Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (153.9 KB).
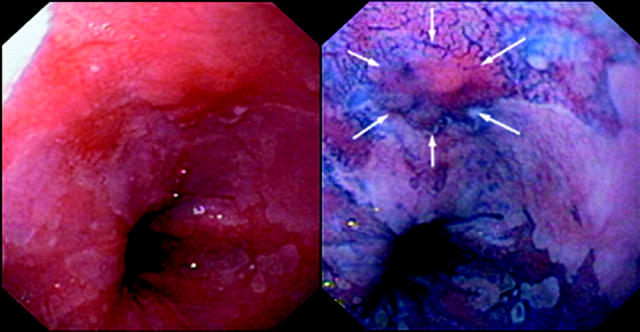
Figure 1.
(A) Barrett's oesophagus with a small inconspicuous area of high grade dysplasia; (B) after staining with indigo carmine the lesion is much easier identified.
Figure 2.
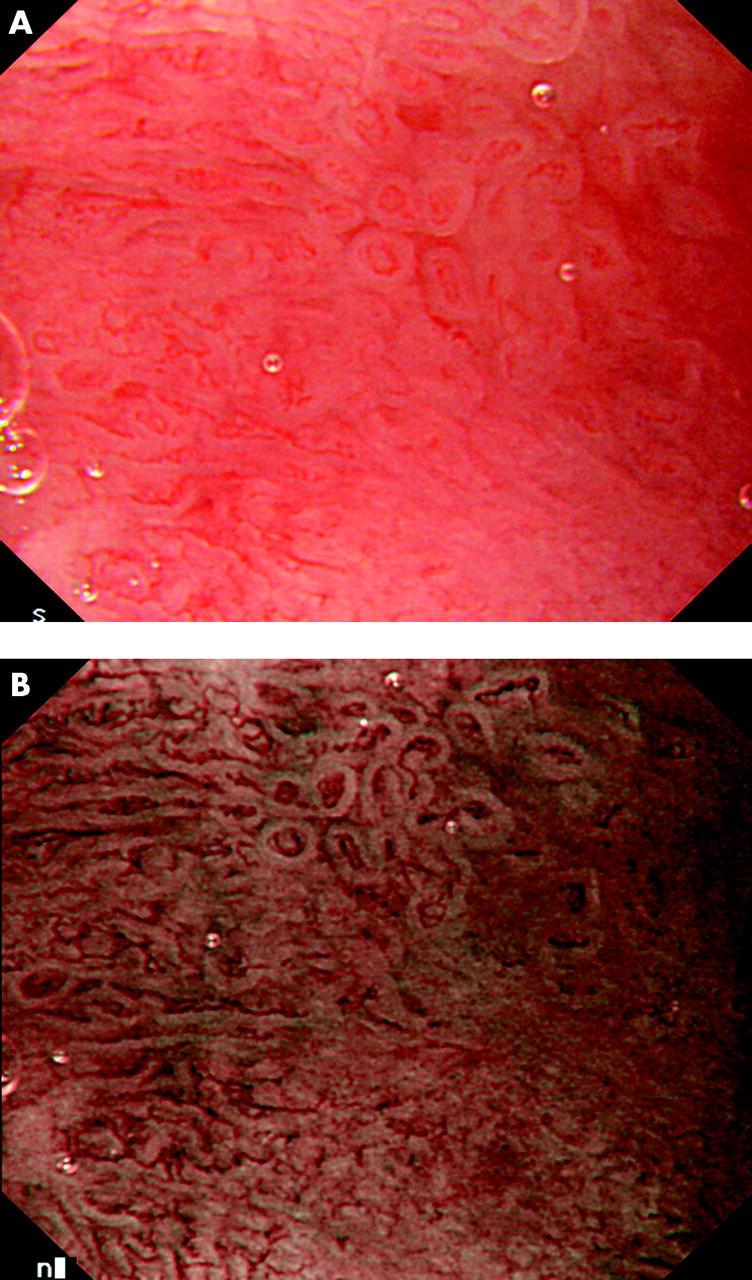
(A) High resolution endoscopy of a Barrett's oesophagus showing an area with an irregular mucosal pattern corresponding to high grade dysplasia; (B) high resolution endoscopy with narrow band imaging (NBI) of the same area. In NBI, the bandwidths of the standard red, green, and blue pass filters have been narrowed and the relative contribution of the blue filter has been increased resulting in improved mucosal contrast and detail.
