Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (220.6 KB).
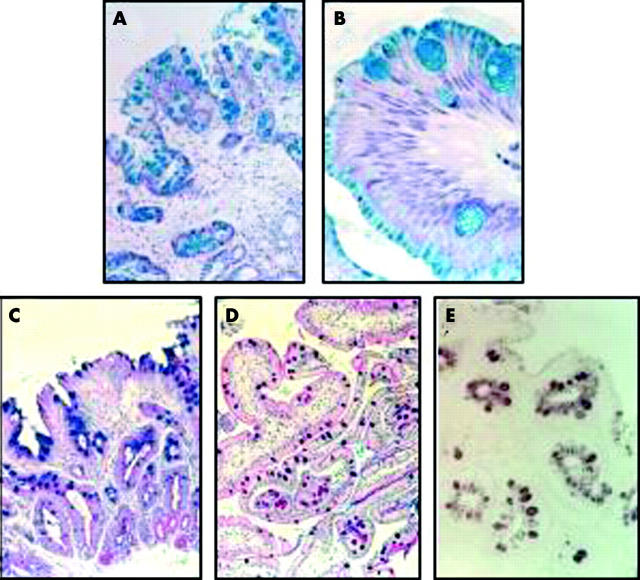
Figure 1.
Abnormal differentiation status of the Barrett's epithelium. (A) and (B) low and high power fields, respectively, of alcian blue staining in Barrett's oesophageal sections showing the blue acidic and neutral mucins in goblet and non-goblet columnar cells. (C) PAS–alcian blue staining for neutral mucins (magenta) and N-acetylated sialo-mucins (blue) found in type IIB intestinal metaplasia. (D) the same PAS–alcian blue staining in duodenal section, note that mucins here are mainly neutral (magenta). (E) a high iron diamine–alcian blue staining showing dark brown sulphomucins characteristic of type IIB incomplete IM.
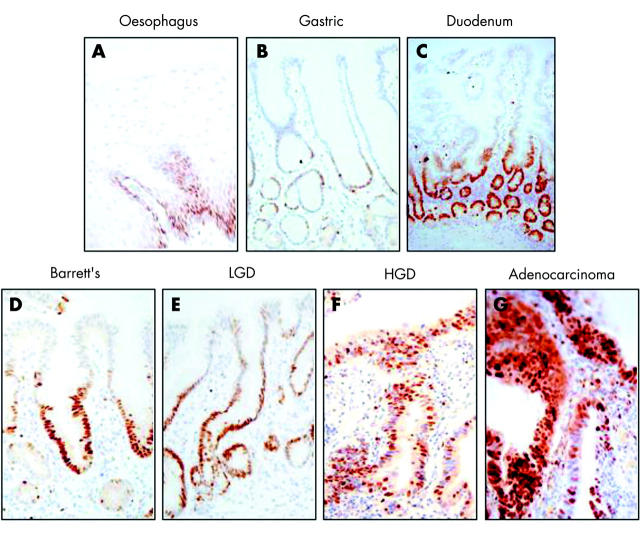
Figure 2.
Abnormal proliferation compartments of Barrett's oesophagus and associated dysplasia. Expression of a proliferation marker mini-chromosome maintenance protein (Mcm2) is shown by immunohistochemistry. Whereas the proliferative compartment is confined to the basal layers (normal squamous oesophagus, (A)) and in the crypts and the glands (normal stomach and duodenum, (B) and (C)), in Barrett's metaplasia proliferation extends towards the surface (D). With increasing dysplasia the number of proliferating cells increases with expansion of the proliferative compartment (E-G).
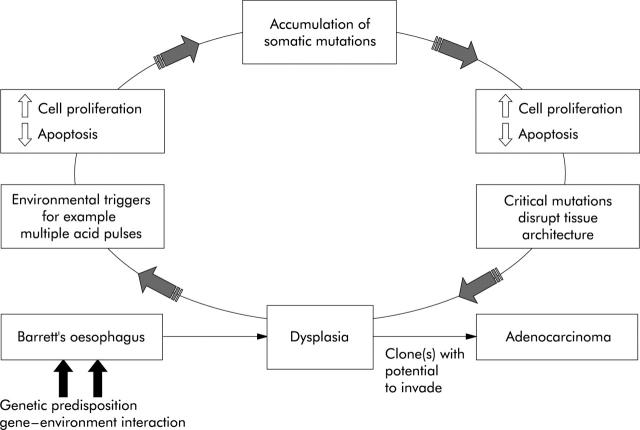
Figure 3.
