Abstract
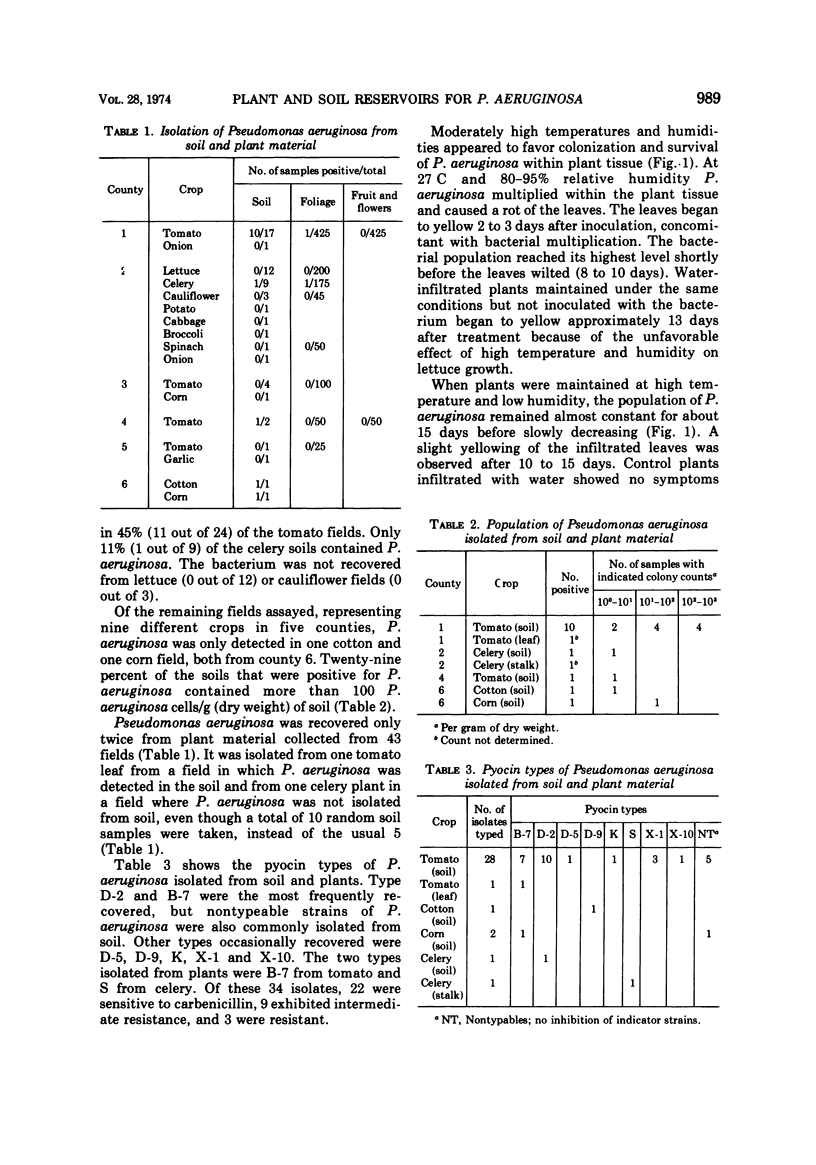
Pseudomonas aeruginosa was detected in 24% of the soil samples but in only 0.13% of the vegetable samples from various agricultural areas of California. The distribution of pyocin types of soil and vegetable isolates was similar to that of clinical strains, and three of the soil isolates were resistant to carbenicillin. Pseudomonas aeruginosa multiplied in lettuce and bean under conditions of high temperature and high relative humidity (27 C and 80-95% relative humidity) but declined when the temperature and humidity were lowered (16 C, 55-75% relative humidity). The results suggest that soil is a reservior for P. aeruginosa and that the bacterium has the capacity to colonize plants during favorable conditions of temperature and moisture.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown V. I., Lowbury E. J. Use of an improved cetrimide agar medium and other culture methods for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Pathol. 1965 Nov;18(6):752–756. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.6.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARRELL J. H., WAHBA A. H. PYOCINE-TYPING OF HOSPITAL STRAINS OF PSEUDOMONAS PYOCYANEA. J Clin Pathol. 1964 May;17:236–242. doi: 10.1136/jcp.17.3.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds P., Suskind R. R., Macmillan B. G., Holder I. A. Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a burns hospital: surveillance by a combined typing system. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Aug;24(2):219–225. doi: 10.1128/am.24.2.219-225.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fierer J., Taylor P. M., Gezon H. M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa epidemic traced to delivery-room resuscitators. N Engl J Med. 1967 May 4;276(18):991–996. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196705042761801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi G. L. Characterization of Pseudomonas species isolated from clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Mar;21(3):414–419. doi: 10.1128/am.21.3.414-419.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYNES W. C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa--its characterization and identification. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Nov;5(5 Suppl):939–950. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-5-939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., WARD M. K., RANEY D. E. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominos S. D., Copeland C. E., Grosiak B. Mode of transmission of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a burn unit and an intensive care unit in a general hospital. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):309–312. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.309-312.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominos S. D., Copeland C. E., Grosiak B., Postic B. Introduction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa into a hospital via vegetables. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Oct;24(4):567–570. doi: 10.1128/am.24.4.567-570.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowbury E. J., Lilly H. A., Kidson A., Ayliffe G. A., Jones R. J. Sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to antibiotics: emergence of strains highly resistant to carbenicillin. Lancet. 1969 Aug 30;2(7618):448–452. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowbury E. J., Thom B. T., Lilly H. A., Babb J. R., Whittall K. Sources of infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with tracheostomy. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Feb;3(1):39–56. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Spencer G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cross-infection due to contaminated respiratory apparatus. Lancet. 1965 Dec 25;2(7426):1325–1327. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92344-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RINGEN L. M., DRAKE C. H. A study of the incidence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from various natural sources. J Bacteriol. 1952 Dec;64(6):841–845. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.6.841-845.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shooter R. A., Cooke E. M., Faiers M. C., Breaden A. L., O'Farrell S. M. Isolation of Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Klebsiella from food in hospitals, canteens, and schools. Lancet. 1971 Aug 21;2(7721):390–392. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shooter R. A., Gaya H., Cooke E. M., Kumar P., Patel N., Parker M. T., Thom B. T., France D. R. Food and medicaments as possible sources of hospital strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Lancet. 1969 Jun 21;1(7608):1227–1229. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92114-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F., Dayton S. L. Use of acetamide broth in the isolation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from rectal swabs. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jul;24(1):143–145. doi: 10.1128/am.24.1.143-145.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabransky R. J., Day F. E. Pyocine typing of clinical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Feb;17(2):293–296. doi: 10.1128/am.17.2.293-296.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


