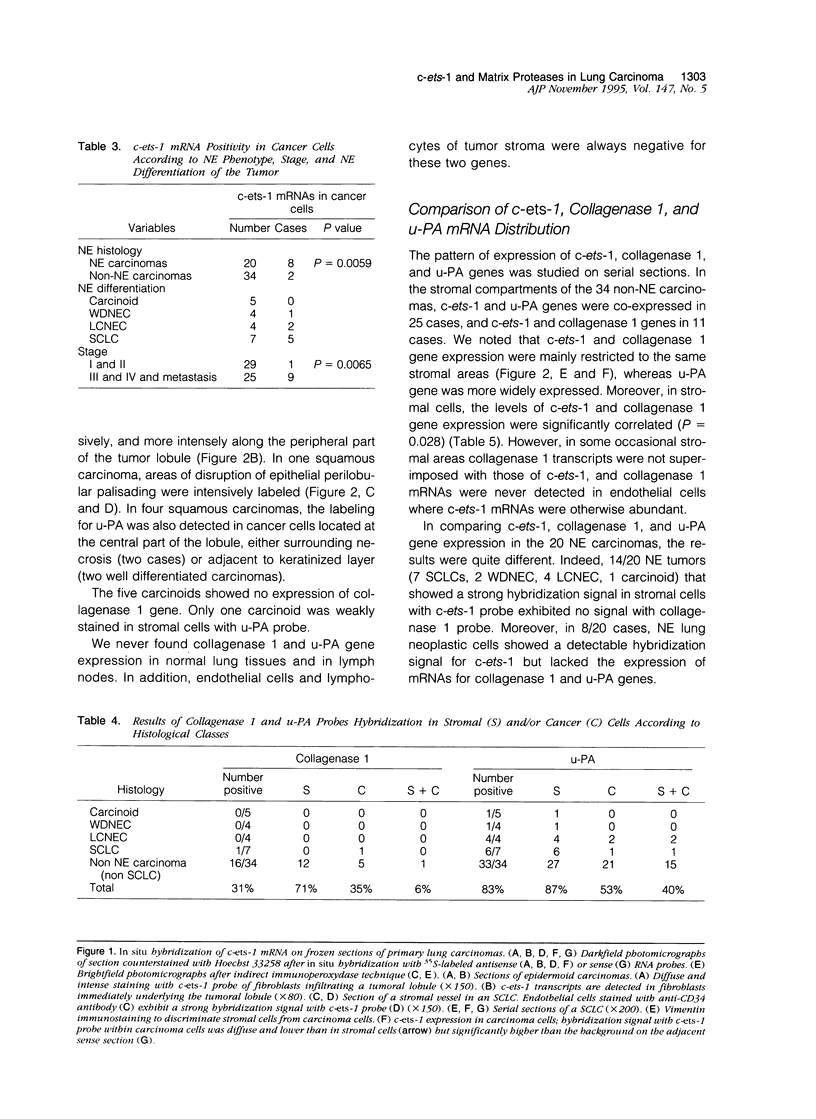
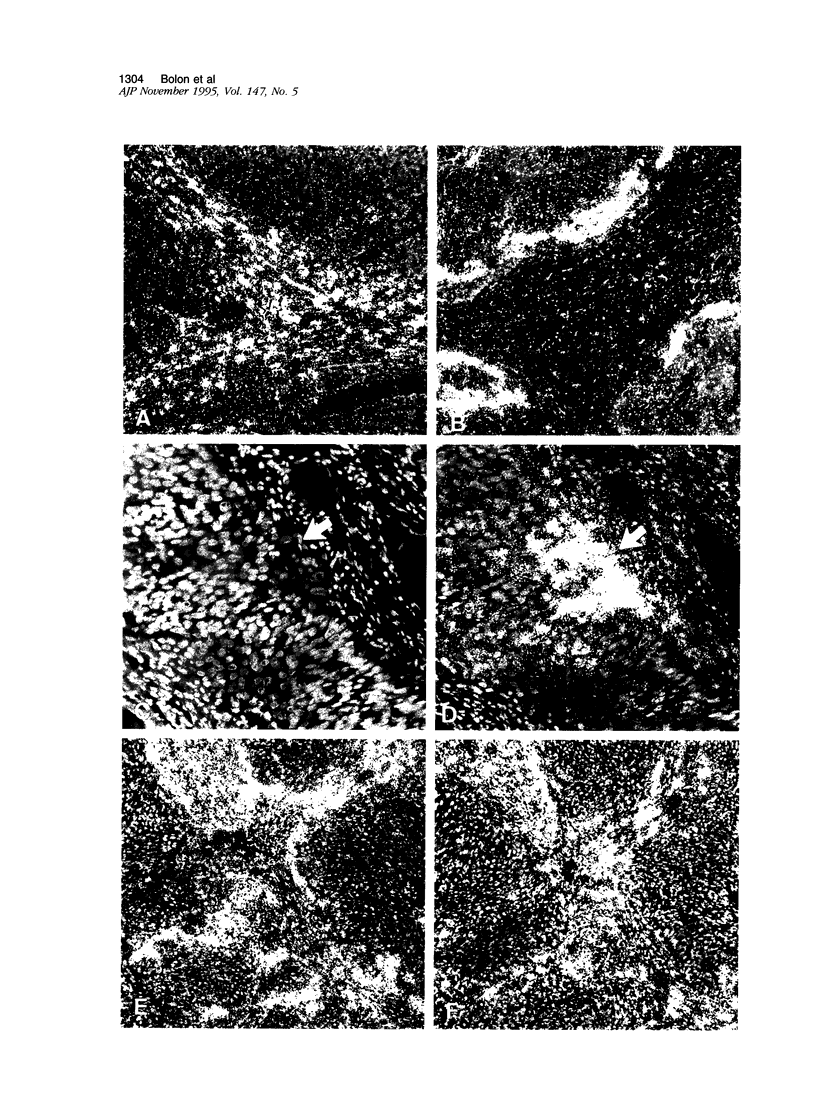
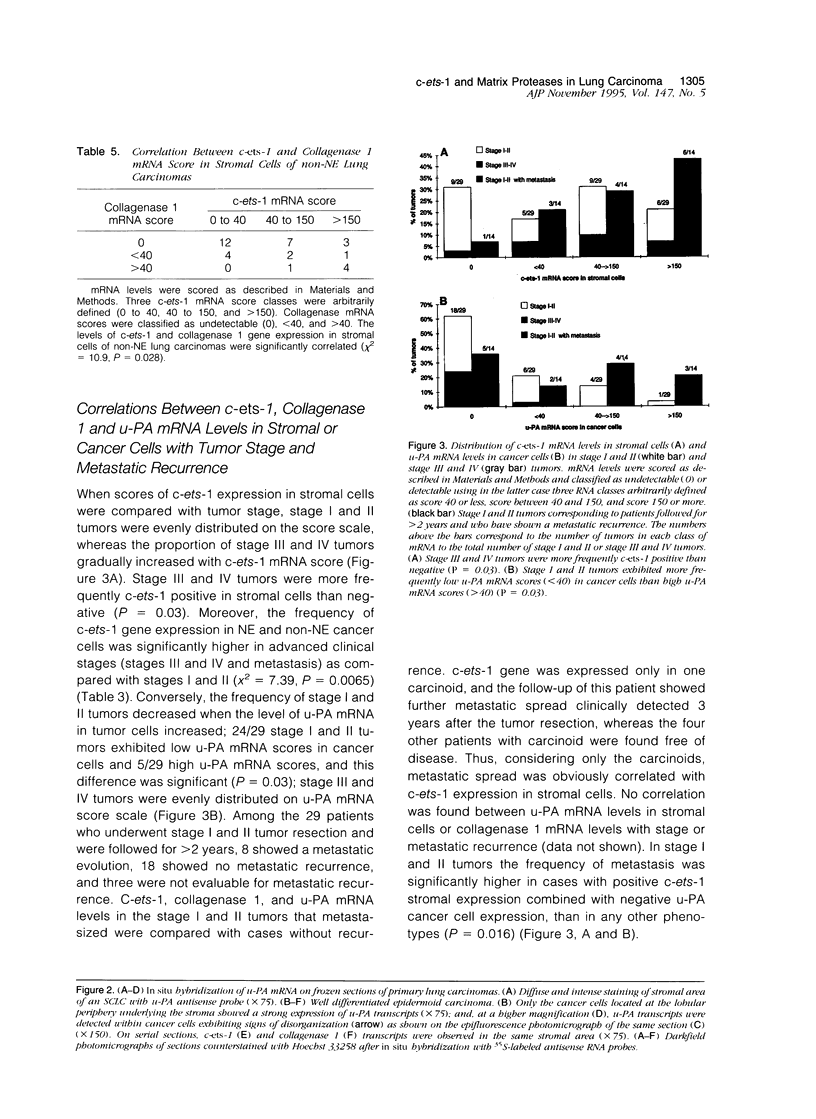
Abstract
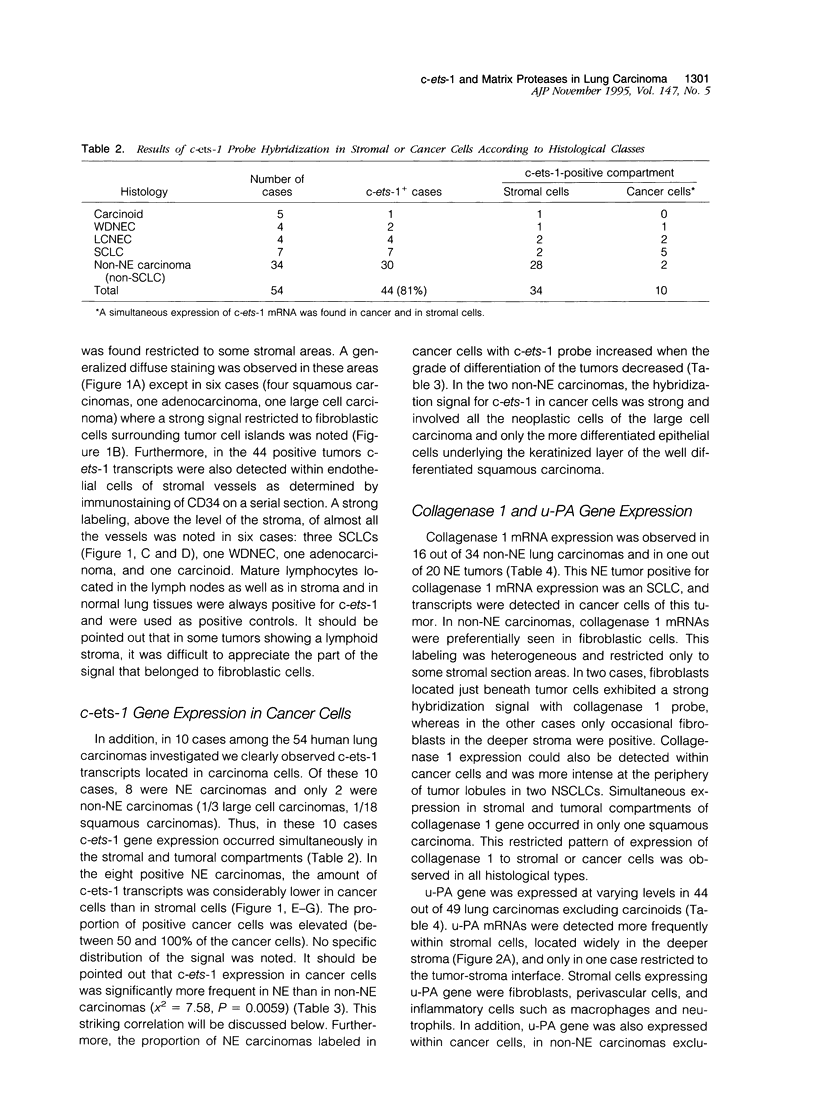
The c-ets-1 transcription factor has been involved in the in vitro transactivation of matrix-degrading protease genes that might play an important role in tumor invasion. Using in situ hybridization, we analyzed serial frozen sections for c-ets-1, collagenase 1, and urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene expression in 54 lung carcinomas including 34 non-neuroendocrine carcinomas (18 squamous carcinomas, 10 adenocarcinomas, 3 large cell carcinomas, and 3 basaloids) and 20 neuroendocrine carcinomas (7 small cell lung carcinomas, 4 large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas, 4 well differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas, and 5 carcinoids). c-ets-1 gene was expressed in stromal cells in 44/54 lung carcinomas including one metastasizing carcinoid. c-ets-1 transcripts were also detected in cancer cells more frequently in neuroendocrine than in non-neuroendocrine carcinomas (P = 0.0059) and in stages III and IV and metastasis more frequently than in stages I and II ( P = 0.0065). Collagenase 1 gene was expressed in 16/34 non-neuroendocrine tumors and in 1/20 neuroendocrine tumors, either in stromal (12/17) or in cancer cells (6/17). Urokinase-type plasminogen activator mRNAs were expressed in 45/54 lung carcinomas in stromal and/or cancer cells. In non-neuroendocrine tumors, c-ets-1 and collagenase 1 gene expressions in stromal cells were correlated. These results demonstrate that the transcription factor c-ets-1, collagenase 1, and urokinase-type plasminogen activator are involved in lung cancer invasion and suggest that c-ets-1 protein might transactivate collagenase 1 gene during tumor invasion.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Baumann I., Stein B., Delius H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate induction of the human collagenase gene is mediated by an inducible enhancer element located in the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2256–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer E. A., Gordon J. M., Reddick M. E., Eisen A. Z. Quantitation and immunocytochemical localization of human skin collagenase in basal cell carcinoma. J Invest Dermatol. 1977 Oct;69(4):363–367. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12510240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borchers A. H., Powell M. B., Fusenig N. E., Bowden G. T. Paracrine factor and cell-cell contact-mediated induction of protease and c-ets gene expression in malignant keratinocyte/dermal fibroblast cocultures. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Jul;213(1):143–147. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brambilla E., Gazzeri S., Moro D., Caron de Fromentel C., Gouyer V., Jacrot M., Brambilla C. Immunohistochemical study of p53 in human lung carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jul;143(1):199–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brambilla E., Moro D., Veale D., Brichon P. Y., Stoebner P., Paramelle B., Brambilla C. Basal cell (basaloid) carcinoma of the lung: a new morphologic and phenotypic entity with separate prognostic significance. Hum Pathol. 1992 Sep;23(9):993–1003. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90260-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brambilla E., Veale D., Moro D., Morel F., Dubois F., Brambilla C. Neuroendocrine phenotype in lung cancers. Comparison of immunohistochemistry with biochemical determination of enolase isoenzymes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1992 Jul;98(1):88–97. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/98.1.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. D., Levy A. T., Margulies I. M., Liotta L. A., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Independent expression and cellular processing of Mr 72,000 type IV collagenase and interstitial collagenase in human tumorigenic cell lines. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 1;50(19):6184–6191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassady A. I., Stacey K. J., Nimmo K. A., Murphy K. M., von der Ahe D., Pearson D., Botteri F. M., Nagamine Y., Hume D. A. Constitutive expression of the urokinase plasminogen activator gene in murine RAW264 macrophages involves distal and 5' non-coding sequences that are conserved between mouse and pig. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6839–6847. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvardsen K., Chen W., Rucklidge G., Walsh F. S., Obrink B., Bock E. Transmembrane neural cell-adhesion molecule (NCAM), but not glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored NCAM, down-regulates secretion of matrix metalloproteinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11463–11467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. The role of angiogenesis in tumor growth. Semin Cancer Biol. 1992 Apr;3(2):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzeri S., Brambilla E., Caron de Fromentel C., Gouyer V., Moro D., Perron P., Berger F., Brambilla C. p53 genetic abnormalities and myc activation in human lung carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1994 Jul 1;58(1):24–32. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910580106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzeri S., Brambilla E., Jacrot M., Chauvin C., Benabid A. L., Brambilla C. Activation of myc gene family in human lung carcinomas and during heterotransplantation into nude mice. Cancer Res. 1991 May 15;51(10):2566–2571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouyer V., Gazzeri S., Brambilla E., Bolon I., Moro D., Perron P., Benabid A. L., Brambilla C. Loss of heterozygosity at the RB locus correlates with loss of RB protein in primary malignant neuro-endocrine lung carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1994 Sep 15;58(6):818–824. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910580612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray S. T., Wilkins R. J., Yun K. Interstitial collagenase gene expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1992 Aug;141(2):301–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray S. T., Yun K., Motoori T., Kuys Y. M. Interstitial collagenase gene expression in colonic neoplasia. Am J Pathol. 1993 Sep;143(3):663–671. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Wasylyk B. The collagenase gene promoter contains a TPA and oncogene-responsive unit encompassing the PEA3 and AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2241–2246. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt R. E., Leach I. H., Powe D. G., Clark I. M., Cawston T. E., Turner D. R. Distribution of collagenase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP) in colorectal tumours. Int J Cancer. 1991 Nov 11;49(5):666–672. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910490507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Keski-Oja J. Growth factors in the regulation of pericellular proteolysis: a review. Cancer Res. 1989 May 15;49(10):2533–2553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin N. M., Teillet M. A. The migration of neural crest cells to the wall of the digestive tract in avian embryo. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1973 Aug;30(1):31–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprince D., Gegonne A., Coll J., de Taisne C., Schneeberger A., Lagrou C., Stehelin D. A putative second cell-derived oncogene of the avian leukaemia retrovirus E26. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):395–397. doi: 10.1038/306395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macchiarini P., Fontanini G., Hardin M. J., Squartini F., Angeletti C. A. Relation of neovascularisation to metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet. 1992 Jul 18;340(8812):145–146. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93217-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus G., Takita H., Camiolo S. M., Corasanti J. G., Evers J. L., Hobika G. H. Content and characterization of plasminogen activators in human lung tumors and normal lung tissue. Cancer Res. 1980 Mar;40(3):841–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauviel A. Cytokine regulation of metalloproteinase gene expression. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Dec;53(4):288–295. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240530404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Robbins E., Rifkin D. B. Tumor invasion through the human amniotic membrane: requirement for a proteinase cascade. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90613-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D., Breathnach R., Engelmann A., Millon R., Bronner G., Flesch H., Dumont P., Eber M., Abecassis J. Expression of collagenase-related metalloproteinase genes in human lung or head and neck tumours. Int J Cancer. 1991 Jun 19;48(4):550–556. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910480412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D., Wolf C., Abecassis J., Millon R., Engelmann A., Bronner G., Rouyer N., Rio M. C., Eber M., Methlin G. Increased stromelysin 3 gene expression is associated with increased local invasiveness in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1993 Jan 1;53(1):165–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagayama M., Sato A., Hayakawa H., Urano T., Takada Y., Takada A. Plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Low content of type 2 plasminogen activator inhibitor associated with tumor dissemination. Cancer. 1994 Mar 1;73(5):1398–1405. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940301)73:5<1398::aid-cncr2820730514>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerlov C., Rørth P., Blasi F., Johnsen M. Essential AP-1 and PEA3 binding elements in the human urokinase enhancer display cell type-specific activity. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1583–1592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Ishida T., Nishino T., Sugimachi K. Immunohistochemical evidence of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in primary and metastatic tumors of pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1991 Jul 1;51(13):3522–3525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L. Invasion of connective tissue by human carcinoma cell lines: requirement for urokinase, urokinase receptor, and interstitial collagenase. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6754–6760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen H., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Francis D., Osterlind K., Hansen H. H., Danø K., Brünner N. Urokinase and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1994 Jan 1;54(1):120–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Belin D., Montesano R., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 modulates basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proteolytic and angiogenic properties of endothelial cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):743–755. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polette M., Clavel C., Muller D., Abecassis J., Binninger I., Birembaut P. Detection of mRNAs encoding collagenase I and stromelysin 2 in carcinomas of the head and neck by in situ hybridization. Invasion Metastasis. 1991;11(2):76–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi N., Wendtner C. M., Thiele C. J. Single-cell detection of ets-1 transcripts in human neuroectodermal cells. Oncogene. 1991 Nov;6(11):2149–2154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Busso N., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Increase of urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene expression in human lung and breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 1;47(15):4043–4046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava A., Laidler P., Davies R. P., Horgan K., Hughes L. E. The prognostic significance of tumor vascularity in intermediate-thickness (0.76-4.0 mm thick) skin melanoma. A quantitative histologic study. Am J Pathol. 1988 Nov;133(2):419–423. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey K. J., Fowles L. F., Colman M. S., Ostrowski M. C., Hume D. A. Regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene transcription by macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;15(6):3430–3441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.6.3430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis W. D., Linnoila R. I., Tsokos M. G., Hitchcock C. L., Cutler G. B., Jr, Nieman L., Chrousos G., Pass H., Doppman J. Neuroendocrine tumors of the lung with proposed criteria for large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. An ultrastructural, immunohistochemical, and flow cytometric study of 35 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991 Jun;15(6):529–553. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199106000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unemori E. N., Ferrara N., Bauer E. A., Amento E. P. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces interstitial collagenase expression in human endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Dec;153(3):557–562. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041530317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbanski S. J., Edwards D. R., Maitland A., Leco K. J., Watson A., Kossakowska A. E. Expression of metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in primary pulmonary carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 1992 Dec;66(6):1188–1194. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbunder B., Pardanaud L., Jaffredo T., Mirabel M. A., Stehelin D. Complementary patterns of expression of c-ets 1, c-myb and c-myc in the blood-forming system of the chick embryo. Development. 1989 Oct;107(2):265–274. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbunder B., Queva C., Desbiens X., Wernert N., Stehelin D. Expression of the transcription factor c-Ets1 correlates with the occurrence of invasive processes during normal and pathological development. Invasion Metastasis. 1994;14(1-6):198–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Baccino D., Belin D. A cellular binding site for the Mr 55,000 form of the human plasminogen activator, urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):86–92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. H., Memoli V. A., Gould V. E. Well differentiated and small cell neuroendocrine carcinomas of the lung. Two related but distinct clinicopathologic entities. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1988;55(5):299–310. doi: 10.1007/BF02896589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Flores P., Begue A., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The c-ets proto-oncogenes encode transcription factors that cooperate with c-Fos and c-Jun for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):191–193. doi: 10.1038/346191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Gutman A., Nicholson R., Wasylyk B. The c-Ets oncoprotein activates the stromelysin promoter through the same elements as several non-nuclear oncoproteins. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1127–1134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Carroll P. R., Flax J., Blumenfeld W., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastasis in invasive prostate carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):401–409. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Semple J. P., Welch W. R., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis--correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 3;324(1):1–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101033240101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernert N., Gilles F., Fafeur V., Bouali F., Raes M. B., Pyke C., Dupressoir T., Seitz G., Vandenbunder B., Stéhelin D. Stromal expression of c-Ets1 transcription factor correlates with tumor invasion. Cancer Res. 1994 Nov 1;54(21):5683–5688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernert N., Raes M. B., Lassalle P., Dehouck M. P., Gosselin B., Vandenbunder B., Stehelin D. c-ets1 proto-oncogene is a transcription factor expressed in endothelial cells during tumor vascularization and other forms of angiogenesis in humans. Am J Pathol. 1992 Jan;140(1):119–127. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf C., Rouyer N., Lutz Y., Adida C., Loriot M., Bellocq J. P., Chambon P., Basset P. Stromelysin 3 belongs to a subgroup of proteinases expressed in breast carcinoma fibroblastic cells and possibly implicated in tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1843–1847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]