Acid and other luminal constituents may lead to a hyperproliferative and anti-apoptotic response of Barrett's epithelial cells. This in turn may lead to an accumulation of genetic abnormalities through a vicious cycle effect. The somatic mutations may be accumulated in a non-predictable order. Cancer will occur once the mutation(s) provides the cells with the capacity to invade.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett M. T., Sanchez C. A., Prevo L. J., Wong D. J., Galipeau P. C., Paulson T. G., Rabinovitch P. S., Reid B. J. Evolution of neoplastic cell lineages in Barrett oesophagus. Nat Genet. 1999 May;22(1):106–109. doi: 10.1038/8816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosetti C., Talamini R., Franceschi S., Negri E., Garavello W., La Vecchia C. Aspirin use and cancers of the upper aerodigestive tract. Br J Cancer. 2003 Mar 10;88(5):672–674. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttar Navtej S., Wang Kenneth K., Leontovich Olga, Westcott Jay Y., Pacifico Rodney J., Anderson Marlys A., Krishnadath Krishnawatie K., Lutzke Lori S., Burgart Lawrence J. Chemoprevention of esophageal adenocarcinoma by COX-2 inhibitors in an animal model of Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2002 Apr;122(4):1101–1112. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.32371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttar Navtej S., Wang Kenneth K., Leontovich Olga, Westcott Jay Y., Pacifico Rodney J., Anderson Marlys A., Krishnadath Krishnawatie K., Lutzke Lori S., Burgart Lawrence J. Chemoprevention of esophageal adenocarcinoma by COX-2 inhibitors in an animal model of Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2002 Apr;122(4):1101–1112. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.32371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron A. J., Lomboy C. T. Barrett's esophagus: age, prevalence, and extent of columnar epithelium. Gastroenterology. 1992 Oct;103(4):1241–1245. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91510-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caygill C. P., Reed P. I., Johnston B. J., Hill M. J., Ali M. H., Levi S. A single centre's 20 years' experience of columnar-lined (Barrett's) oesophagus diagnosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999 Dec;11(12):1355–1358. doi: 10.1097/00042737-199912000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow D. C., Vaughan T. L., Hansten P. D., Stanford J. L., Risch H. A., Gammon M. D., Chow W. H., Dubrow R., Ahsan H., Mayne S. T. Use of aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of esophageal and gastric cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1998 Feb;7(2):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald R. C., Abdalla S., Onwuegbusi B. A., Sirieix P., Saeed I. T., Burnham W. R., Farthing M. J. G. Inflammatory gradient in Barrett's oesophagus: implications for disease complications. Gut. 2002 Sep;51(3):316–322. doi: 10.1136/gut.51.3.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald R. C., Lascar R., Triadafilopoulos G. Review article: Barrett's oesophagus, dysplasia and pharmacologic acid suppression. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001 Mar;15(3):269–276. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2001.00939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald R. C., Omary M. B., Triadafilopoulos G. Altered sodium-hydrogen exchange activity is a mechanism for acid-induced hyperproliferation in Barrett's esophagus. Am J Physiol. 1998 Jul;275(1 Pt 1):G47–G55. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1998.275.1.G47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald R. C., Omary M. B., Triadafilopoulos G. Dynamic effects of acid on Barrett's esophagus. An ex vivo proliferation and differentiation model. J Clin Invest. 1996 Nov 1;98(9):2120–2128. doi: 10.1172/JCI119018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald R. C., Onwuegbusi B. A., Bajaj-Elliott M., Saeed I. T., Burnham W. R., Farthing M. J. G. Diversity in the oesophageal phenotypic response to gastro-oesophageal reflux: immunological determinants. Gut. 2002 Apr;50(4):451–459. doi: 10.1136/gut.50.4.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher J., Wirz A., Young J., Vallance R., McColl K. E. Unbuffered highly acidic gastric juice exists at the gastroesophageal junction after a meal. Gastroenterology. 2001 Oct;121(4):775–783. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.27997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillen P., Keeling P., Byrne P. J., Healy M., O'Moore R. R., Hennessy T. P. Implication of duodenogastric reflux in the pathogenesis of Barrett's oesophagus. Br J Surg. 1988 Jun;75(6):540–543. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800750612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Going J. J., Keith W. N., Neilson L., Stoeber K., Stuart R. C., Williams G. H. Aberrant expression of minichromosome maintenance proteins 2 and 5, and Ki-67 in dysplastic squamous oesophageal epithelium and Barrett's mucosa. Gut. 2002 Mar;50(3):373–377. doi: 10.1136/gut.50.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S. R., Yang G. Y., Curtis S. K., Reuhl K. R., Liu B. C., Mirvish S. S., Newmark H. L., Yang C. S. Development of esophageal metaplasia and adenocarcinoma in a rat surgical model without the use of a carcinogen. Carcinogenesis. 