Abstract
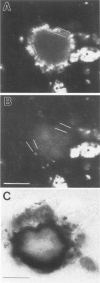
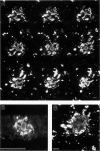
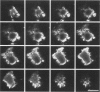
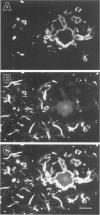
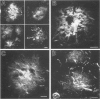
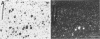
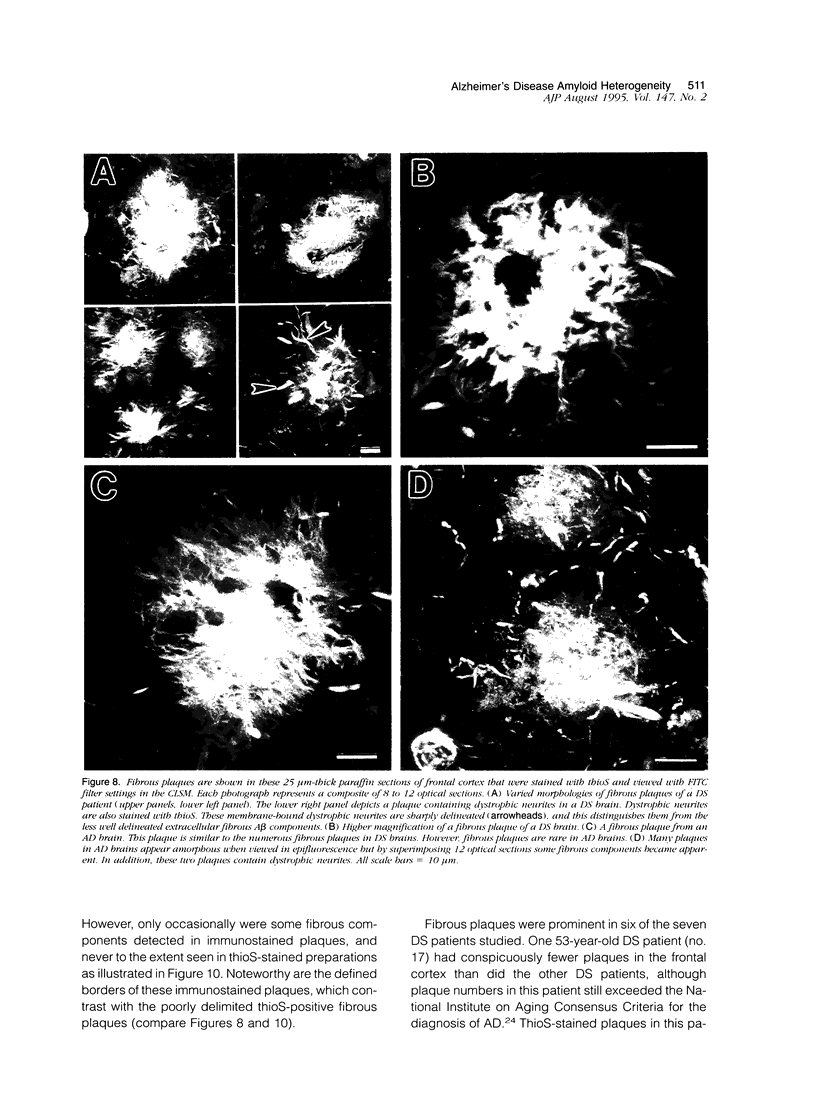
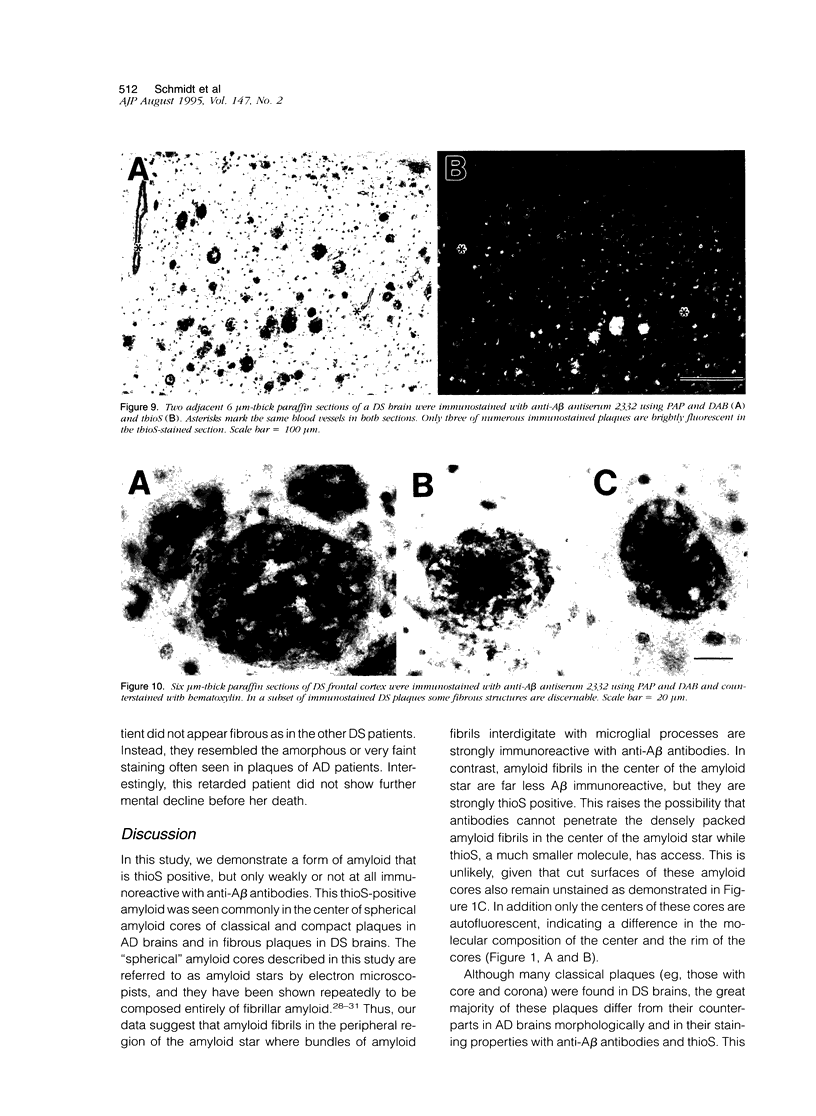
Amyloid beta peptides (A beta) are deposited in the brains of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and elderly Down's syndrome (DS) patients in a variety of amyloid plaques. Among these are classical plaques composed of a spherical core and corona. Analyzing AD tissue sections single and double stained with anti-A beta antibodies and thioflavin S (thioS) by bright field, fluorescence, and confocal microscopy revealed that spherical plaque cores consist of a thioS-positive center and an anti-A beta antibody immunoreactive rim. This indicates that there is a fibrillar form of amyloid that is thioS positive but not immunoreactive with anti-A beta antibodies. In contrast, classical plaques in DS patients have irregular cores that are thioS positive as well as anti-A beta immunoreactive. In addition, a subset of plaques in both DS and AD patients have a distinct "fibrous" appearance when stained with thioS, but are amorphous when immunostained. These findings suggest that anti-A beta antibodies and thioS stain similar; as well as different forms of fibrillar amyloid. A beta may become thioS positive by interacting with one or more of its known molecular chaperons, and this may be important for the pathogenesis of AD, given that thioS-positive A beta deposits are associated with neuritic and synaptic damage.
