Abstract
We recently determined that the sequential development of interstitial pneumonitis and lymphocytic bronchiolitis/bronchitis occurs as a direct result of acute lethal graft-versus-host disease. Interstitial pneumonitis develops before lymphocytic bronchiolitis/bronchitis primarily from the dissemination of perivascular mononuclear infiltrates. We have used the adult, nonirradiated (DA x LEW) F1 hybrid rat in the absence of chemotherapy, immunosuppression, or overt infection to determine the phenotype of infiltrating perivascular mononuclear cells throughout acute lethal graft-versus-host disease. F1 animals were intravenously injected with 1 x 10(6) DA parental lymphoid cells/g body weight, which produced 100% morbidity and mortality by day 21. Graft-versus-host disease animals were killed on days 3, 7, 10, 14, and 15 to 21 after injection. Whole left lung lobes were frozen, serially sectioned (4 microns), and incubated with a panel of mouse anti-rat monoclonal antibodies. Labeled antibody density was determined by computerized image analysis. Perivascular infiltration was observed first for ED1+, OX8+, and W3/25+ cells, and then OX41+, W3/13+ and OX19/25+ populations. OX6 was expressed in control tissues and at all time points tested. OX12+, OX39+ and MOM/3F12/F2+ cells were not quantifiable. The present study has determined that the process of perivascular infiltration was produced through a biphasic influx of OX6+, T-cell, and macrophage populations.
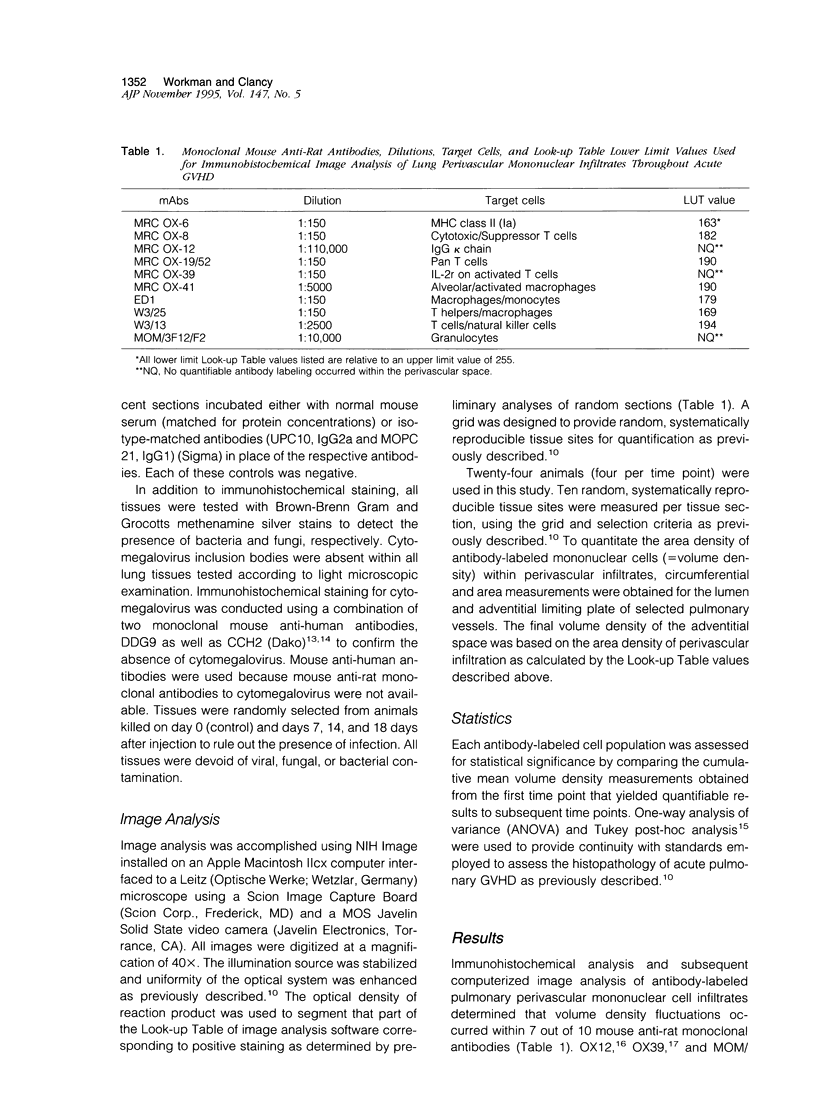
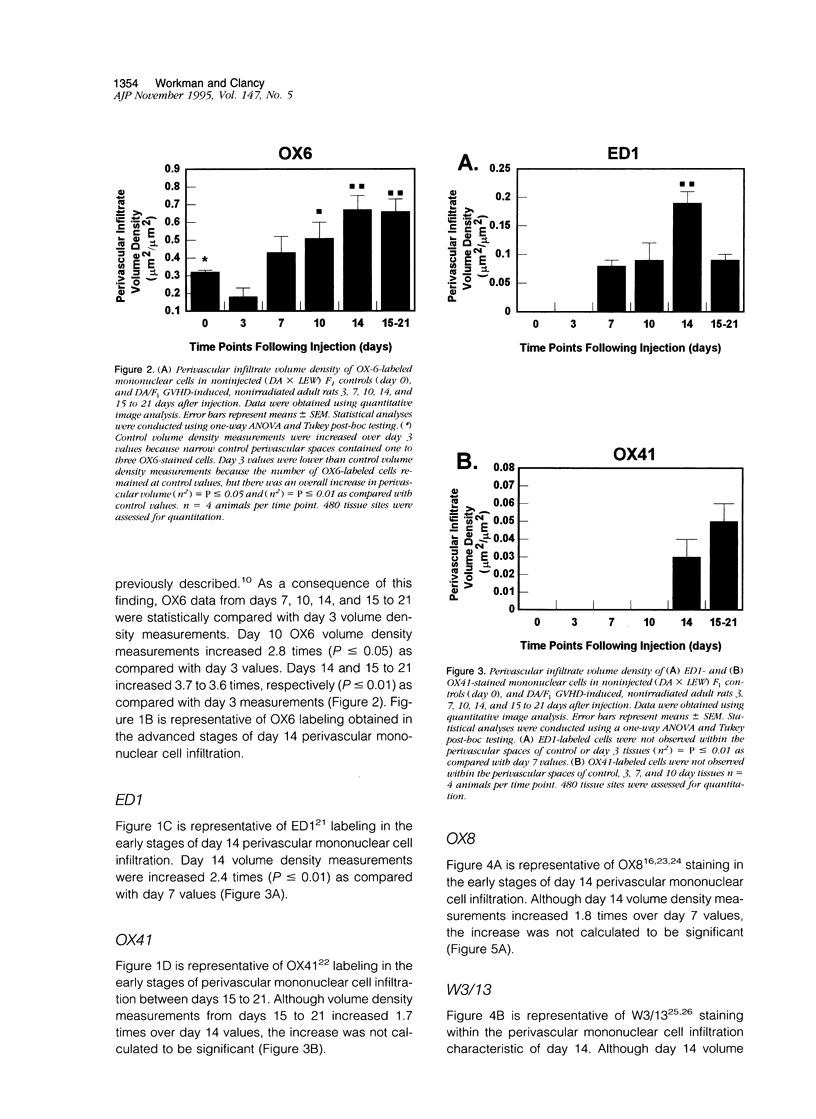
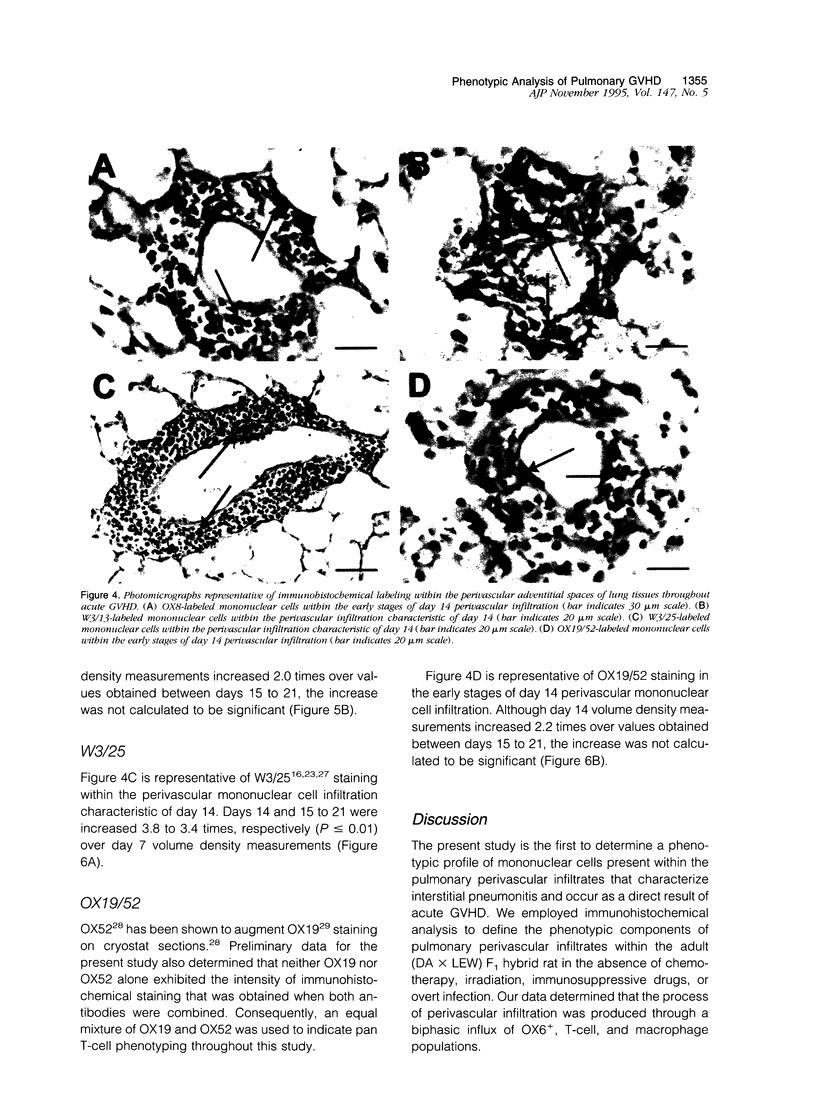
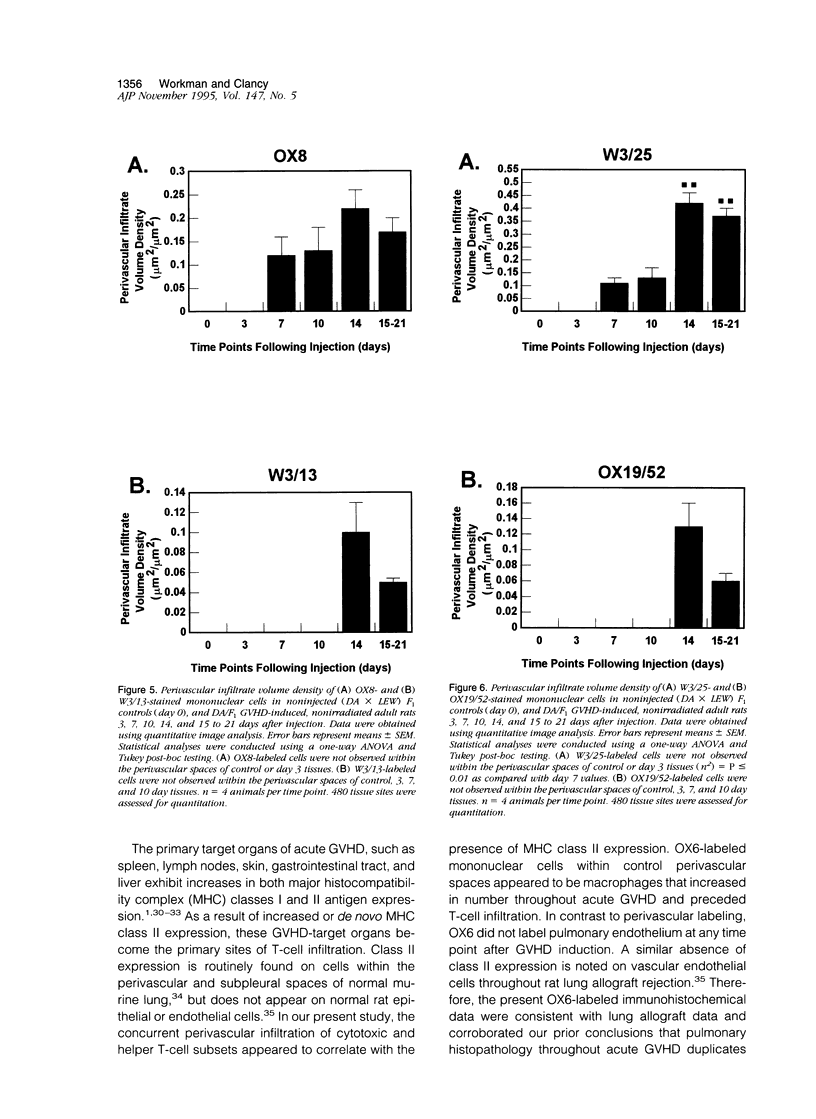
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson K., Turner J., Biggs J. C., Dodds A., Concannon A. An acute pulmonary syndrome possibly representing acute graft-versus-host disease involving the lung interstitium. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1991 Sep;8(3):231–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barclay A. N. The localization of populations of lymphocytes defined by monoclonal antibodies in rat lymphoid tissues. Immunology. 1981 Apr;42(4):593–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beschorner W. E., Saral R., Hutchins G. M., Tutschka P. J., Santos G. W. Lymphocytic bronchitis associated with graft-versus-host disease in recipients of bone-marrow transplants. N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 9;299(19):1030–1036. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811092991902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billett E. E., Gunn B., Mayer R. J. Characterization of two monoclonal antibodies obtained after immunization with human liver mitochondrial membrane preparations. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 1;221(3):765–776. doi: 10.1042/bj2210765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach S. M., Katz S. I. Keratinocytes synthesize Ia antigen in acute cutaneous graft-vs-host disease. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2741–2745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brideau R. J., Carter P. B., McMaster W. R., Mason D. W., Williams A. F. Two subsets of rat T lymphocytes defined with monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):609–615. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Barclay A. N., Sunderland C. A., Williams A. F. Identification of a glycophorin-like molecule at the cell surface of rat thymocytes. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):456–460. doi: 10.1038/289456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy J., Jr Cellular basis of graft-versus-host reactions. Am J Anat. 1984 Jul;170(3):491–499. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001700320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy J., Jr, Klein R. M., Weddle S. L. Stimulation of cellular proliferation in the adult rat submandibular gland during acute graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation. 1981 Apr;31(4):296–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy J., Jr, Mauser L. The absolute level of IgG Fc and C3 receptor-positive T, B, and null leukocytes within various lymphoid compartments during acute graft-versus-host disease in the adult rat. Transplantation. 1981 Nov;32(5):401–408. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198111000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallman M. J., Mason D. W., Webb M. The roles of host and donor cells in the rejection of skin allografts by T cell-deprived rats injected with syngeneic T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jun;12(6):511–518. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallman M. J., Thomas M. L., Green J. R. MRC OX-19: a monoclonal antibody that labels rat T lymphocytes and augments in vitro proliferative responses. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Mar;14(3):260–267. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester S. R., Rolfe M. W., Kunkel S. L., Swiderski D. L., Lincoln P. M., Deeb G. M., Strieter R. M. The bimodal expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in association with rat lung reimplantation and allograft rejection. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2494–2505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra C. D., Döpp E. A., Joling P., Kraal G. The heterogeneity of mononuclear phagocytes in lymphoid organs: distinct macrophage subpopulations in the rat recognized by monoclonal antibodies ED1, ED2 and ED3. Immunology. 1985 Mar;54(3):589–599. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duquesnoy R. J., Trager J. D., Zeevi A. Propagation and characterization of lymphocytes from transplant biopsies. Crit Rev Immunol. 