Abstract
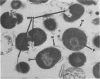
Stable protoplasts of several strains of group H streptococci (Streptococcus sanguis) can be prepared by use of group C streptococcal phage-associated lysin in the presence of 30% raffinose. Sucrose cannot be substituted for raffinose. Protoplast formation did not require the addition of Mg2+; however, this cation enhanced their stability. Some other strains, also presumptive group H streptococci, were not sensitive to phage-associated lysin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas G. D., Ravin A. W. Heterospecific transformation of Pneumococcus and Streptococcus. IV. Variations in hybrid DNA produced by recombination. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;110(1):1–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00276040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman S. E., van de Rijn I., Bleiweis A. S. Lysis of grouped and ungrouped streptococci by lysozyme. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):563–569. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.563-569.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corner T. R., Marquis R. E. Why do bacterial protoplasts burst in hypotonic solutions? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;183(3):544–558. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX E. N. INTRACELLULAR M PROTEIN OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Mar;85:536–540. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.3.536-540.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend P. L., Slade M. D. Characteristics of group A streptococcal bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):148–154. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.148-154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODER H., MAXTED W. R. Protoplasts of group A beta-haemolytic streptococci. Nature. 1958 Sep 20;182(4638):808–809. doi: 10.1038/182808b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard C. G., Ranhand J. M., Cole R. M. Competence factor production in chemically defined media by noncompetent cells of group H Streptococcus strain Challis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):674–683. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.674-683.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKOVITZ A., DORFMAN A. Synthesis of capsular polysaccharide (hyaluronic acid) by protoplastmembrane preparations of group A Streptococcus. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:273–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXTED W. R. The active agent in nascent phage lysis of streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Jun;16(3):584–595. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-3-584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAKULA R., PIECHOWSKA M., BANKOWSKA E., WALCZAK W. A characteristic of DNA mediated transformation systems of two streptococcal strains. Acta Microbiol Pol. 1962;11:205–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAKULA R., TYC M. Zastosowanie czynnika litycznego ze szczepów z rodzaju Streptomyces (Aktynomycetyny) do ekstrakcji kwasu dezoksyrybonukleinowego z bakterii. Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 1956;8(4):523–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY D., SLADE H. D. Transformation of streptococci to streptomycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:443–449. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.443-449.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry D. Binding of streptococcal competence factor by the spheroplast membrane of a group H streptococcus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):702–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.702-707.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranhand J. M., Cole R. M. Demonstration of transforming deoxyribonucleic acid in an autolysate of a group H Streptococcus. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):712–713. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.712-713.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranhand J. M., Cole R. M. Lysis of streptococci by an extracellular lysin produced by competent group H streptococcus strain CHALLIS. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jun;71(1):199–202. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-1-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranhand J. M. Inhibition of the development of competence in Streptococcus sanguis (Wicky) by reagents that interact with sulfhydryl groups: discernment of the competence process. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):1041–1050. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.1041-1050.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]