Abstract
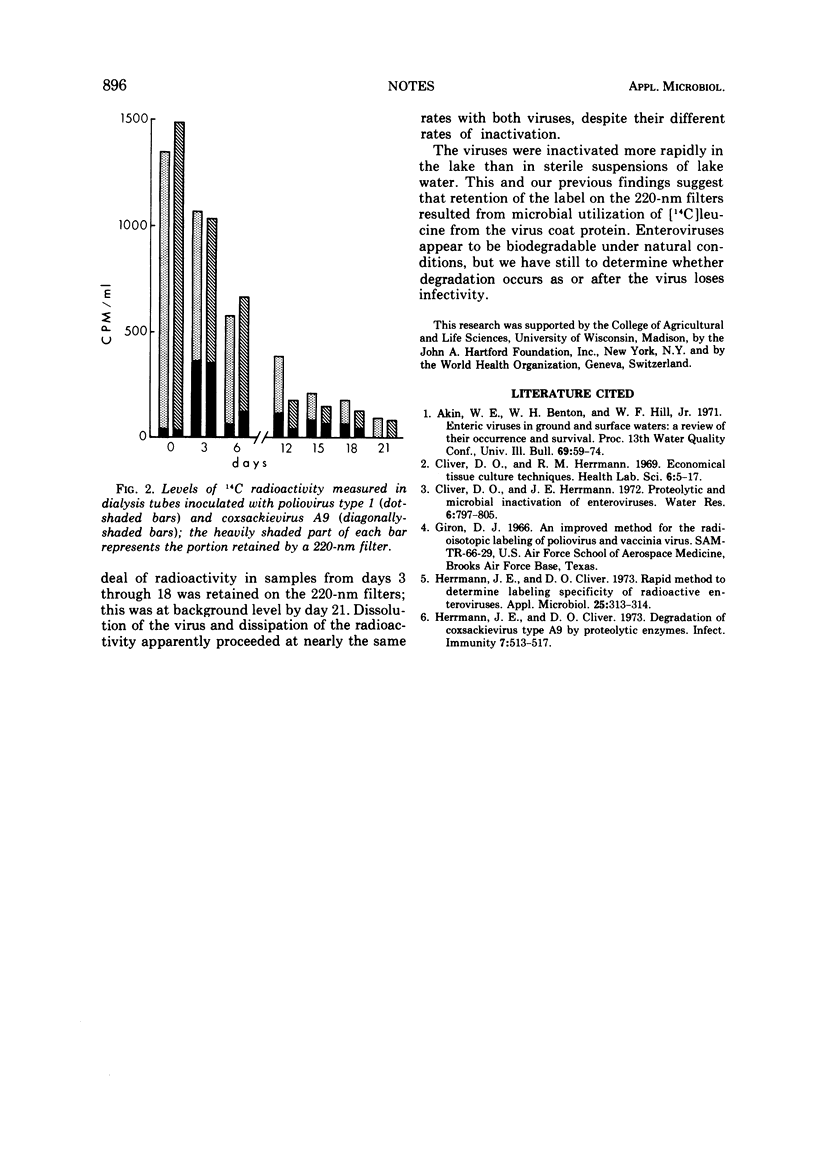
Two enteroviruses were inactivated more rapidly in a lake than in sterile lake water; then their coat proteins were degraded and, perhaps, used by microorganisms.
Full text
PDF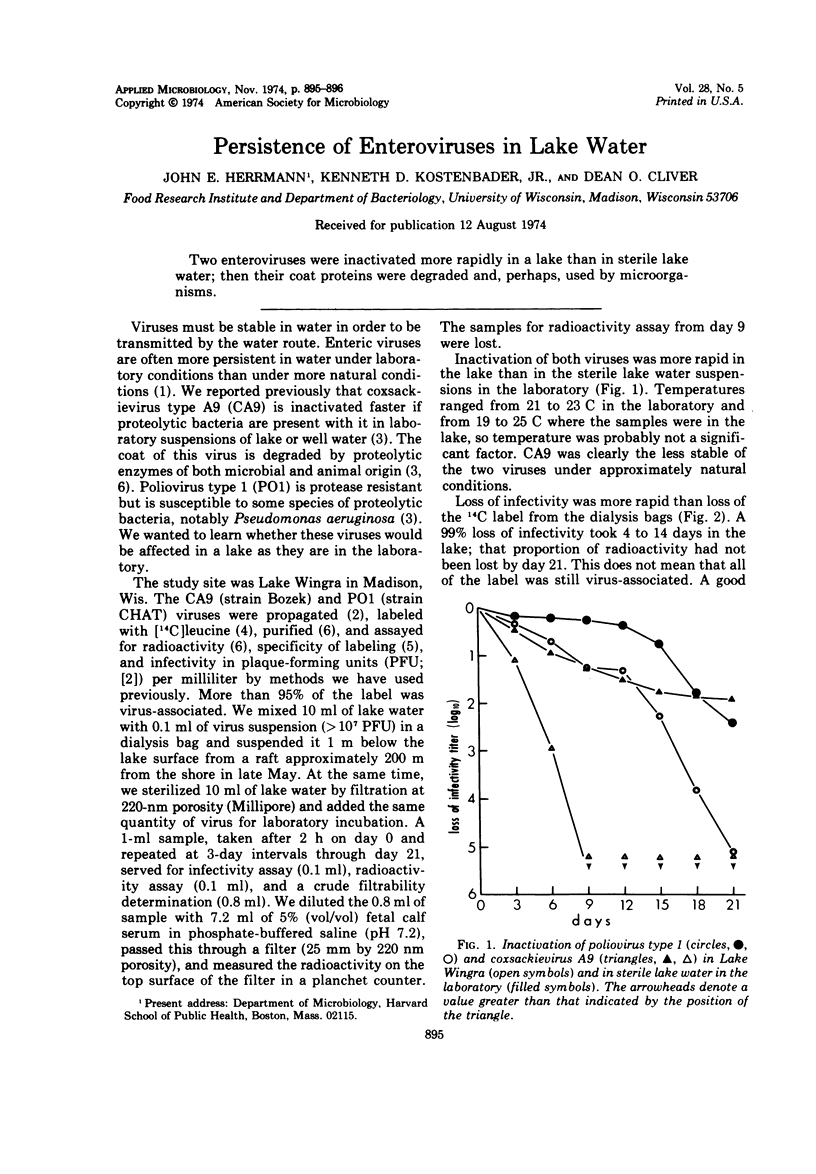
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cliver D. O., Herrmann R. M. Economical tissue culture technics. Health Lab Sci. 1969 Jan;6(1):5–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. E., Cliver D. O. Degradation of coxsackievirus type A9 by proteolytic enzymes. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):513–517. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.513-517.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. E., Cliver D. O. Rapid method to determine labeling specificity of radioactive enteroviruses. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Feb;25(2):313–314. doi: 10.1128/am.25.2.313-314.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


