Abstract
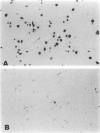
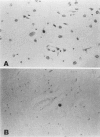
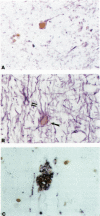
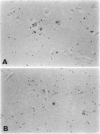
The mechanism of cell death in the brains of patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome was examined in 15 cases, 8 of whom had human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) encephalitis, and in 8 control cases. Postmortem formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections were prepared for routine histology and immunohistochemistry to detect cell-specific antigens. Apoptosis was detected by its morphology and by in situ end labeling of its characteristic oligonucleosomal fragments. Combined in situ end labeling and immunohistochemistry identified specific cell types. Six acquired immune deficiency syndrome brains, 5 of which had HIV encephalitis, contained positive nuclei by in situ end labeling. Co-labeling studies identified the cells as neurons, reactive astrocytes, and, rarely, the multinucleated giant cells of HIV encephalitis. The only control with nuclei positive by in situ end labeling had hepatic encephalopathy and Alzheimer type II astrocytes; the location and absence of cell-specific markers suggested a glial origin for the labeled cells. These results demonstrate that at least some neuronal and astrocytic death in HIV infection occurs by apoptosis. Its stimuli are unknown, but likely candidates include tumor necrosis factor or HIV viral products. Additionally, we hypothesize that apoptotic death of reactive astrocytes may be a normal mechanism whereby the brain removes an excess number of astrocytes that have proliferated after certain types of brain injury.
Full text
PDF


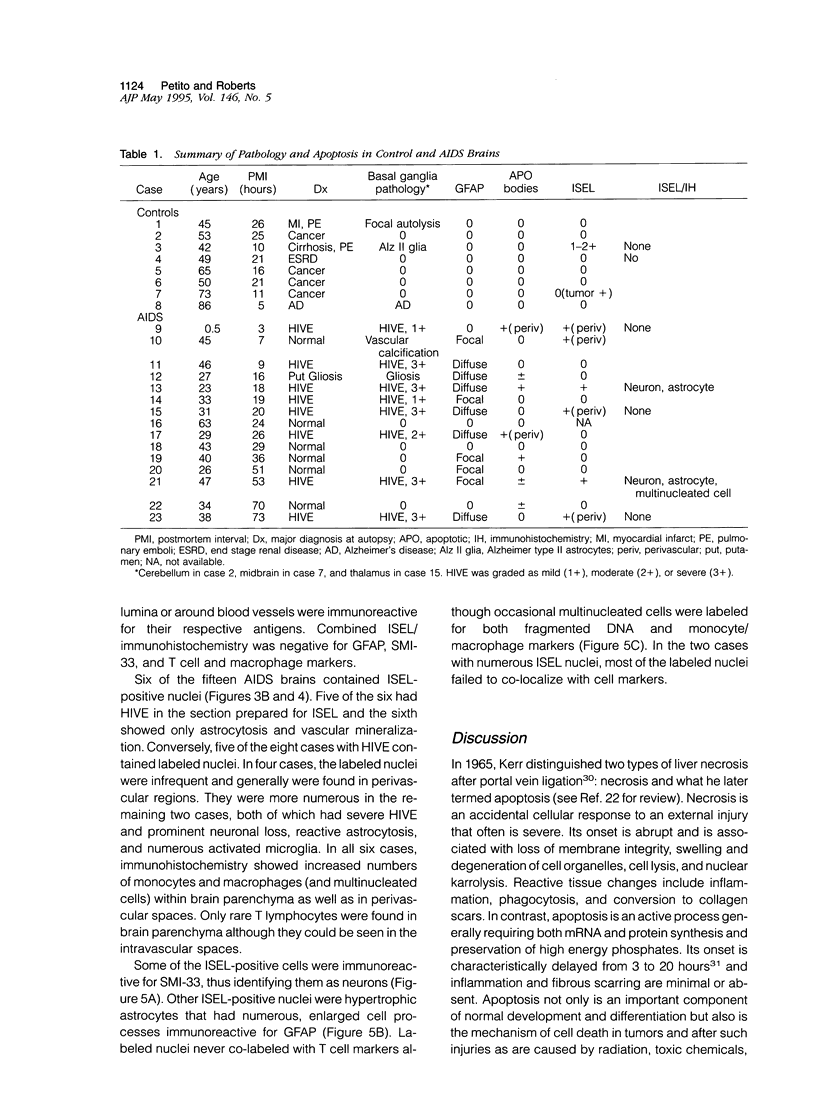
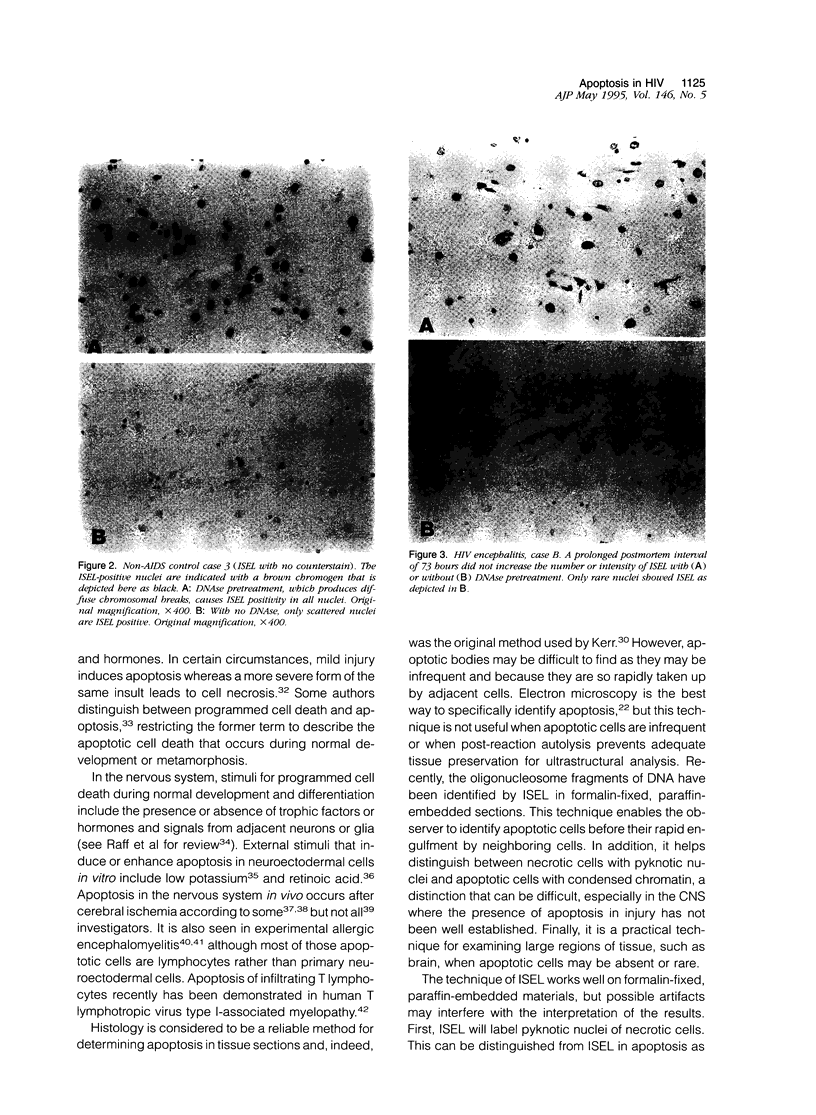





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allsopp T. E., Wyatt S., Paterson H. F., Davies A. M. The proto-oncogene bcl-2 can selectively rescue neurotrophic factor-dependent neurons from apoptosis. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):295–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90230-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ameisen J. C. Programmed cell death and AIDS: from hypothesis to experiment. Immunol Today. 1992 Oct;13(10):388–391. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90086-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aylward E. H., Henderer J. D., McArthur J. C., Brettschneider P. D., Harris G. J., Barta P. E., Pearlson G. D. Reduced basal ganglia volume in HIV-1-associated dementia: results from quantitative neuroimaging. Neurology. 1993 Oct;43(10):2099–2104. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.10.2099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barres B. A. New roles for glia. J Neurosci. 1991 Dec;11(12):3685–3694. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-12-03685.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenneman D. E., Westbrook G. L., Fitzgerald S. P., Ennist D. L., Elkins K. L., Ruff M. R., Pert C. B. Neuronal cell killing by the envelope protein of HIV and its prevention by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):639–642. doi: 10.1038/335639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciardi A., Sinclair E., Scaravilli F., Harcourt-Webster N. J., Lucas S. The involvement of the cerebral cortex in human immunodeficiency virus encephalopathy: a morphological and immunohistochemical study. