Abstract
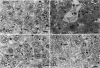
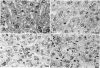
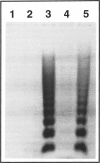
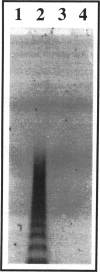
We investigated the role of hepatocyte apoptosis in four different murine models of acute inflammatory liver failure. Liver damage induced in D-galactosamine-sensitized mice by endotoxin infection was initiated by processes typical of apoptosis, ie, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and formation of intracellular apoptotic bodies. DNA was cleaved into oligonucleosomal fragments in the liver before a significant rise of alanine aminotransferase in plasma occurred. Passive immunization against tumor necrosis factor (TNF) completely inhibited the injury caused by endotoxin. Direct injection of recombinant TNF-alpha also caused DNA fragmentation followed by alanine aminotransferase release into the plasma. Pretreatment of mice with interleukin-1 beta, which is known to suppress TNF-induced lethality, completely prevented apoptosis and liver failure in this model. These results demonstrate the causal role of TNF in endotoxin-induced hepatic apoptosis. TNF-inducible hepatocyte apoptosis in vivo was not only observed in D-galactosamine-sensitized mice, but also when the alternative transcriptional inhibitor actinomycin D was used. In mice injected with the TNF-inducing T cell mitogen concanavalin A, hepatic apoptosis was even noticed without requirement of additional sensitizers. We conclude that TNF-induced hepatocyte apoptosis is an early, general, and possibly causal event during experimental liver failure triggered by inflammatory stimuli.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe Y., Gatanaga M., Osuka Y., Kimura S., Burger R. A., Granger G. A., Gatanaga T. Role of 55- and 75-kDa tumor necrosis factor membrane receptors in the regulation of intercellular adhesion molecules-1 expression by HL-60 human promyelocytic leukemia cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 1;150(11):5070–5079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcorn J. M., Fierer J., Chojkier M. The acute-phase response protects mice from D-galactosamine sensitization to endotoxin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Hepatology. 1992 Jan;15(1):122–129. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anukarahanonta T., Shinozuka H., Farber E. Inhibition of protein synthesis in rat liver by D-galactosamine. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1973 Mar;5(2):481–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate C. A., Taverne J., Playfair J. H. Soluble malarial antigens are toxic and induce the production of tumour necrosis factor in vivo. Immunology. 1989 Apr;66(4):600–605. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Grau G. E. Tumor necrosis factor in the pathogenesis of infectious diseases. Crit Care Med. 1993 Oct;21(10 Suppl):S423–S435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C., Balk R. A., Cerra F. B., Dellinger R. P., Fein A. M., Knaus W. A., Schein R. M., Sibbald W. J. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest. 1992 Jun;101(6):1644–1655. doi: 10.1378/chest.101.6.1644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøe R., Gjertsen B. T., Vintermyr O. K., Houge G., Lanotte M., Døskeland S. O. The protein phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid induces morphological changes typical of apoptosis in mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Jul;195(1):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90523-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. R., Vesin C., Grau G. E., Pointaire P., Arsenijevic D., Strath M., Pechère J. C., Piguet P. F. Respective role of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and their integrins (CD-11/18) in the local or systemic toxicity of lipopolysaccharide. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Jun;53(6):636–639. doi: 10.1002/jlb.53.6.636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Child P. L., Ruiz A. Acidophilic bodies. Their chemical and physical nature in patients with Bolivian hemorrhagic fever. Arch Pathol. 1968 Jan;85(1):45–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chojkier M., Fierer J. D-Galactosamine hepatotoxicity is associated with endotoxin sensitivity and mediated by lymphoreticular cells in mice. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jan;88(1 Pt 1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czaja M. J., Xu J., Ju Y., Alt E., Schmiedeberg P. Lipopolysaccharide-neutralizing antibody reduces hepatocyte injury from acute hepatotoxin administration. Hepatology. 1994 May;19(5):1282–1289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker K., Keppler D. Galactosamine hepatitis: key role of the nucleotide deficiency period in the pathogenesis of cell injury and cell death. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1974;(71):77–106. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Mofty S. K., Scrutton M. C., Serroni A., Nicolini C., Farber J. L. Early, reversible plasma membrane injury in galactosamine-induced liver cell death. Am J Pathol. 1975 Jun;79(3):579–596. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Nissen-Meyer J. A highly sensitive cell line, WEHI 164 clone 13, for measuring cytotoxic factor/tumor necrosis factor from human monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 4;95(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber E., Roberts J. J. Response of cells to inhibition of synthesis of DNA, RNA and protein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 May;20(5):1023–1028. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90328-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesus L., Thomazy V., Falus A. Induction and activation of tissue transglutaminase during programmed cell death. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):104–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80430-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenberg M. A., Keppler D., Galanos C. Requirement for lipopolysaccharide-responsive macrophages in galactosamine-induced sensitization to endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):891–895. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.891-895.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Freudenberg M. A., Reutter W. Galactosamine-induced sensitization to the lethal effects of endotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5939–5943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantner F., Leist M., Lohse A. W., Germann P. G., Tiegs G. Concanavalin A-induced T-cell-mediated hepatic injury in mice: the role of tumor necrosis factor. Hepatology. 1995 Jan;21(1):190–198. doi: 10.1016/0270-9139(95)90428-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilles P. N., Guerrette D. L., Ulevitch R. J., Schreiber R. D., Chisari F. V. HBsAg retention sensitizes the hepatocyte to injury by physiological concentrations of interferon-gamma. Hepatology. 1992 Sep;16(3):655–663. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gut J. P., Schmitt S., Bingen A., Anton M., Kirn A. Probable role of endogenous endotoxins in hepatocytolysis during murine hepatitis caused by frog virus 3. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):621–629. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung T., Wendel A. Endotoxin-inducible cytotoxicity in liver cell cultures--I. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Aug 8;42(5):1129–1135. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90298-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai S., Kasai S., Mito M. Encapsulated hepatocyte transplantation for the treatment of D-galactosamine-induced acute hepatic failure in rats. Eur Surg Res. 1993;25(4):193–202. doi: 10.1159/000129278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu N., Hayashi N., Katayama K., Mochizuki K., Kawanishi Y., Kasahara A., Fusamoto H., Kamada T. Immunohistochemical detection of Fas antigen in liver tissue of patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 1994 Jun;19(6):1354–1359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang K. M., Yang L. C., Carrico C. K., Schulz R. A., Schenkman J. B., Sartorelli A. C. Production of membrane whorls in rat liver by some inhibitors of protein synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):20–31. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeschke H., Farhood A., Smith C. W. Neutrophil-induced liver cell injury in endotoxin shock is a CD11b/CD18-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 1):G1051–G1056. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.6.G1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings G., Bourgeois C., Elia M. The magnitude of the acute phase protein response is attenuated by protein deficiency in rats. J Nutr. 1992 Jun;122(6):1325–1331. doi: 10.1093/jn/122.6.1325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. P., McConkey D. J., Nicotera P., Orrenius S. Calcium-activated DNA fragmentation in rat liver nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6398–6403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppler D., Lesch R., Reutter W., Decker K. Experimental hepatitis induced by D-galactosamine. Exp Mol Pathol. 1968 Oct;9(2):279–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(68)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F., Cooksley W. G., Searle J., Halliday J. W., Halliday W. J., Holder L., Roberts I., Burnett W., Powell L. W. The nature of piecemeal necrosis in chronic active hepatitis. Lancet. 1979 Oct 20;2(8147):827–828. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92178-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F. Shrinkage necrosis: a distinct mode of cellular death. J Pathol. 1971 Sep;105(1):13–20. doi: 10.1002/path.1711050103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F., Wyllie A. H., Currie A. R. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 1972 Aug;26(4):239–257. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1972.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klion F. M., Schaffner F. The ultrastructure of acidophilic "Councilman-like" bodies in the liver. Am J Pathol. 1966 May;48(5):755–767. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi Y., Shinozuka H., Farber J. L. The inhibition of rat liver nuclear ribonucleic acid synthesis by galactosamine and its reversal by uridine. Lab Invest. 1974 Jun;30(6):751–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann V., Freudenberg M. A., Galanos C. Lethal toxicity of lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor in normal and D-galactosamine-treated mice. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):657–663. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Slusser R. J., Ruebner B. H. Hepatic changes produced by a single dose of endotoxin in the mouse. Electron microscopy. Am J Pathol. 