Abstract
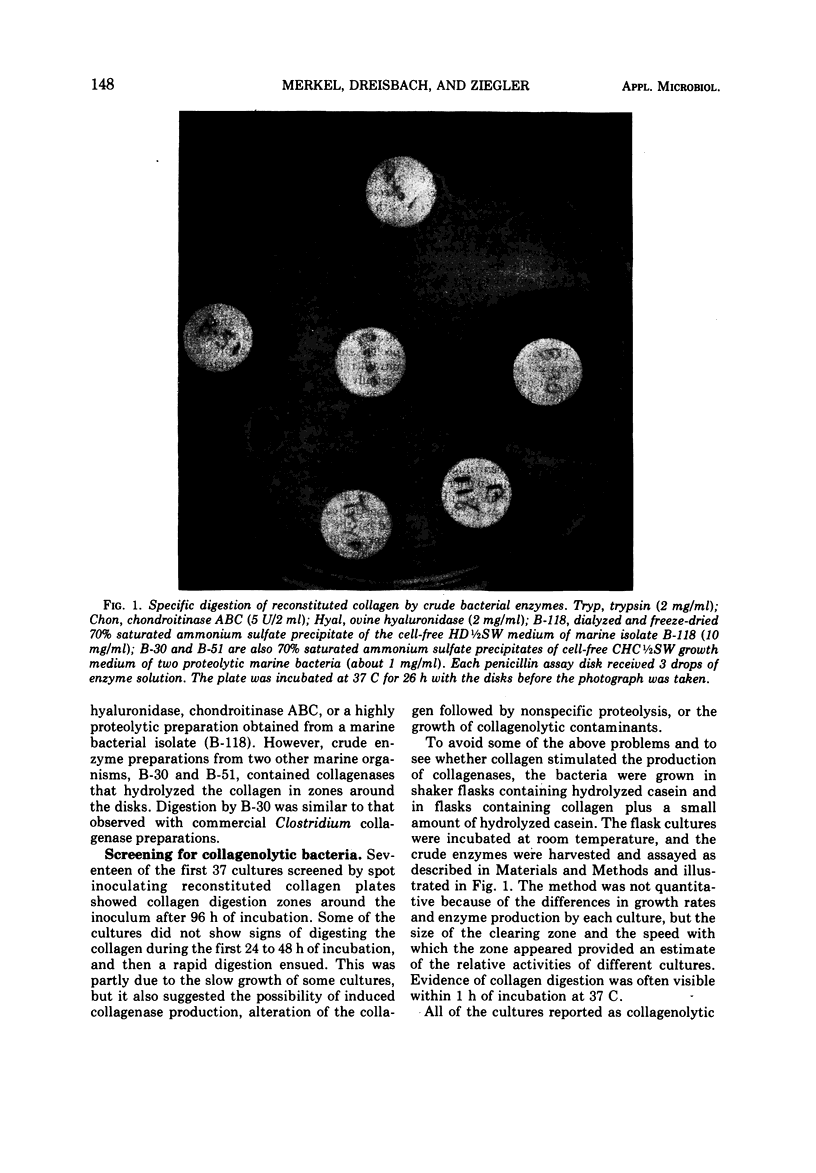
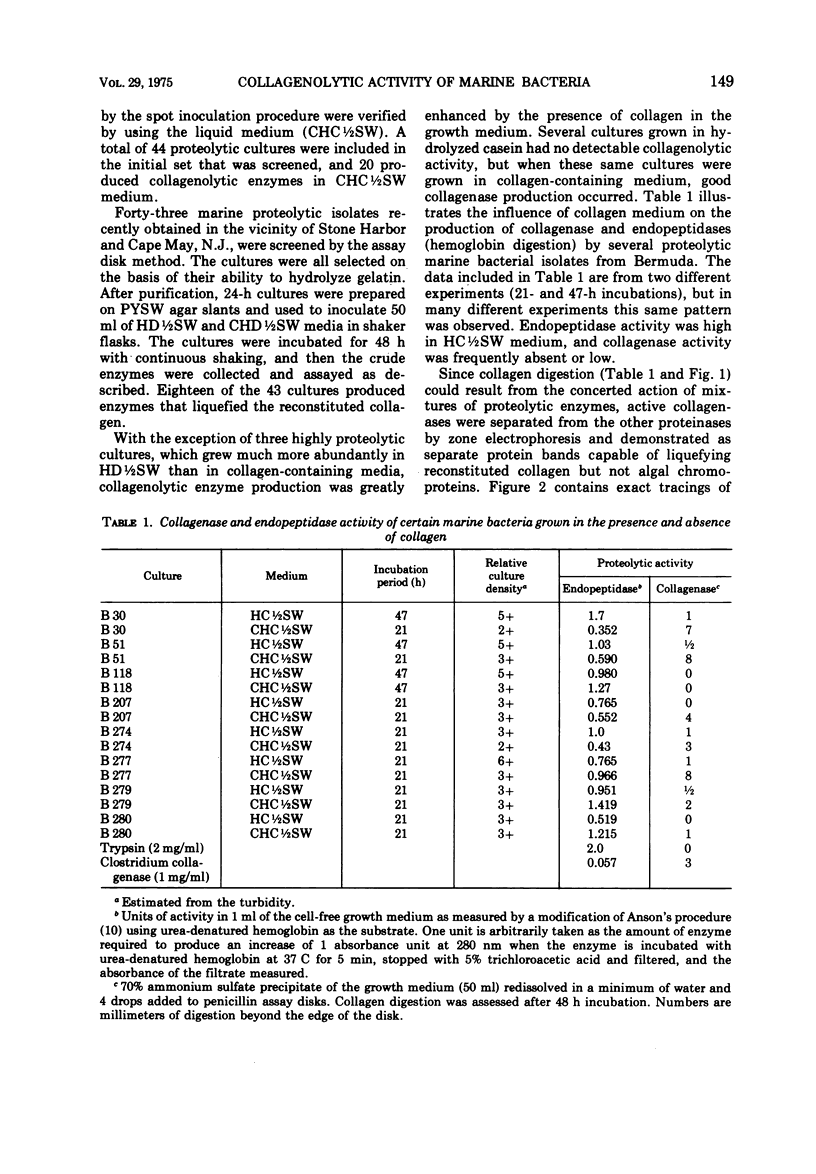
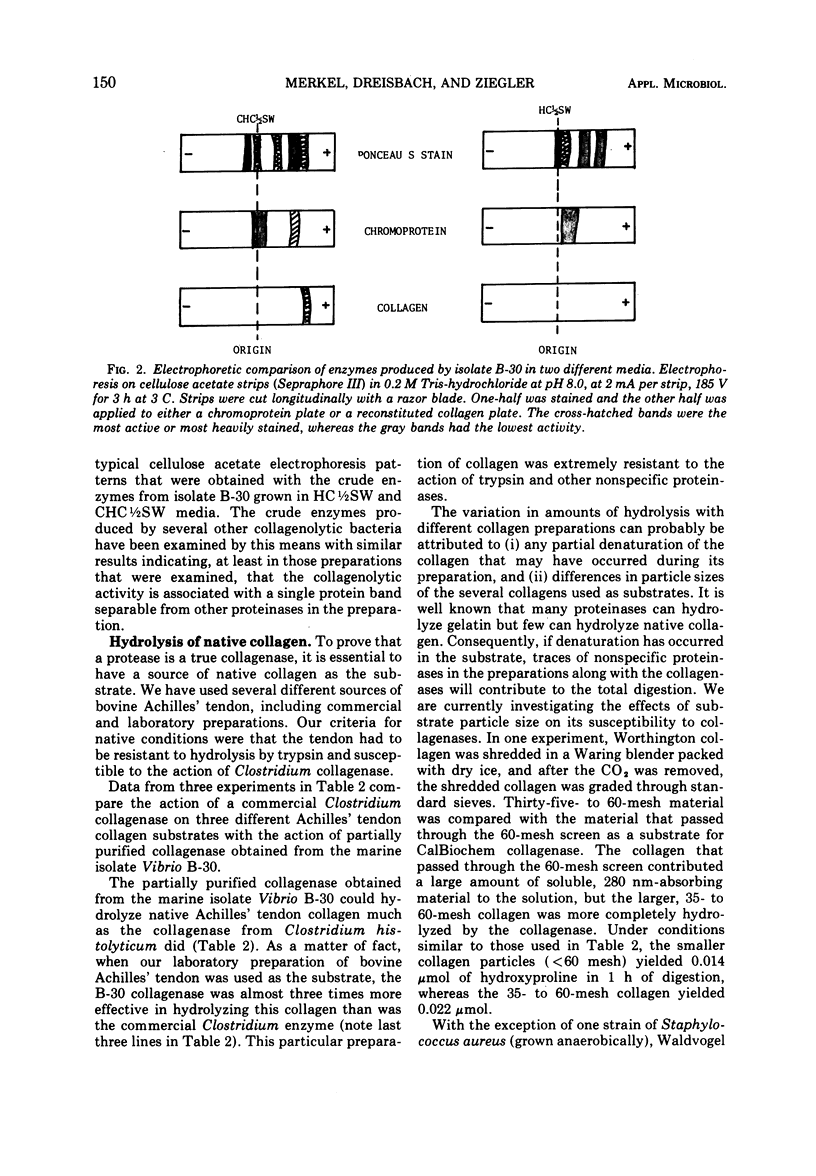
Reconstituted, acid-extracted collagen was used to prepare a medium to screen proteolytic marine bacteria for their ability to elaborate collagenolytic enzymes. The medium was resistant to solubilization by trypsin, hyaluronidase, chondroitinase ABC, and various marine proteinases, but was readily hydrolyzed by commercial Clostridium collagenases. Eighty-seven marine isolates collected in the vicinity of Bermuda, Oahu (Hawaii), and Stone Harbor and Cape May, N.J., were screened. Approximately 44% of the isolates were capable of elaborating enzymes that hydrolyzed reconstituted collagen gels. Several cultures produced collagenolytic enzymes only when grown in the presence of collagen or degradation products of collagen, and with very few exceptions the presence of collagen in the medium greatly enhanced collagenolytic enzyme production. The enzymes from a collagenolytic Bermuda marine isolate were studied in more detail to illustrate that the enzymes capable of hydrolyzing reconstituted collagen were separable from nonspecific proteinases by zone electrophoresis and that these enzymes were true collagenases by virtue of their ability to hydrolyze native bovine Achilles' tendon obtained from three different sources.