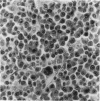
Abstract
Transplant recipients are at increased risk for the development of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders (PTLDs). PTLDs harbor genomes of the Epstein-Barr virus, a herpesvirus that immortalizes B cells in vitro. At least five viral proteins are required for immortalization. Two of them are particularly important. Latent membrane protein (LMP) has transforming activity in fibroblasts, and Epstein-Barr antigen (EBNA)2 transactivates the expression of numerous cellular and viral genes. To determine whether the expression of EBNA2 and LMP is related to the histological and clinical presentation of PTLD, we tested their expression in 14 Epstein-Barr virus-positive cases. Using monoclonal antibodies to EBNA2 and LMP on paraffin sections, we found an expression of both proteins in 2 of 3 polymorphic PTLD and in 7 of 8 cases of monomorphic, large cell PTLD, without plasmacytic differentiation. One polymorphic and one large cell PTLD expressed LMP only. LMP and EBNA2 were found particularly in immunoblasts. The number of positive cells was extremely variable in the different cases as well as within the same biopsy. Three cases of PTLD had morphological and phenotypical features of plasmacytomas and did not stain for EBNA2 or LMP. This suggests that the expression of EBNA2 and LMP is related to the differentiation stage of the infected cells and that other viral or cellular proteins may contribute to tumor growth.
Full text
PDF


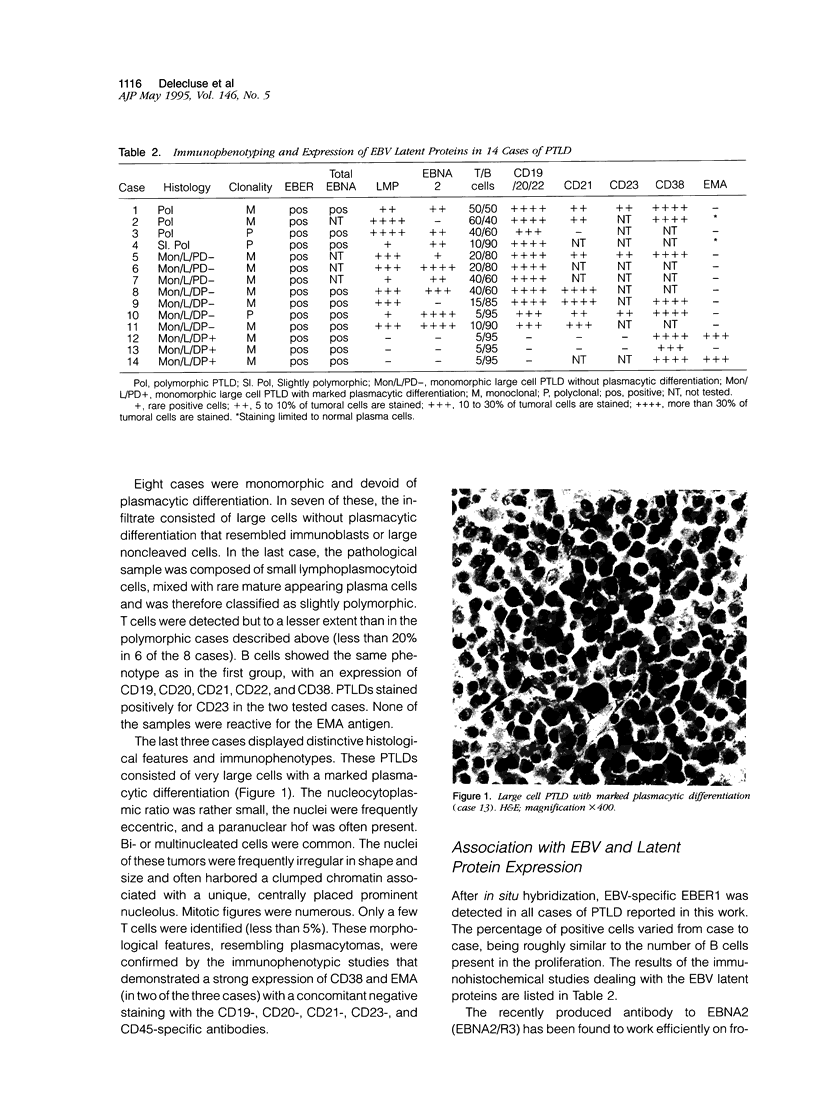
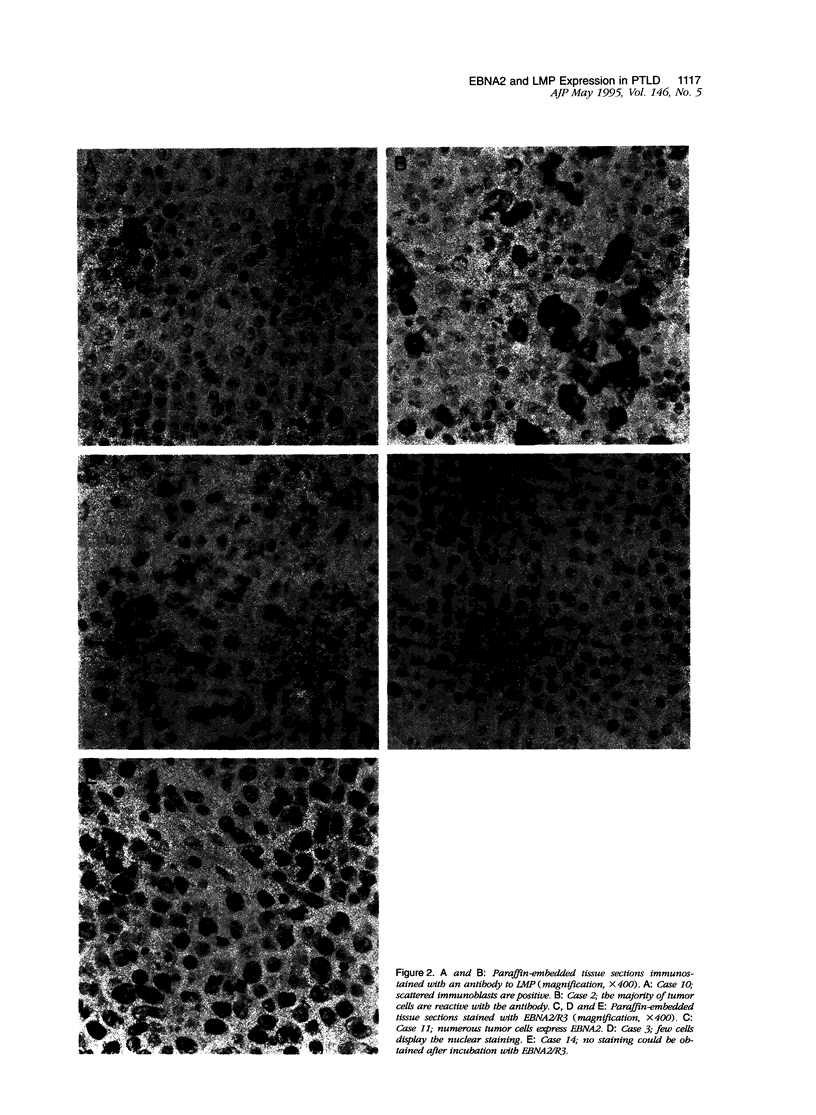



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calender A., Cordier M., Billaud M., Lenoir G. M. Modulation of cellular gene expression in B lymphoma cells following in vitro infection by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Int J Cancer. 1990 Oct 15;46(4):658–663. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910460418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cen H., Williams P. A., McWilliams H. P., Breinig M. C., Ho M., McKnight J. L. Evidence for restricted Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression and anti-EBNA antibody response in solid organ transplant recipients with posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood. 1993 Mar 1;81(5):1393–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordier M., Calender A., Billaud M., Zimber U., Rousselet G., Pavlish O., Banchereau J., Tursz T., Bornkamm G., Lenoir G. M. Stable transfection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 2 in lymphoma cells containing the EBV P3HR1 genome induces expression of B-cell activation molecules CD21 and CD23. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1002–1013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1002-1013.