1997 Nov;18(11):2265–2270. doi: 10.1093/carcin/18.11.2265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigh Chris R., Attwood Stephen E. A., Thompson David G., Jankowski Janusz A., Kirton Chris M., Pritchard D. Mark, Varro Andrea, Dimaline Rod. Gastrin induces proliferation in Barrett's metaplasia through activation of the CCK2 receptor. Gastroenterology. 2003 Mar;124(3):615–625. doi: 10.1053/gast.2003.50091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon J. W., Johnson L. F., Maydonovitch C. L. Effects of acid and bile salts on the rabbit esophageal mucosa. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 Jan;26(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF01307977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski J. A., Harrison R. F., Perry I., Balkwill F., Tselepis C. Barrett's metaplasia. Lancet. 2000 Dec 16;356(9247):2079–2085. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)03411-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D., Rothstein R., Schned A., Dunn J., Seaver K., Antonioli D. The development of dysplasia and adenocarcinoma during endoscopic surveillance of Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998 Apr;93(4):536–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.161_b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz Philip O., Frissora Christine. The pharmacology and clinical relevance of proton pump inhibitors. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2002 Dec;4(6):459–462. doi: 10.1007/s11894-002-0021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzka D. A., Castell D. O. Successful elimination of reflux symptoms does not insure adequate control of acid reflux in patients with Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994 Jul;89(7):989–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzka D. A., Castell D. O. Successful elimination of reflux symptoms does not insure adequate control of acid reflux in patients with Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994 Jul;89(7):989–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur Baljeet S., Khamnehei Niloufar, Iravani Mohamed, Namburu Sai S., Lin Otto, Triadafilopoulos George. Rofecoxib inhibits cyclooxygenase 2 expression and activity and reduces cell proliferation in Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2002 Jul;123(1):60–67. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.34244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur Baljeet S., Triadafilopoulos George. Acid- and bile-induced PGE(2) release and hyperproliferation in Barrett's esophagus are COX-2 and PKC-epsilon dependent. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002 Aug;283(2):G327–G334. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00543.2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagergren J., Bergström R., Lindgren A., Nyrén O. Symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux as a risk factor for esophageal adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1999 Mar 18;340(11):825–831. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199903183401101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Walsh T. N., O'Dowd G., Gillen P., Byrne P. J., Hennessy T. P. Mechanisms of columnar metaplasia and squamous regeneration in experimental Barrett's esophagus. Surgery. 1994 Feb;115(2):176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann N. S., Tsai M. F., Nair P. K. Barrett's esophagus in patients with symptomatic reflux esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989 Dec;84(12):1494–1496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald M. L., Trastek V. F., Allen M. S., Deschamps C., Pairolero P. C., Pairolero P. C. Barretts's esophagus: does an antireflux procedure reduce the need for endoscopic surveillance? J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1996 Jun;111(6):1135–1140. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5223(96)70214-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan Claire, Alazawi William, Sirieix Pierre, Freeman Tom, Coleman Nicholas, Fitzgerald Rebecca. In vitro acid exposure has a differential effect on apoptotic and proliferative pathways in a Barrett's adenocarcinoma cell line. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004 Feb;99(2):218–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.04054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehra D., Howell P., Williams C. P., Pye J. K., Beynon J. Toxic bile acids in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: influence of gastric acidity. Gut. 1999 May;44(5):598–602. doi: 10.1136/gut.44.5.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouatu-Lascar R., Fitzgerald R. C., Triadafilopoulos G. Differentiation and proliferation in Barrett's esophagus and the effects of acid suppression. Gastroenterology. 1999 Aug;117(2):327–335. doi: 10.1053/gast.1999.0029900327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouatu-Lascar R., Triadafilopoulos G. Complete elimination of reflux symptoms does not guarantee normalization of intraesophageal acid reflux in patients with Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998 May;93(5):711–716. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.211_a.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prach A. T., MacDonald T. A., Hopwood D. A., Johnston D. A. Increasing incidence of Barrett's oesophagus: education, enthusiasm, or epidemiology? Lancet. 1997 Sep 27;350(9082):933–933. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)63269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney Luanna K., Barber Diane L. Na-H exchange-dependent increase in intracellular pH times G2/M entry and transition. J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 28;278(45):44645–44649. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308099200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid B. J., Sanchez C. A., Blount P. L., Levine D. S. Barrett's esophagus: cell cycle abnormalities in advancing stages of neoplastic progression. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jul;105(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampliner Richard E., Camargo Lisa, Fass Ronnie. Impact of esophageal acid exposure on the endoscopic reversal of Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002 Feb;97(2):270–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seery John P. Stem cells of the oesophageal epithelium. J Cell Sci. 2002 May 1;115(Pt 9):1783–1789. doi: 10.1242/jcs.115.9.1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirvani V. N., Ouatu-Lascar R., Kaur B. S., Omary M. B., Triadafilopoulos G. Cyclooxygenase 2 expression in Barrett's esophagus and adenocarcinoma: Ex vivo induction by bile salts and acid exposure. Gastroenterology. 2000 Mar;118(3):487–496. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(00)70254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberg Debra G., Sullivan Jessica, Kang Eugene, Swain Gary P., Moffett Jennifer, Sund Newman J., Sackett Sara D., Kaestner Klaus H. Cdx2 ectopic expression induces gastric intestinal metaplasia in transgenic mice. Gastroenterology. 2002 Mar;122(3):689–696. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.31902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirieix Pierre S., O'Donovan Maria, Brown John, Save Vicki, Coleman Nicholas, Fitzgerald Rebecca C. Surface expression of minichromosome maintenance proteins provides a novel method for detecting patients at risk for developing adenocarcinoma in Barrett's esophagus. Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Jul;9(7):2560–2566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza R. F., Shewmake K., Beer D. G., Cryer B., Spechler S. J. Selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 suppresses growth and induces apoptosis in human esophageal adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2000 Oct 15;60(20):5767–5772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza Rhonda F., Shewmake Kenneth, Terada Lance S., Spechler Stuart Jon. Acid exposure activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2002 Feb;122(2):299–307. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.30993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler Stuart Jon. Carcinogenesis at the gastroesophageal junction: free radicals at the frontier. Gastroenterology. 2002 May;122(5):1518–1520. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.33368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H. J., Hoeft S., DeMeester T. R. Functional foregut abnormalities in Barrett's esophagus. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1993 Jan;105(1):107–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H. J., Kauer W. K., Feussner H., Siewert J. R. Bile reflux in benign and malignant Barrett's esophagus: effect of medical acid suppression and nissen fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg. 1998 Jul-Aug;2(4):333–341. doi: 10.1016/s1091-255x(98)80072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosh David, Slack Jonathan M. W. How cells change their phenotype. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Mar;3(3):187–194. doi: 10.1038/nrm761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umansky M., Yasui W., Hallak A., Brill S., Shapira I., Halpern Z., Hibshoosh H., Rattan J., Meltzer S., Tahara E. Proton pump inhibitors reduce cell cycle abnormalities in Barrett's esophagus. Oncogene. 2001 Nov 29;20(55):7987–7991. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaezi M. F., Richter J. E. Role of acid and duodenogastroesophageal reflux in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 1996 Nov;111(5):1192–1199. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v111.pm8898632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson W. A., Ellis F. H., Jr, Gibb S. P., Shahian D. M., Aretz H. T. Effect of antireflux operation on Barrett's mucosa. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990 Apr;49(4):537–542. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(90)90298-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. T., Fu S., Ramanujam K. S., Meltzer S. J. Increased expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in Barrett's esophagus and associated adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1998 Jul 15;58(14):2929–2934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters C., Jr, Spurling T. J., Chobanian S. J., Curtis D. J., Esposito R. L., Hacker J. F., 3rd, Johnson D. A., Cruess D. F., Cotelingam J. D., Gurney M. S. Barrett's esophagus. A prevalent, occult complication of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jan;92(1):118–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye W., Chow W. H., Lagergren J., Yin L., Nyrén O. Risk of adenocarcinomas of the esophagus and gastric cardia in patients with gastroesophageal reflux diseases and after antireflux surgery. Gastroenterology. 2001 Dec;121(6):1286–1293. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.29569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Serag H. B., Sonnenberg A. Opposing time trends of peptic ulcer and reflux disease. Gut. 1998 Sep;43(3):327–333. doi: 10.1136/gut.43.3.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]