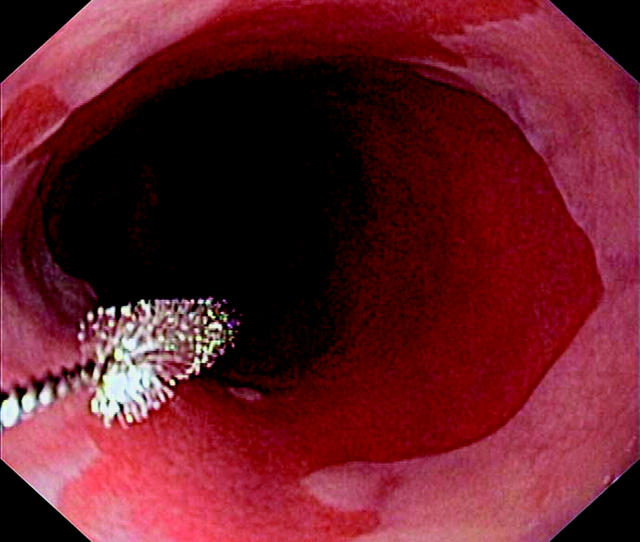
Figure 3.
Transendoscopic brush cytology of a Barrett's oesophagus.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ardekani Ali M., Liotta Lance A., Petricoin Emanuel F., 3rd Clinical potential of proteomics in the diagnosis of ovarian cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2002 Jul;2(4):312–320. doi: 10.1586/14737159.2.4.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwood S. E., Morris C. D. Who defines Barrett's oesophagus: endoscopist or pathologist? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001 Feb;13(2):97–99. doi: 10.1097/00042737-200102000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskens Christianne J., Van Rees Bastiaan P., Sivula Anna, Reitsma Johannes B., Haglund Caj, Bosma Piter J., Offerhaus G. Johan A., Van Lanschot J. Jan B., Ristimäki Ari. Prognostic significance of elevated cyclooxygenase 2 expression in patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2002 Jun;122(7):1800–1807. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.33580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canto M. I., Setrakian S., Willis J., Chak A., Petras R., Powe N. R., Sivak M. V., Jr Methylene blue-directed biopsies improve detection of intestinal metaplasia and dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000 May;51(5):560–568. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(00)70290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacosta Ralph S., Wilson Brian C., Marcon Norman E. New optical technologies for earlier endoscopic diagnosis of premalignant gastrointestinal lesions. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002 Feb;17 (Suppl):S85–104. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.17.s1.8.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dave U., Shousha S., Westaby D. Methylene blue staining: is it really useful in Barrett's esophagus? Gastrointest Endosc. 2001 Mar;53(3):333–335. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(01)70408-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Takao, Awakawa Teruhito, Takahashi Hiroaki, Arimura Yoshiaki, Itoh Fumio, Yamashita Kentaro, Sasaki Sigeru, Yamamoto Hiroyuki, Tang Xiufen, Imai Kohzoh. Classification of Barrett's epithelium by magnifying endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002 May;55(6):641–647. doi: 10.1067/mge.2002.123420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk G. W., Chittajallu R., Goldblum J. R., Biscotti C. V., Geisinger K. R., Petras R. E., Birgisson S., Rice T. W., Richter J. E. Surveillance of patients with Barrett's esophagus for dysplasia and cancer with balloon cytology. Gastroenterology. 1997 Jun;112(6):1787–1797. doi: 10.1053/gast.1997.v112.pm9178668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgakoudi I., Jacobson B. C., Van Dam J., Backman V., Wallace M. B., Müller M. G., Zhang Q., Badizadegan K., Sun D., Thomas G. A. Fluorescence, reflectance, and light-scattering spectroscopy for evaluating dysplasia in patients with Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2001 Jun;120(7):1620–1629. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.24842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guelrud M., Herrera I., Essenfeld H., Castro J. Enhanced magnification endoscopy: a new technique to identify specialized intestinal metaplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001 May;53(6):559–565. doi: 10.1067/mge.2001.114059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggitt R. C., Reid B. J., Rabinovitch P. S., Rubin C. E. Barrett's esophagus. Correlation between mucin histochemistry, flow cytometry, and histologic diagnosis for predicting increased cancer risk. Am J Pathol. 