79-year-old men and women in an urban population. Dysphagia. 1991;6(4):187–192. doi: 10.1007/BF02493524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locke G. R., Talley N. J., Weaver A. L., Zinsmeister A. R. A new questionnaire for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1994 Jun;69(6):539–547. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)62245-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord Reginald V. N., Kaminski Anna, Oberg Stefan, Bowrey David J., Hagen Jeffrey A., DeMeester Steven R., Sillin Lelan F., Peters Jeffrey H., Crookes Peter F., DeMeester Tom R. Absence of gastroesophageal reflux disease in a majority of patients taking acid suppression medications after Nissen fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg. 2002 Jan-Feb;6(1):3–10. doi: 10.1016/s1091-255x(01)00031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundell L. R., Dent J., Bennett J. R., Blum A. L., Armstrong D., Galmiche J. P., Johnson F., Hongo M., Richter J. E., Spechler S. J. Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut. 1999 Aug;45(2):172–180. doi: 10.1136/gut.45.2.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lydeard S., Jones R. Factors affecting the decision to consult with dyspepsia: comparison of consulters and non-consulters. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1989 Dec;39(329):495–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen L. G., Bytzer P. The value of alarm features in identifying organic causes of dyspepsia. Can J Gastroenterol. 2000 Sep;14(8):713–720. doi: 10.1155/2000/783950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangione-Smith R., McGlynn E. A., Elliott M. N., McDonald L., Franz C. E., Kravitz R. L. Parent expectations for antibiotics, physician-parent communication, and satisfaction. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001 Jul;155(7):800–806. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.155.7.800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias S. D., Colwell H. H., Miller D. P., Pasta D. J., Henning J. M., Ofman J. J. Health-Related quality-of-life and quality-days incrementally gained in symptomatic nonerosive GERD patients treated with lansoprazole or ranitidine. Dig Dis Sci. 2001 Nov;46(11):2416–2423. doi: 10.1023/a:1012363501101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moayyedi P., Axon A. T. The usefulness of the likelihood ratio in the diagnosis of dyspepsia and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999 Nov;94(11):3122–3125. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moayyedi P., Forman D., Braunholtz D., Feltbower R., Crocombe W., Liptrott M., Axon A. The proportion of upper gastrointestinal symptoms in the community associated with Helicobacter pylori, lifestyle factors, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Leeds HELP Study Group. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000 Jun;95(6):1448–1455. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.2126_1.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numans M. E., van der Graaf Y., de Wit N. J., de Melker R. A. How useful is selection based on alarm symptoms in requesting gastroscopy? An evaluation of diagnostic determinants for gastro-oesophageal malignancy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2001 Apr;36(4):437–443. doi: 10.1080/003655201300051379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor A. M., Rostom A., Fiset V., Tetroe J., Entwistle V., Llewellyn-Thomas H., Holmes-Rovner M., Barry M., Jones J. Decision aids for patients facing health treatment or screening decisions: systematic review. BMJ. 1999 Sep 18;319(7212):731–734. doi: 10.1136/bmj.319.7212.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ours T. M., Kavuru M. S., Schilz R. J., Richter J. E. A prospective evaluation of esophageal testing and a double-blind, randomized study of omeprazole in a diagnostic and therapeutic algorithm for chronic cough. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999 Nov;94(11):3131–3138. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J., McConkey C. C. The rising trend in oesophageal adenocarcinoma and gastric cardia. Eur J Cancer Prev. 1992 Apr;1(3):265–269. doi: 10.1097/00008469-199204000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell Jean, McConkey Chris C., Gillison E. Walford, Spychal Robert T. Continuing rising trend in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2002 Dec 1;102(4):422–427. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redekop W. Ken, Koopmanschap Marc A., Stolk Ronald P., Rutten Guy E. H. M., Wolffenbuttel Bruce H. R., Niessen Louis W. Health-related quality of life and treatment satisfaction in Dutch patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002 Mar;25(3):458–463. doi: 10.2337/diacare.25.3.