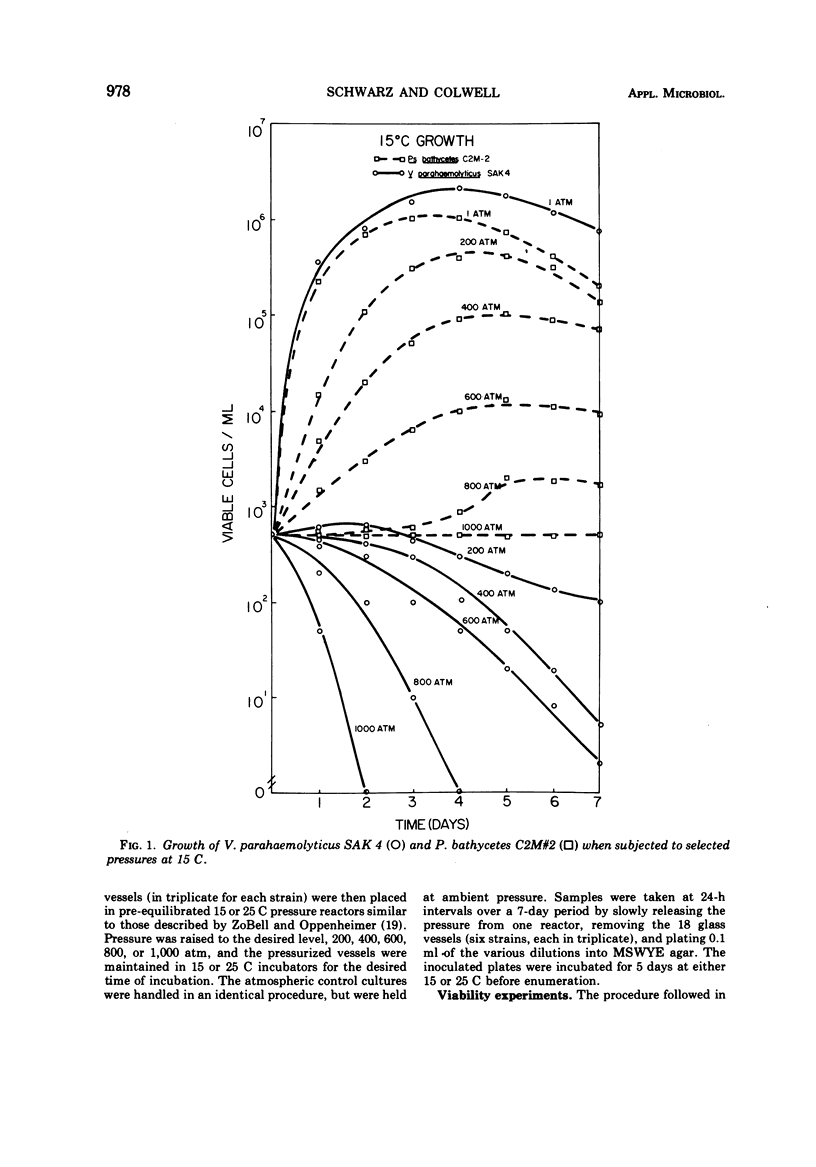
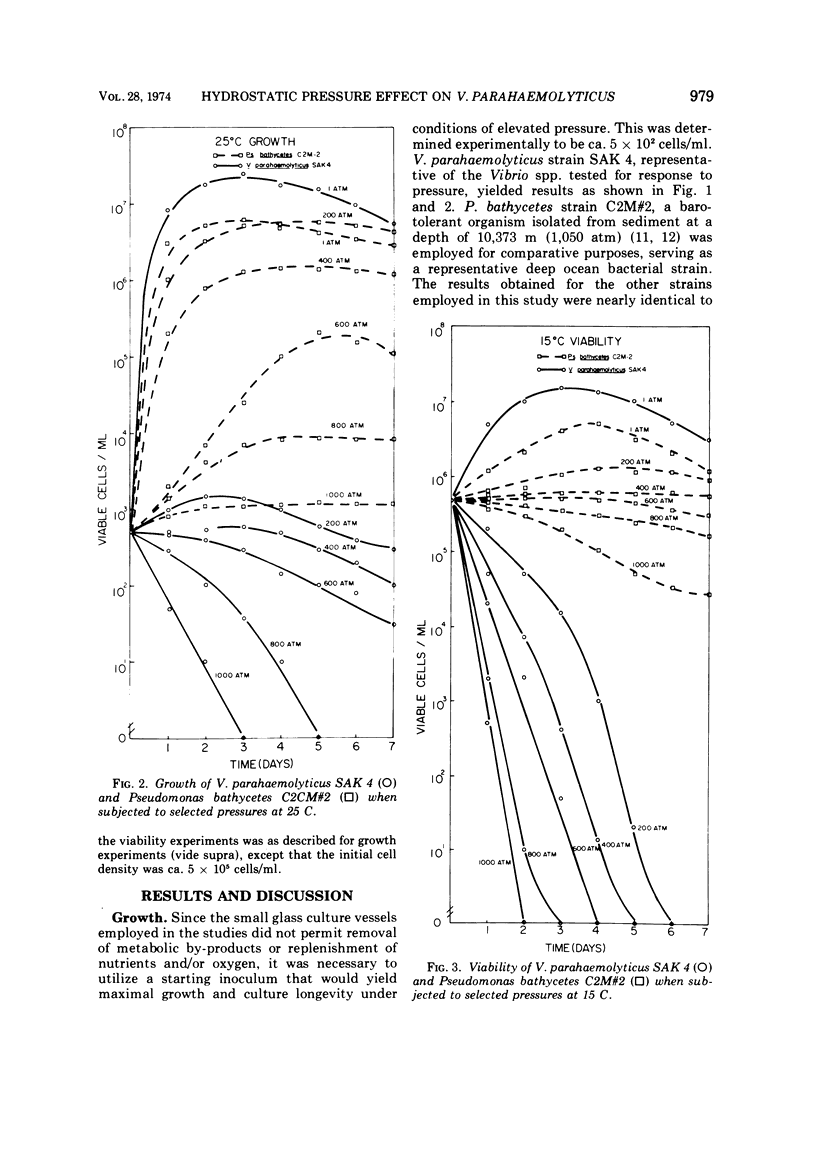
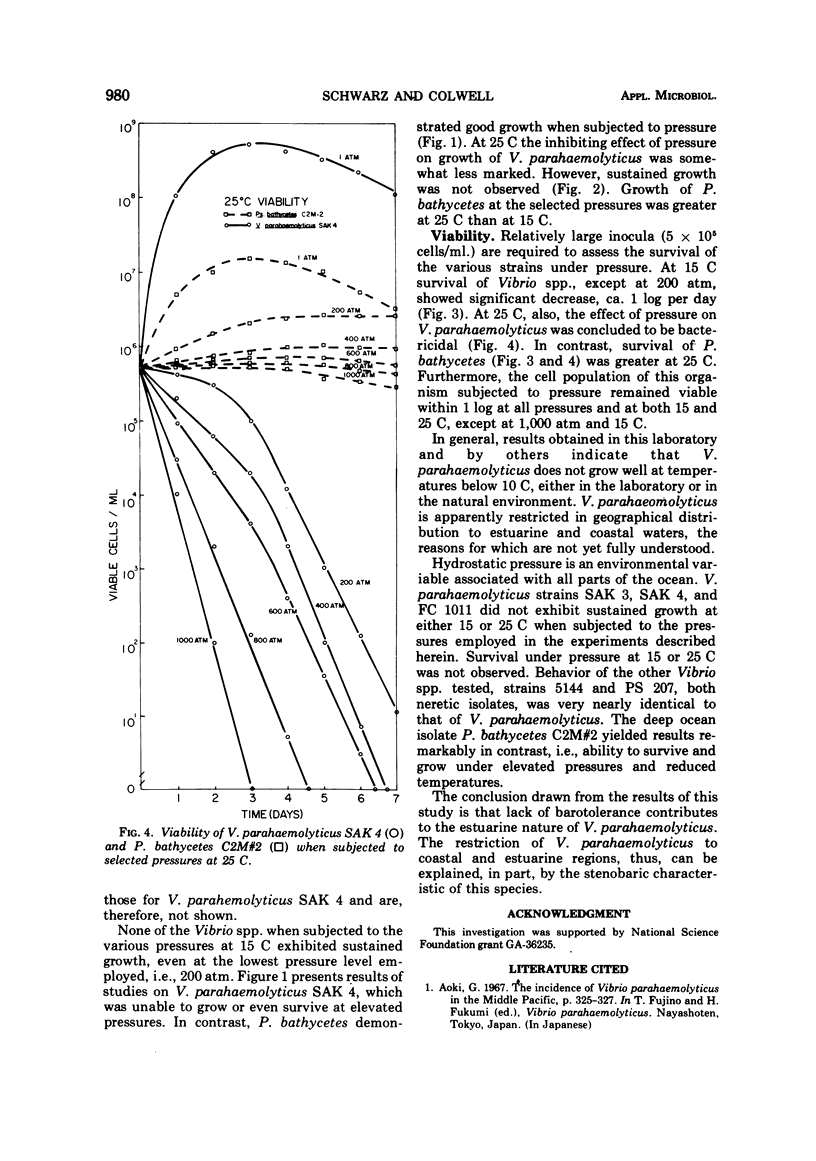
Abstract
Six strains of marine bacteria, including three strains of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, two Vibrio spp isolated from coastal regions, and the deep ocean isolate Pseudomonas bathycetes, were examined for ability to survive and grow at deep ocean hydrostatic pressures. V. parahaemolyticus and the coastal Vibrio spp. were unable to survive or grow at 200, 400, 600, 800, or 1,000 atm of pressure. In contrast, the deep ocean isolate P. bathycetes was capable of survival and growth at these pressures. The evidence strongly supports the neritic or estuarine origin and habitat for V. parahaemolyticus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kaneko T., Colwell R. R. Ecology of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Chesapeake Bay. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):24–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.24-32.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenda J. R., Johnson W. G., Fishbein M., Wentz B., Mehlman I. J., Dadisman T. A., Jr Vibrio parahaemolyticus gastroenteritis in Maryland: laboratory aspects. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Sep;24(3):444–448. doi: 10.1128/am.24.3.444-448.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley M. M., Colwell R. R. Properties of bacteria isolated from deep-sea sediments. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):211–220. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.211-220.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAKAZAKI R., IWANAMI S., FUKUMI H. STUDIES ON THE ENTEROPATHOGENIC, FACULTATIVELY HALOPHILIC BACTERIA, VIBRIO PARAHAEMOLYTICUS. I. MORPHOLOGICAL, CULTURAL AND BIOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES AND ITS TAXONOMICAL POSITION. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1963 Aug;16:161–188. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.16.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki R. Proposal of Vibrio alginolyticus for the biotype 2 of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1968 Oct;21(5):359–362. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.21.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz J. R., Landau J. V. Inhibition of cell-free protein synthesis by hydrostatic pressure. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1222–1227. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1222-1227.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZOBELL C. E., OPPENHEIMER C. H. Some effects of hydrostatic pressure on the multiplication and morphology of marine bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1950 Dec;60(6):771–781. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.6.771-781.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