1968 Feb;52(2):477–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert C., Van Bladel S., Brouckaert P., Shaw A., Fiers W. Involvement of the liver, but not of IL-6, in IL-1-induced desensitization to the lethal effects of tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2625–2632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liehr H., Grün M., Seelig H. P., Seelig R., Reutter W., Heine W. D. On the pathogenesis of galactosamine hepatitis. Indications of extrahepatocellular mechanisms responsible for liver cell death. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1978 Feb 14;26(4):331–344. doi: 10.1007/BF02889560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandl J., Mészáros K., Antoni F., Spolarics Z., Garzó T. Reversible inhibition of RNA synthesis and irreversible inhibition of protein synthesis by D-galactosamine in isolated mouse hepatocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Jul 7;46(1):25–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00215578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medline A., Schaffner F., Popper H. Ultrastructural features in galactosamine-induced hepatitis. Exp Mol Pathol. 1970 Apr;12(2):201–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(70)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miethke T., Duschek K., Wahl C., Heeg K., Wagner H. Pathogenesis of the toxic shock syndrome: T cell mediated lethal shock caused by the superantigen TSST-1. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jul;23(7):1494–1500. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miethke T., Wahl C., Heeg K., Echtenacher B., Krammer P. H., Wagner H. T cell-mediated lethal shock triggered in mice by the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B: critical role of tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):91–98. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihas A. A., Ceballos R., Mihas T. A., Hirschowitz B. I. Modification of the hepatotoxicity of D-galactosamine in the rat by an anti-endotoxin. J Med. 1990;21(6):301–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuhara H., O'Neill E., Seki N., Ogawa T., Kusunoki C., Otsuka K., Satoh S., Niwa M., Senoh H., Fujiwara H. T cell activation-associated hepatic injury: mediation by tumor necrosis factors and protection by interleukin 6. J Exp Med. 1994 May 1;179(5):1529–1537. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.5.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori W., Aoki N., Shiga J. Acute hepatic cell necrosis experimentally produced by viral agents in rabbits. Am J Pathol. 1981 Apr;103(1):31–38. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaki M., Muto Y., Ohnishi H., Yasuda S., Sano K., Naito T., Maeda T., Yamada T., Moriwaki H. Hepatic injury and lethal shock in galactosamine-sensitized mice induced by the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Gastroenterology. 1994 Feb;106(2):450–458. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90604-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan J. P. Intestinal endotoxins as mediators of hepatic injury--an idea whose time has come again. Hepatology. 1989 Nov;10(5):887–891. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhammer F., Bursch W., Tiefenbacher R., Fröschl G., Pavelka M., Purchio T., Schulte-Hermann R. Apoptosis is induced by transforming growth factor-beta 1 within 5 hours in regressing liver without significant fragmentation of the DNA. Hepatology. 1993 Nov;18(5):1238–1246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara J., Watanabe-Fukunaga R., Adachi M., Matsuzawa A., Kasugai T., Kitamura Y., Itoh N., Suda T., Nagata S. Lethal effect of the anti-Fas antibody in mice. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):806–809. doi: 10.1038/364806a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pausch J., Keppler D., Decker K. Activity and distribution of the enzymes of uridylate synthesis from orotate in animal tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90231-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer K., Matsuyama T., Kündig T. M., Wakeham A., Kishihara K., Shahinian A., Wiegmann K., Ohashi P. S., Krönke M., Mak T. W. Mice deficient for the 55 kd tumor necrosis factor receptor are resistant to endotoxic shock, yet succumb to L. monocytogenes infection. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):457–467. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90134-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piacentini M., Autuori F., Dini L., Farrace M. G., Ghibelli L., Piredda L., Fesus L. "Tissue" transglutaminase is specifically expressed in neonatal rat liver cells undergoing apoptosis upon epidermal growth factor-stimulation. Cell Tissue Res. 1991 Feb;263(2):227–235. doi: 10.1007/BF00318764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piacentini M., Sartori C., Beninati S., Bargagli A. M., Cerù-Argento M. P. Ornithine decarboxylase, transglutaminase, diamine oxidase and total diamines and polyamines in maternal liver and kidney throughout rat pregnancy. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 1;234(2):435–440. doi: 10.1042/bj2340435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray S. D., Kamendulis L. M., Gurule M. W., Yorkin R. D., Corcoran G. B. Ca2+ antagonists inhibit DNA fragmentation and toxic cell death induced by acetaminophen. FASEB J. 1993 Mar;7(5):453–463. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.5.8462787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redl H., Bahrami S., Schlag G., Traber D. L. Clinical detection of LPS and animal models of endotoxemia. Immunobiology. 