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. H., Thomas J. A., Janossy G., Sweny P., Fernando O. N., Moorhead J. F., Thompson J. H. Epstein Barr virus nuclear antigen positive lymphoma after cyclosporin A treatment in patient with renal allograft. Lancet. 1980 Jun 21;1(8182):1355–1356. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91800-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delecluse H. J., Rouault J. P., Ffrench M., Dureau G., Magaud J. P., Berger F. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders with genetic abnormalities commonly found in malignant tumours. Br J Haematol. 1995 Jan;89(1):90–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1995.tb08905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzera G., Hanto D. W., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Rosai J., McKenna R. W., Sibley R. K., Holahan K. P., Lindquist L. L. Polymorphic diffuse B-cell hyperplasias and lymphomas in renal transplant recipients. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4262–4279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratama J. W., Zutter M. M., Minarovits J., Oosterveer M. A., Thomas E. D., Klein G., Ernberg I. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded growth-transformation-associated proteins in lymphoproliferations of bone-marrow transplant recipients. Int J Cancer. 1991 Jan 21;47(2):188–192. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Rea D., Raphael M., Sandvej K., Delecluse H. J., Gisselbrecht C., Marelle L., van Krieken H. J., Pallesen G. Epstein-Barr virus-latent gene expression and tumor cell phenotype in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Correlation of lymphoma phenotype with three distinct patterns of viral latency. Am J Pathol. 1993 Oct;143(4):1072–1085. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanto D. W., Frizzera G., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Simmons R. L. Epstein-Barr virus, immunodeficiency, and B cell lymphoproliferation. Transplantation. 1985 May;39(5):461–472. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198505000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker J., Nalesnik M. Molecular genetic analysis of lymphoid tumors arising after organ transplantation. Am J Pathol. 1989 Dec;135(6):977–987. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton T., Gahn T. A., Martin J. M., Sugden B. Immortalizing genes of Epstein-Barr virus. Adv Virus Res. 1991;40:19–55. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60276-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalesnik M. A., Jaffe R., Starzl T. E., Demetris A. J., Porter K., Burnham J. A., Makowka L., Ho M., Locker J. The pathology of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders occurring in the setting of cyclosporine A-prednisone immunosuppression. Am J Pathol. 