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;81(1):51–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00662637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Mello S. R., Galli C., Ciotti T., Calissano P. Induction of apoptosis in cerebellar granule neurons by low potassium: inhibition of death by insulin-like growth factor I and cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):10989–10993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.10989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Pan G. J., McArthur J. H., Aylward E., Selnes O. A., Nance-Sproson T. E., Kumar A. J., Mellits E. D., McArthur J. C. Patterns of cerebral atrophy in HIV-1-infected individuals: results of a quantitative MRI analysis. Neurology. 1992 Nov;42(11):2125–2130. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.11.2125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande J., Bergstedt K., Lindén T., Kalimo H., Wieloch T. Ultrastructural changes in the hippocampal CA1 region following transient cerebral ischemia: evidence against programmed cell death. Exp Brain Res. 1992;88(1):91–105. doi: 10.1007/BF02259131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer E. B., Kaiser P. K., Offermann J. T., Lipton S. A. HIV-1 coat protein neurotoxicity prevented by calcium channel antagonists. Science. 1990 Apr 20;248(4953):364–367. doi: 10.1126/science.2326646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis H. M., Horvitz H. R. Genetic control of programmed cell death in the nematode C. elegans. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everall I. P., Luthert P. J., Lantos P. L. Neuronal loss in the frontal cortex in HIV infection. Lancet. 1991 May 11;337(8750):1119–1121. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92786-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer I., Tortosa A., Macaya A., Sierra A., Moreno D., Munell F., Blanco R., Squier W. Evidence of nuclear DNA fragmentation following hypoxia-ischemia in the infant rat brain, and transient forebrain ischemia in the adult gerbil. Brain Pathol. 1994 Apr;4(2):115–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1994.tb00821.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagliardini V., Fernandez P. A., Lee R. K., Drexler H. C., Rotello R. J., Fishman M. C., Yuan J. Prevention of vertebrate neuronal death by the crmA gene. Science. 1994 Feb 11;263(5148):826–828. doi: 10.1126/science.8303301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrieli Y., Sherman Y., Ben-Sasson S. A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):493–501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman B. B. Diffuse microgliosis associated with cerebral atrophy in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1993 Jul;34(1):65–70. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman B. B., Guinto F. C., Jr Morphometry, histopathology, and tomography of cerebral atrophy in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1992 Jul;32(1):31–40. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold R., Schmied M., Rothe G., Zischler H., Breitschopf H., Wekerle H., Lassmann H. Detection of DNA fragmentation in apoptosis: application of in situ nick translation to cell culture systems and tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Jul;41(7):1023–1030. doi: 10.1177/41.7.8515045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Epstein L. G., Paul D. A., van der Helm H. J., Dawson G. J., Asher D. M., Yanagihara R., Wolff A. V., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Intra-blood-brain barrier synthesis of human immunodeficiency virus antigen and antibody in humans and chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3876–3880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gougeon M. L., Montagnier L. Apoptosis in AIDS. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1269–1270. doi: 10.1126/science.8098552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi L. M., Martino G. V., Franciotta D. M., Brustia R., Castagna A., Pristerà R., Lazzarin A. Elevated alpha-tumor necrosis factor levels in spinal fluid from HIV-1-infected patients with central nervous system involvement. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jan;29(1):21–25. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson E. Astroglia from defined brain regions as studied with primary cultures. Prog Neurobiol. 1988;30(5):369–397. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(88)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon B. V., Corder A. M., Collins R. J., Gobé G. C., Allen J., Allan D. J., Kerr J. F. Cell death induced in a murine mastocytoma by 42-47 degrees C heating in vitro: evidence that the form of death changes from apoptosis to necrosis above a critical heat load. Int J Radiat Biol. 1990 Nov;58(5):845–858. doi: 10.1080/09553009014552221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M. K., Burke L. C., Mailhos C., Pizzey A., Gilbert C. S., Lawson W. D., Collins M. K., Thomas N. S., Latchman D. S. Cell cycle arrest of proliferating neuronal cells by serum deprivation can result in either apoptosis or differentiation. J Neurochem. 1993 May;60(5):1783–1791. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb13404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser P. K., Offermann J. T., Lipton S. A. Neuronal injury due to HIV-1 envelope protein is blocked by anti-gp120 antibodies but not by anti-CD4 antibodies. Neurology. 1990 Nov;40(11):1757–1761. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.11.1757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane D. J., Sarafian T. A., Anton R., Hahn H., Gralla E. B., Valentine J. S., Ord T., Bredesen D. E. Bcl-2 inhibition of neural death: decreased generation of reactive oxygen species. Science. 1993 Nov 19;262(5137):1274–1277. doi: 10.1126/science.8235659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F. A histochemical study of hypertrophy and ischaemic injury of rat liver with special reference to changes in lysosomes. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(2):419–435. doi: 10.1002/path.1700900210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketzler S., Weis S., Haug H., Budka H. Loss of neurons in the frontal cortex in AIDS brains. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;80(1):92–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00294228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leoncini L., Del Vecchio M. T., Megha T., Barbini P., Galieni P., Pileri S., Sabattini E., Gherlinzoni F., Tosi P., Kraft R. Correlations between apoptotic and proliferative indices in malignant non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Am J Pathol. 1993 Mar;142(3):755–763. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mailhos C., Howard M. K., Latchman D. S. Heat shock protects neuronal cells from programmed cell death by apoptosis. Neuroscience. 1993 Aug;55(3):621–627. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90428-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masliah E., Achim C. L., Ge N., DeTeresa R., Terry R. D., Wiley C. A. Spectrum of human immunodeficiency virus-associated neocortical damage. Ann Neurol. 1992 Sep;32(3):321–329. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migheli A., Cavalla P., Marino S., Schiffer D. A study of apoptosis in normal and pathologic nervous tissue after in situ end-labeling of DNA strand breaks. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1994 Nov;53(6):606–616. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199411000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Schröder H. C., Ushijima H., Dapper J., Bormann J. gp120 of HIV-1 induces apoptosis in rat cortical cell cultures: prevention by memantine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 1;226(3):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odeh M. The role of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Intern Med. 1990 Dec;228(6):549–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1990.tb00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oster S., Christoffersen P., Gundersen H. J., Nielsen J. O., Pakkenberg B., Pedersen C. Cerebral atrophy in AIDS: a stereological study. Acta Neuropathol. 1993;85(6):617–622. doi: 10.1007/BF00334671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pender M. P., Nguyen K. B., McCombe P. A., Kerr J. F. Apoptosis in the nervous system in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neurol Sci. 1991 Jul;104(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(91)90219-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petito C. K., Cash K. S. Blood-brain barrier abnormalities in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: immunohistochemical localization of serum proteins in postmortem brain. Ann Neurol. 1992 Nov;32(5):658–666. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petito C. K., Cho E. S., Lemann W., Navia B. A., Price R. W. Neuropathology of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS): an autopsy review. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1986 Nov;45(6):635–646. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198611000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petito C. K., Morgello S., Felix J. C., Lesser M. L. The two patterns of reactive astrocytosis in postischemic rat brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1990 Nov;10(6):850–859. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1990.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petito C. K. What causes brain atrophy in human immunodeficiency virus infection? Ann Neurol. 1993 Aug;34(2):128–129. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. N., Wang S., DiBenedetto A. J., Mills J. C. A system for characterizing cellular and molecular events in programmed neuronal cell death. J Neurosci. 1993 Sep;13(9):3669–3680. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-09-03669.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post M. J., Berger J. R., Quencer R. M. Asymptomatic and neurologically symptomatic HIV-seropositive individuals: prospective evaluation with cranial MR imaging. Radiology. 1991 Jan;178(1):131–139. doi: 10.1148/radiology.178.1.1984291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power C., Kong P. A., Crawford T. O., Wesselingh S., Glass J. D., McArthur J. C., Trapp B. D. Cerebral white matter changes in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome dementia: alterations of the blood-brain barrier. Ann Neurol. 1993 Sep;34(3):339–350. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulliam L., West D., Haigwood N., Swanson R. A. HIV-1 envelope gp120 alters astrocytes in human brain cultures. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 May;9(5):439–444. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Barres B. A., Burne J. F., Coles H. S., Ishizaki Y., Jacobson M. D. Programmed cell death and the control of cell survival: lessons from the nervous system. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):695–700. doi: 10.1126/science.8235590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidbauer M., Huemer M., Cristina S., Trabattoni G. R., Budka H. Morphological spectrum, distribution and clinical correlation of white matter lesions in AIDS brains. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1992 Oct;18(5):489–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1992.tb00816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmied M., Breitschopf H., Gold R., Zischler H., Rothe G., Wekerle H., Lassmann H. Apoptosis of T lymphocytes in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Evidence for programmed cell death as a mechanism to control inflammation in the brain. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):446–452. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhean D., Duyckaerts C., Vazeux R., Bolgert F., Brunet P., Katlama C., Gentilini M., Hauw J. J. HIV-1-associated cognitive/motor complex: absence of neuronal loss in the cerebral neocortex. Neurology. 1993 Aug;43(8):1492–1499. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.8.1492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmaj K. W., Raine C. S. Tumor necrosis factor mediates myelin and oligodendrocyte damage in vitro. Ann Neurol. 1988 Apr;23(4):339–346. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmaj K., Raine C. S., Farooq M., Norton W. T., Brosnan C. F. Cytokine cytotoxicity against oligodendrocytes. Apoptosis induced by lymphotoxin. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1522–1529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharer L. R. Pathology of HIV-1 infection of the central nervous system. A review. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1992 Jan;51(1):3–11. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199201000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga T., Kure S., Narisawa K., Yoshimoto T. Endonuclease activation following focal ischemic injury in the rat brain. Brain Res. 1993 Apr 9;608(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90768-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyor W. R., Glass J. D., Griffin J. W., Becker P. S., McArthur J. C., Bezman L., Griffin D. E. Cytokine expression in the brain during the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1992 Apr;31(4):349–360. doi: 10.1002/ana.410310402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umehara F., Nakamura A., Izumo S., Kubota R., Ijichi S., Kashio N., Hashimoto K., Usuku K., Sato E., Osame M. Apoptosis of T lymphocytes in the spinal cord lesions in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy: a possible mechanism to control viral infection in the central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1994 Nov;53(6):617–624. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199411000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis S., Haug H., Budka H. Astroglial changes in the cerebral cortex of AIDS brains: a morphometric and immunohistochemical investigation. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1993 Aug;19(4):329–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1993.tb00448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis S., Haug H., Budka H. Neuronal damage in the cerebral cortex of AIDS brains: a morphometric study. Acta Neuropathol. 1993;85(2):185–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00227766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijsman J. H., Jonker R. R., Keijzer R., van de Velde C. J., Cornelisse C. J., van Dierendonck J. H. A new method to detect apoptosis in paraffin sections: in situ end-labeling of fragmented DNA. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Jan;41(1):7–12. doi: 10.1177/41.1.7678025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Masliah E., Morey M., Lemere C., DeTeresa R., Grafe M., Hansen L., Terry R. Neocortical damage during HIV infection. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jun;29(6):651–657. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]