1991;10(6):455–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Singer K. H., Tuck D. T., Springer T. A. Adhesion of T lymphoblasts to epidermal keratinocytes is regulated by interferon gamma and is mediated by intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1). J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1323–1340. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer M. J., Hunt S. V. Committed T lymphocyte stem cells of rats. Characterization by surface W3/13 antigen and radiosensitivity. J Exp Med. 1981 Oct 1;154(4):1164–1177. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.4.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huchet R., Bruley-Rosset M., Mathiot C., Grandjon D., Halle-Pannenko O. Involvement of IFN-gamma and transforming growth factor-beta in graft-vs-host reaction-associated immunosuppression. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2517–2524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. M., Clancy J., Jr, Stuart S. Acute lethal graft-versus-host disease stimulates cellular proliferation in the adult rat liver. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1982 Nov;15(6):651–660. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1982.tb01071.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert I. A., Janossy G., Suitters A. J., Bofill M., Palmer S., Gordon-Smith E., Prentice H. G., Thomas J. A. Immunological analysis of the skin in graft versus host disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Oct;50(1):123–131. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever R., Turbitt M., Mackie R., Hann I., Gibson B., Burnett A., Willoughby M. A prospective study of the histological changes in the skin in patients receiving bone marrow transplants. Br J Dermatol. 1986 Feb;114(2):161–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1986.tb02794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Arthur R. P., Dallman M. J., Green J. R., Spickett G. P., Thomas M. L. Functions of rat T-lymphocyte subsets isolated by means of monoclonal antibodies. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:57–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Dallman M., Barclay A. N. Graft-versus-host disease induces expression of Ia antigen in rat epidermal cells and gut epithelium. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):150–151. doi: 10.1038/293150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster W. R., Williams A. F. Identification of Ia glycoproteins in rat thymus and purification from rat spleen. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jun;9(6):426–433. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. M. Antibodies to IFN-gamma prevent immunologically mediated intestinal damage in murine graft-versus-host reaction. Immunology. 