1988 Oct;133(1):173–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalesnik M. A. Lymphoproliferative disease in organ transplant recipients. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1991;13(2):199–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00201469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen G., Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Rowe M., Young L. S. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene products in tumour cells of Hodgkin's disease. Lancet. 1991 Feb 9;337(8737):320–322. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90943-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochford R., Hobbs M. V., Garnier J. L., Cooper N. R., Cannon M. J. Plasmacytoid differentiation of Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B cells in vivo is associated with reduced expression of viral latent genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):352–356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Hotchin N. A., Allday M. J., Amlot P., Rose M., Yacoub M., Crawford D. H. Immunohistology of Epstein-Barr virus-associated antigens in B cell disorders from immunocompromised individuals. Transplantation. 1990 May;49(5):944–953. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199005000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veronese M. L., Veronesi A., D'Andrea E., Del Mistro A., Indraccolo S., Mazza M. R., Mion M., Zamarchi R., Menin C., Panozzo M. Lymphoproliferative disease in human peripheral blood mononuclear cell-injected SCID mice. I. T lymphocyte requirement for B cell tumor generation. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1763–1767. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendel-Hansen V., Rosén A., Klein G. EBV-transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines down-regulate EBNA in parallel with secretory differentiation. Int J Cancer. 1987 Mar 15;39(3):404–408. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910390322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimber-Strobl U., Kremmer E., Grässer F., Marschall G., Laux G., Bornkamm G. W. The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 interacts with an EBNA2 responsive cis-element of the terminal protein 1 gene promoter. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):167–175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05642.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Knebel Doeberitz M., Bornkamm G. W., zur Hausen H. Establishment of spontaneously outgrowing lymphoblastoid cell lines with Cyclosporin A. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1983;172(2):87–99. doi: 10.1007/BF02124509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]