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revicki D. A., Wood M., Maton P. N., Sorensen S. The impact of gastroesophageal reflux disease on health-related quality of life. Am J Med. 1998 Mar;104(3):252–258. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(97)00354-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. E., Kahrilas P. J., Johanson J., Maton P., Breiter J. R., Hwang C., Marino V., Hamelin B., Levine J. G., Esomeprazole Study Investigators Efficacy and safety of esomeprazole compared with omeprazole in GERD patients with erosive esophagitis: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001 Mar;96(3):656–665. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.3600_b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M., Earnest D., Rodriguez-Stanley S., Greenwood-Van Meerveld B., Jaffe P., Silver M. T., Kleoudis C. S., Wilson L. E., Murdock R. H. Heartburn requiring frequent antacid use may indicate significant illness. Arch Intern Med. 1998 Nov 23;158(21):2373–2376. doi: 10.1001/archinte.158.21.2373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero Yvonne, Cameron Alan J., Schaid Daniel J., McDonnell Shannon K., Burgart Lawrence J., Hardtke Cyndy L., Murray Joseph A., Locke G. Richard., 3rd Barrett's esophagus: prevalence in symptomatic relatives. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002 May;97(5):1127–1132. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman M., Farup C., Stewart W., Helbers L., Zeldis J. Symptoms associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease: development of a questionnaire for use in clinical trials. Dig Dis Sci. 2001 Jul;46(7):1540–1549. doi: 10.1023/a:1010660425522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell J. F., Feehan E., Reid I., Walsh T. N., Hennessy T. P. Delay in treatment for oesophageal cancer. Br J Surg. 1997 May;84(5):690–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruth M., Månsson I., Sandberg N. The prevalence of symptoms suggestive of esophageal disorders. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1991 Jan;26(1):73–81. doi: 10.3109/00365529108996486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandbu R., Khamis H., Gustavsson S., Haglund U. Long-term results of antireflux surgery indicate the need for a randomized clinical trial. Br J Surg. 2002 Feb;89(2):225–230. doi: 10.1046/j.0007-1323.2001.01990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk B. E., Kuipers E. J., Klinkenberg-Knol E. C., Festen H. P., Jansen E. H., Tuynman H. A., Schrijver M., Dieleman L. A., Meuwissen S. G. Omeprazole as a diagnostic tool in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997 Nov;92(11):1997–2000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindlbeck N. E., Klauser A. G., Voderholzer W. A., Müller-Lissner S. A. Empiric therapy for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Arch Intern Med. 1995 Sep 11;155(16):1808–1812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaheen N. J., Crosby M. A., Bozymski E. M., Sandler R. S. Is there publication bias in the reporting of cancer risk in Barrett's esophagus? Gastroenterology. 2000 Aug;119(2):333–338. doi: 10.1053/gast.2000.9302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw M. J., Talley N. J., Beebe T. J., Rockwood T., Carlsson R., Adlis S., Fendrick A. M., Jones R., Dent J., Bytzer P. Initial validation of a diagnostic questionnaire for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001 Jan;96(1):52–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.03451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So J. B., Zeitels S. M., Rattner D. W. Outcomes of atypical symptoms attributed to gastroesophageal reflux treated by laparoscopic fundoplication. Surgery. 1998 Jul;124(1):28–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J., Lee E., Ahnen D., Goyal R. K., Hirano I., Ramirez F., Raufman J. P., Sampliner R., Schnell T., Sontag S. Long-term outcome of medical and surgical therapies for gastroesophageal reflux disease: follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2001 May 9;285(18):2331–2338. doi: 10.1001/jama.285.18.2331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey J. H., Miocevich M. L., Sacks G. E. The effect of ranitidine (as effervescent tablets) on the quality of life of GORD patients. Br J Clin Pract. 1996 Jun;50(4):190-4, 196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone Arthur A., Shiffman Saul, Schwartz Joseph E., Broderick Joan E., Hufford Michael R. Patient non-compliance with paper diaries. BMJ. 2002 May 18;324(7347):1193–1194. doi: 10.1136/bmj.324.7347.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Fullerton S., Junghard O., Wiklund I. Quality of life in patients with endoscopy-negative heartburn: reliability and sensitivity of disease-specific instruments. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001 Jul;96(7):1998–2004. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.03932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Meineche-Schmidt V., Paré P., Duckworth M., Räisänen P., Pap A., Kordecki H., Schmid V. Efficacy of omeprazole in functional dyspepsia: double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trials (the Bond and Opera studies). Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1998 Nov;12(11):1055–1065. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1998.00410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley Nicholas J., Venables Thomas L., Green Jonathan R. B., Armstrong David, O'Kane Kevin P. J., Giaffer Mustafa, Bardhan Karna D., Carlsson Rolf G. S., Chen Samuel, Hasselgren Göran S. Esomeprazole 40 mg and 20 mg is efficacious in the long-term management of patients with endoscopy-negative gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a placebo-controlled trial of on-demand therapy for 6 months. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002 Aug;14(8):857–863. doi: 10.1097/00042737-200208000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vakil Nimish, Shaw Michael, Kirby Russell. Clinical effectiveness of laparoscopic fundoplication in a U.S. community. Am J Med. 2003 Jan;114(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldhuyzen van Zanten S. J., Tytgat K. M., Pollak P. T., Goldie J., Goodacre R. L., Riddell R. H., Hunt R. H. Can severity of symptoms be used as an outcome measure in trials of non-ulcer dyspepsia and Helicobacter pylori associated gastritis? J Clin Epidemiol. 1993 Mar;46(3):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(93)90075-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venables T. L., Newland R. D., Patel A. C., Hole J., Wilcock C., Turbitt M. L. Omeprazole 10 milligrams once daily, omeprazole 20 milligrams once daily, or ranitidine 150 milligrams twice daily, evaluated as initial therapy for the relief of symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in general practice. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997 Oct;32(10):965–973. doi: 10.3109/00365529709011211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizcaino A. Paloma, Moreno Victor, Lambert Rene, Parkin D. Maxwell. Time trends incidence of both major histologic types of esophageal carcinomas in selected countries, 1973-1995. Int J Cancer. 2002 Jun 20;99(6):860–868. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. B., Durkalski V. L., Vaughan J., Palesch Y. Y., Libby E. D., Jowell P. S., Nickl N. J., Schutz S. M., Leung J. W., Cotton P. B. Age and alarm symptoms do not predict endoscopic findings among patients with dyspepsia: a multicentre database study. Gut. 2001 Jul;49(1):29–34. doi: 10.1136/gut.49.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westbrook J. I., McIntosh J., Talley N. J. Factors associated with consulting medical or non-medical practitioners for dyspepsia: an australian population-based study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000 Dec;14(12):1581–1588. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2000.00878.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiersma D., van Busschbach J. Are needs and satisfaction of care associated with quality of life? An epidemiological survey among the severely mentally ill in the Netherlands. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001 Oct;251(5):239–246. doi: 10.1007/s004060170033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijnhoven Bas P. L., Louwman Marieke W. J., Tilanus Hugo W., Coebergh Jan-Willem W. Increased incidence of adenocarcinomas at the gastro-oesophageal junction in Dutch males since the 1990s. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002 Feb;14(2):115–122. doi: 10.1097/00042737-200202000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiklund I., Dimenäs E., Wahl M. Factors of importance when evaluating quality of life in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1990 Jun;11(3):169–179. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(90)90011-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen I., Hatlebakk J. G., Olafsson S., Berstad A. On demand therapy of reflux oesophagitis--a prospective study of symptoms, patient satisfaction and quality of life. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999 Aug;13(8):1035–1040. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1999.00575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters C., Jr, Spurling T. J., Chobanian S. J., Curtis D. J., Esposito R. L., Hacker J. F., 3rd, Johnson D. A., Cruess D. F., Cotelingam J. D., Gurney M. S. Barrett's esophagus. A prevalent, occult complication of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jan;92(1):118–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Hanson D. G., Waring P. J., Shaw G. ENT manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000 Aug;95(8 Suppl):S15–S22. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9270(00)01074-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]