1993 Apr;187(3-5):330–345. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80348-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reutter W., Bauer C., Lesch R. On the mechanism of action of galactosamine: different response to D-galactosamine of rat liver during development. Naturwissenschaften. 1970 Dec;57(12):674–675. doi: 10.1007/BF00598804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reutter W., Lesch R., Keppler D., Decker K. Galactosamin-Hepatitis. Naturwissenschaften. 1968 Oct;55(10):497–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00599726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe J., Lesslauer W., Lötscher H., Lang Y., Koebel P., Köntgen F., Althage A., Zinkernagel R., Steinmetz M., Bluethmann H. Mice lacking the tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 are resistant to TNF-mediated toxicity but highly susceptible to infection by Listeria monocytogenes. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):798–802. doi: 10.1038/364798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVOBODA D., NIELSON A., WERBER A., HIGGINSON J. An electron microscopic study of viral hepatitis in mice. Am J Pathol. 1962 Aug;41:205–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozuka H., Farber J. L., Konishi Y., Anukarahanonta T. D-galactosamine and acute liver cell injury. Fed Proc. 1973 Apr;32(4):1516–1526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozuka H., Martin J. T., Farber J. L. The induction of fibrillar nucleoli in rat liver cells by D-galactosamine and their subsequent re-formation into normal nucleoli. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Aug;44(3):279–292. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)80061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiratori Y., Tanaka M., Hai K., Kawase T., Shirna S., Sugimoto T. Role of endotoxin-responsive macrophages in hepatic injury. Hepatology. 1990 Feb;11(2):183–192. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda T., Takahashi T., Golstein P., Nagata S. Molecular cloning and expression of the Fas ligand, a novel member of the tumor necrosis factor family. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1169–1178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90326-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D. Y., Jiang S., Zheng L. M., Ojcius D. M., Young J. D. Separate metabolic pathways leading to DNA fragmentation and apoptotic chromatin condensation. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):559–568. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiegs G., Hentschel J., Wendel A. A T cell-dependent experimental liver injury in mice inducible by concanavalin A. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):196–203. doi: 10.1172/JCI115836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiegs G., Niehörster M., Wendel A. Leukocyte alterations do not account for hepatitis induced by endotoxin or TNF alpha in galactosamine-sensitized mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Sep 15;40(6):1317–1322. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90398-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiegs G., Wolter M., Wendel A. Tumor necrosis factor is a terminal mediator in galactosamine/endotoxin-induced hepatitis in mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Feb 15;38(4):627–631. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tietze F. Enzymic method for quantitative determination of nanogram amounts of total and oxidized glutathione: applications to mammalian blood and other tissues. Anal Biochem. 1969 Mar;27(3):502–522. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis factor: an updated review of its biology. Crit Care Med. 1993 Oct;21(10 Suppl):S415–S422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaisman N., Schattner A., Hahn T. Tumor necrosis factor production during starvation. Am J Med. 1989 Jul;87(1):115–115. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(89)80497-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli P. The pathophysiology of tumor necrosis factors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:411–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Holtmann H., Engelmann H., Nophar Y. Sensitization and desensitization to lethal effects of tumor necrosis factor and IL-1. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):2994–2999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendel A. Biochemical pharmacology of inflammatory liver injury in mice. Methods Enzymol. 1990;186:675–680. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)86166-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R. Properties of rapidly labelled deoxyribonucleic acid fragments isolated from the cytoplasm of primary cultures of embryonic mouse liver cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 14;51(1):157–168. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90277-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):555–556. doi: 10.1038/284555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H., Gonzalo J. A., St Pierre Y., Williams I. R., Kupper T. S., Cotran R. S., Springer T. A., Gutierrez-Ramos J. C. Leukocytosis and resistance to septic shock in intercellular adhesion molecule 1-deficient mice. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):95–109. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]