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EINBINDER J., SCHUBERT M. Binding of mucopolysaccharides and dyes by collagen. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jan;188(1):335–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANT N. H., ALBURN H. E. Studies on the collagenases of Clostridium histolyticum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Jun;82(2):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., KIRK D. The heat precipitation of collagen from neutral salt solutions: some rate-regulating factors. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):355–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., LAPIERE C. M. Collagenolytic activity in amphibian tissues: a tissue culture assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jun 15;48:1014–1022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.6.1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDL I., MACLENNAN J. D., HOWES E. L. Isolation and characterization of proteinase and collagenase from Cl. histolyticum. J Clin Invest. 1953 Dec;32(12):1323–1329. doi: 10.1172/JCI102861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERKEL J. R. METHOD FOR DETECTING AND ISOLATING PROTEOLYTIC MARINE BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:903–904. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.903-904.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkel J. R. Direct detection of proteolytic enzymes that have been separated by zone electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1966 Oct;17(1):84–92. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkel J. R., Sipos T. Marine bacterial proteases. I. Characterization of an endopeptidase produced by Vibrio B-30. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jul;145(1):126–136. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordwig A. Collagenolytic enzymes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1971;34:155–205. doi: 10.1002/9780470122792.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. M., Wilkes S. H. Aeromonas aminopeptidase: purification and some general properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Nov;117(2):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90420-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H. L., Jr, GOODNER K. Detection of bacterial gelatinases by gelatin-agar plate methods. J Bacteriol. 1958 Dec;76(6):662–665. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.6.662-665.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldvogel F. A., Swartz M. N. Collagenolytic activity of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):662–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.662-667.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]