1989 Sep;68(1):18–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman P. E., Reeves W., Ray G., Flournoy N., Lerner K. G., Sale G. E., Thomas E. D. A prospective analysis interstitial pneumonia and opportunistic viral infection among recipients of allogeneic bone marrow grafts. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):754–767. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedobitek G., Finn T., Herbst H., Gerdes J., Grillner L., Landqvist M., Wirgart B. Z., Stein H. Detection of cytomegalovirus by in situ hybridisation and immunohistochemistry using new monoclonal antibody CCH2: a comparison of methods. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Sep;41(9):1005–1009. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.9.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton J., Sloane J. P. ICAM-1 expression on epidermal keratinocytes in cutaneous graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation. 1991 Jun;51(6):1203–1206. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199106000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton J., Sloane J. P., al-Saffar N., Haskard D. O. Vessel associated adhesion molecules in normal skin and acute graft-versus-host disease. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Jul;44(7):586–591. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.7.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson D. J., Jefferies W. A., Green J. R., Brandon M. R., Corthesy P., Puklavec M., Williams A. F. Antigens of activated rat T lymphocytes including a molecule of 50,000 Mr detected only on CD4 positive T blasts. Mol Immunol. 1987 Dec;24(12):1281–1290. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Grau G. E., Allet B., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin is an effector of skin and gut lesions of the acute phase of graft-vs.-host disease. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1280–1289. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Grau G. E., Collart M. A., Vassalli P., Kapanci Y. Pneumopathies of the graft-versus-host reaction. Alveolitis associated with an increased level of tumor necrosis factor mRNA and chronic interstitial pneumonitis. Lab Invest. 1989 Jul;61(1):37–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Lapierre L. A., Mendrick D. L., Fiers W., Rothlein R., Springer T. A. Overlapping patterns of activation of human endothelial cells by interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, and immune interferon. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1893–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. P., Puklavec M., Mason D. W. MRC OX-52: a rat T-cell antigen. Immunology. 1986 Apr;57(4):527–531. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. P., White T. M., Mason D. W. Macrophage heterogeneity in the rat as delineated by two monoclonal antibodies MRC OX-41 and MRC OX-42, the latter recognizing complement receptor type 3. Immunology. 1986 Feb;57(2):239–247. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk A., Prop J., Petersen A. H., Wildevuur C. R., Nieuwenhuis P. Expression of class II major histocompatibility complex antigens by bronchial epithelium in rat lung allografts. Transplantation. 1987 Aug;44(2):209–214. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198708000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoskiewicz M. J., Colvin R. B., Schneeberger E. E., Russell P. S. Widespread and selective induction of major histocompatibility complex-determined antigens in vivo by gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1645–1664. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloane J. P., Depledge M. H., Powles R. L., Morgenstern G. R., Trickey B. S., Dady P. J. Histopathology of the lung after bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Pathol. 1983 May;36(5):546–554. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.5.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloane J. P., Norton J. The pathology of bone marrow transplantation. Histopathology. 1993 Mar;22(3):201–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1993.tb00109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. M., Meyers J. D., Flournoy N., Storb R., Thomas E. D. Early and late interstitial pneumonia following human bone marrow transplantation. Int J Cell Cloning. 1986;4 (Suppl 1):107–121. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530040712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tutschka P. J., Berkowitz S. D., Tuttle S., Klein J. Graft-versus-leukemia in the rat--the antileukemic efficacy of syngeneic and allogeneic graft-versus-host disease. Transplant Proc. 1987 Feb;19(1 Pt 3):2668–2673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiden P. L., Flournoy N., Sanders J. E., Sullivan K. M., Thomas E. D. Antileukemic effect of graft-versus-host disease contributes to improved survival after allogeneic marrow transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1981 Mar;13(1 Pt 1):248–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousem S. A., Suncan S. R., Ohori N. P., Sonmez-Alpan E. Architectural remodeling of lung allografts in acute and chronic rejection. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1992 Nov;116(11):1175–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweygberg Wirgart B., Landqvist M., Hökeberg I., Eriksson B. M., Olding-Stenkvist E., Grillner L. Early detection of cytomegalovirus in cell culture by a new monoclonal antibody, CCH2. J Virol Methods. 1990 Feb;27(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(90)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