1988 Apr;131(1):53–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haringsma J., Tytgat G. N., Yano H., Iishi H., Tatsuta M., Ogihara T., Watanabe H., Sato N., Marcon N., Wilson B. C. Autofluorescence endoscopy: feasibility of detection of GI neoplasms unapparent to white light endoscopy with an evolving technology. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001 May;53(6):642–650. doi: 10.1067/mge.2001.114419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnadath K. K., Reid B. J., Wang K. K. Biomarkers in Barrett esophagus. Mayo Clin Proc. 2001 Apr;76(4):438–446. doi: 10.4065/76.4.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. D., Boppart S. A., Van Dam J., Mashimo H., Mutinga M., Drexler W., Klein M., Pitris C., Krinsky M. L., Brezinski M. E. Optical coherence tomography: advanced technology for the endoscopic imaging of Barrett's esophagus. Endoscopy. 2000 Dec;32(12):921–930. doi: 10.1055/s-2000-9626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery E., Goldblum J. R., Greenson J. K., Haber M. M., Lamps L. W., Lauwers G. Y., Lazenby A. J., Lewin D. N., Robert M. E., Washington K. Dysplasia as a predictive marker for invasive carcinoma in Barrett esophagus: a follow-up study based on 138 cases from a diagnostic variability study. Hum Pathol. 2001 Apr;32(4):379–388. doi: 10.1053/hupa.2001.23511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morales Carmela P., Souza Rhonda F., Spechler Stuart J. Hallmarks of cancer progression in Barrett's oesophagus. Lancet. 2002 Nov 16;360(9345):1587–1589. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11569-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panjehpour M., Overholt B. F., Vo-Dinh T., Haggitt R. C., Edwards D. H., Buckley F. P., 3rd Endoscopic fluorescence detection of high-grade dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 1996 Jul;111(1):93–101. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v111.pm8698231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polkowski W., van Lanschot J. J., Ten Kate F. J., Baak J. P., Tytgat G. N., Obertop H., Voorn W. J., Offerhaus G. J. The value of p53 and Ki67 as markers for tumour progression in the Barrett's dysplasia-carcinoma sequence. Surg Oncol. 1995 Jun;4(3):163–171. doi: 10.1016/s0960-7404(10)80021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddell R. H. Early detection of neoplasia of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996 May;91(5):853–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampliner R. E. Practice guidelines on the diagnosis, surveillance, and therapy of Barrett's esophagus. The Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998 Jul;93(7):1028–1032. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma P., Weston A. P., Topalovski M., Cherian R., Bhattacharyya A., Sampliner R. E. Magnification chromoendoscopy for the detection of intestinal metaplasia and dysplasia in Barrett's oesophagus. Gut. 2003 Jan;52(1):24–27. doi: 10.1136/gut.52.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler Stuart Jon. Clinical practice. Barrett's Esophagus. N Engl J Med. 2002 Mar 14;346(11):836–842. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp012118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler Stuart Jon. Columnar-lined esophagus. Definitions. Chest Surg Clin N Am. 2002 Feb;12(1):1-13, vii. doi: 10.1016/s1052-3359(03)00087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tselepis Chris, Perry Ian, Dawson Chris, Hardy Rob, Darnton S. Jane, McConkey Chris, Stuart Rob C., Wright Nick, Harrison Rebecca, Jankowski Janusz Antoni Z. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha in Barrett's oesophagus: a potential novel mechanism of action. Oncogene. 2002 Sep 5;21(39):6071–6081. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]