Full text
PDF
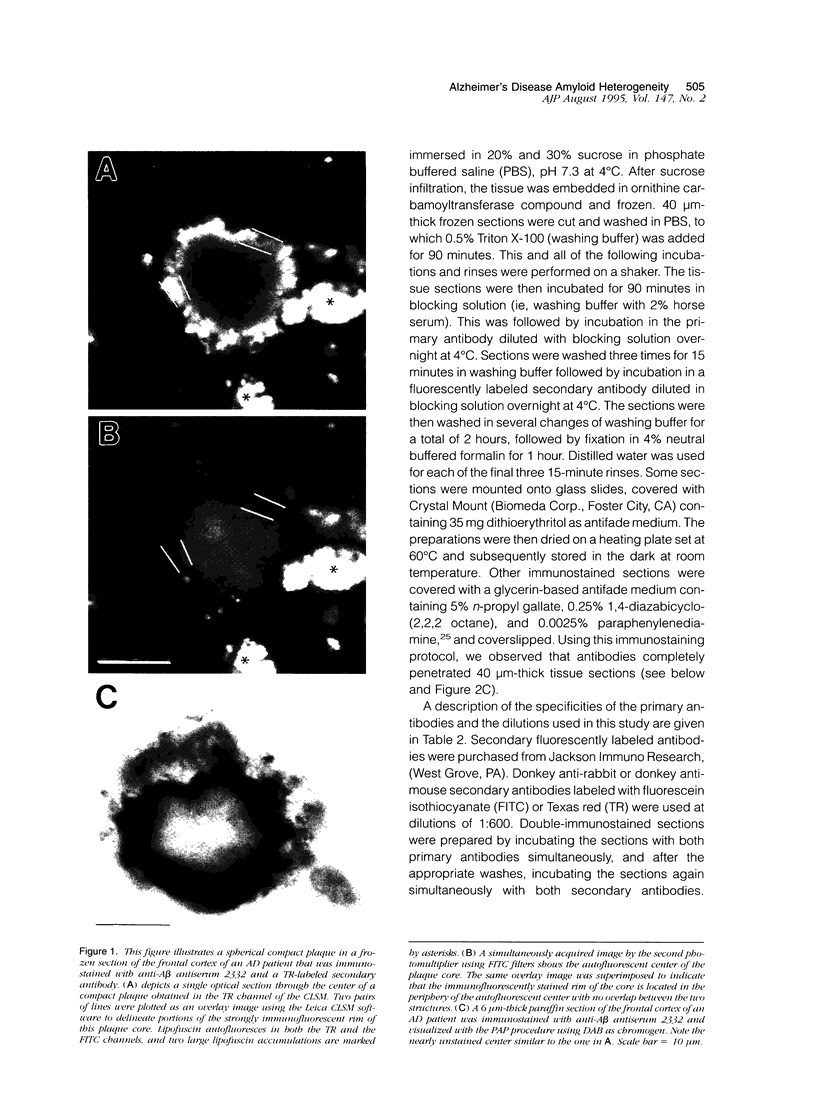
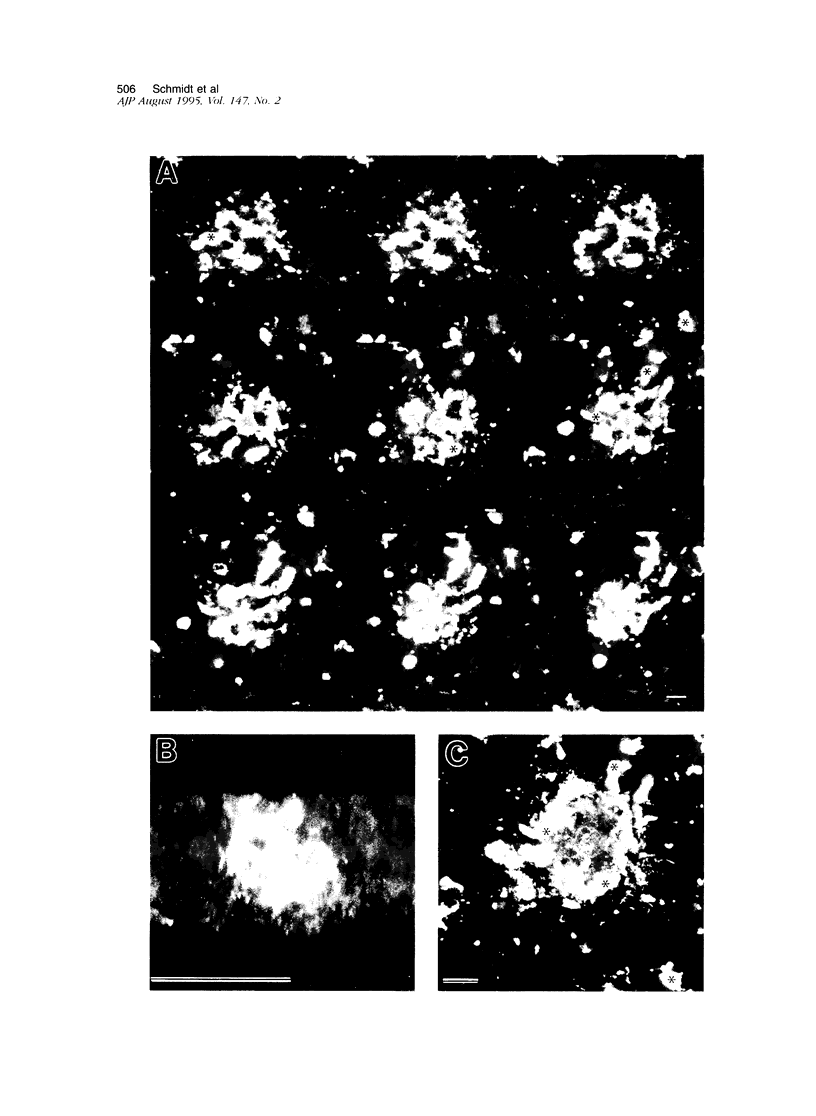

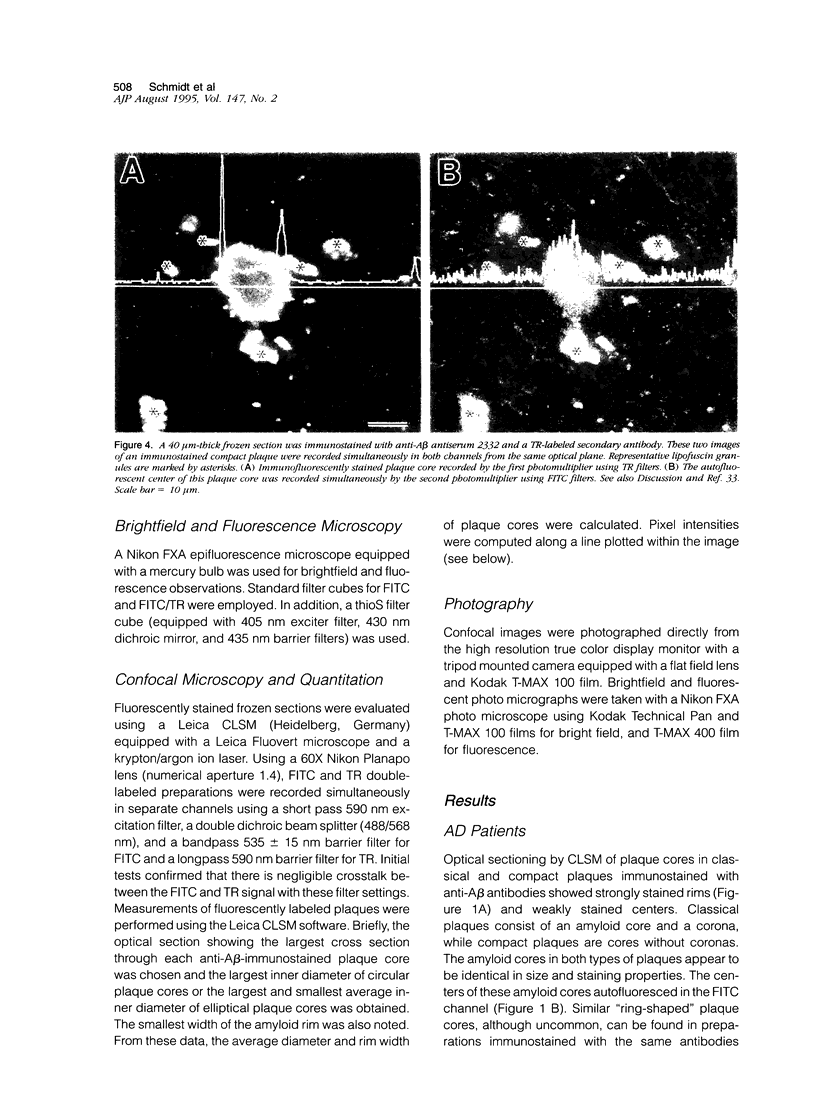
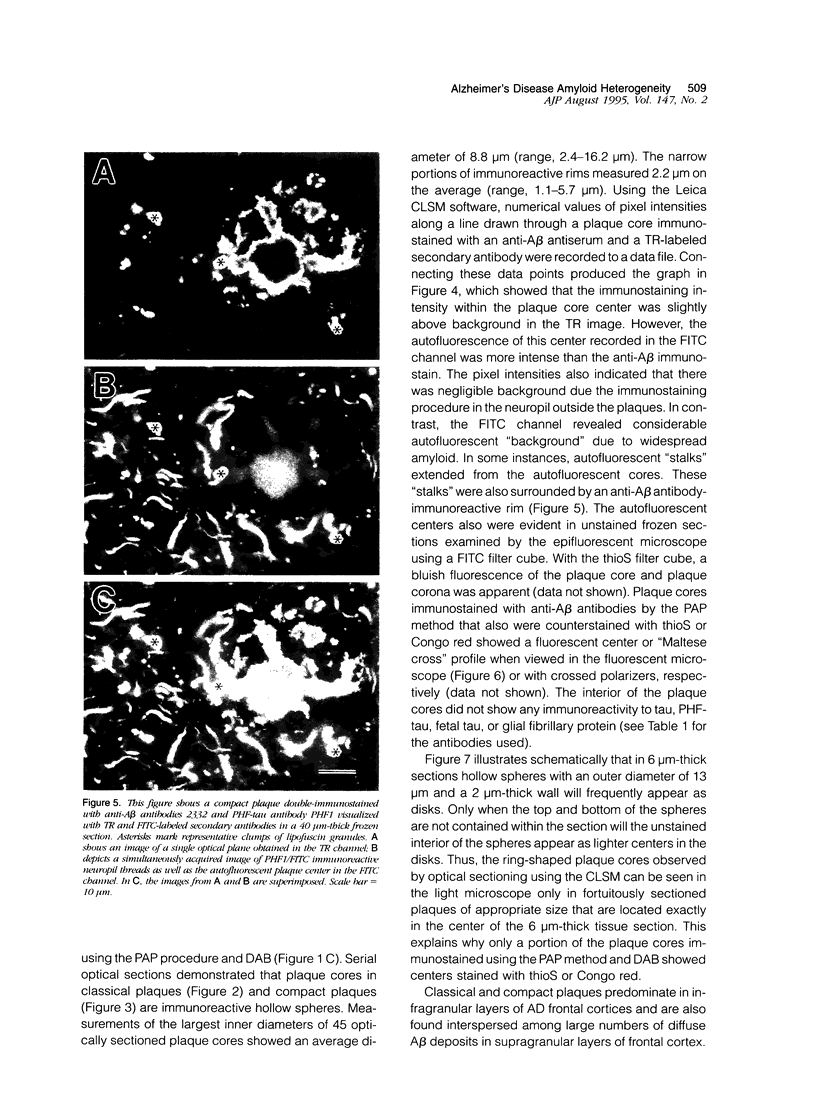




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allsop D., Haga S. I., Haga C., Ikeda S. I., Mann D. M., Ishii T. Early senile plaques in Down's syndrome brains show a close relationship with cell bodies of neurons. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1989 Nov-Dec;15(6):531–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1989.tb01252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allsop D., Kidd M., Landon M., Tomlinson A. Isolated senile plaque cores in Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome show differences in morphology. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Aug;49(8):886–892. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.8.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Lee V. M., Otvos L., Jr, Greenberg B. D., Lowery D. E., Sharma S. K., Schmidt M. L., Trojanowski J. Q. Defined neurofilament, tau, and beta-amyloid precursor protein epitopes distinguish Alzheimer from non-Alzheimer senile plaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2249–2253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcikowska M., Wisniewski H. M., Bancher C., Grundke-Iqbal I. About the presence of paired helical filaments in dystrophic neurites participating in the plaque formation. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;78(3):225–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00687751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramblett G. T., Goedert M., Jakes R., Merrick S. E., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M. Abnormal tau phosphorylation at Ser396 in Alzheimer's disease recapitulates development and contributes to reduced microtubule binding. Neuron. 1993 Jun;10(6):1089–1099. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush A. I., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L. Beta A4 amyloid protein and its precursor in Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacol Ther. 1992;56(1):97–117. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(92)90039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cras P., Kawai M., Siedlak S., Mulvihill P., Gambetti P., Lowery D., Gonzalez-DeWhitt P., Greenberg B., Perry G. Neuronal and microglial involvement in beta-amyloid protein deposition in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):241–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duyckaerts C., Delaère P., Poulain V., Brion J. P., Hauw J. J. Does amyloid precede paired helical filaments in the senile plaque? A study of 15 cases with graded intellectual status in aging and Alzheimer disease. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Sep 12;91(3):354–359. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90706-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiso J., Wisniewski T., Vidal R., Rostagno A., Frangione B. Epitope map of two polyclonal antibodies that recognize amyloid lesions in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Biochem J. 1992 Mar 1;282(Pt 2):517–522. doi: 10.1042/bj2820517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaccone G., Tagliavini F., Linoli G., Bouras C., Frigerio L., Frangione B., Bugiani O. Down patients: extracellular preamyloid deposits precede neuritic degeneration and senile plaques. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Feb 13;97(1-2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G. Alzheimer's disease: its proteins and genes. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):307–308. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. G., Davies P. A preparation of Alzheimer paired helical filaments that displays distinct tau proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5827–5831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass C., Schlossmacher M. G., Hung A. Y., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Mellon A., Ostaszewski B. L., Lieberburg I., Koo E. H., Schenk D., Teplow D. B. Amyloid beta-peptide is produced by cultured cells during normal metabolism. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):322–325. doi: 10.1038/359322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., Tanzi R. E., Marzloff K., Barbour R., Schenk D. Kunitz protease inhibitor-containing amyloid beta protein precursor immunoreactivity in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1992 Jan;51(1):76–83. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199201000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S., Allsop D., Glenner G. G. Morphology and distribution of plaque and related deposits in the brains of Alzheimer's disease and control cases. An immunohistochemical study using amyloid beta-protein antibody. Lab Invest. 1989 Jan;60(1):113–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S., Yanagisawa N., Allsop D., Glenner G. G. Evidence of amyloid beta-protein immunoreactive early plaque lesions in Down's syndrome brains. Lab Invest. 1989 Jul;61(1):133–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsubo T., Odaka A., Suzuki N., Mizusawa H., Nukina N., Ihara Y. Visualization of A beta 42(43) and A beta 40 in senile plaques with end-specific A beta monoclonals: evidence that an initially deposited species is A beta 42(43). Neuron. 1994 Jul;13(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90458-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Maggot's hair and bug's eye: role of cell interactions and intrinsic factors in cell fate specification. Neuron. 1995 Jan;14(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalaria R. N., Galloway P. G., Perry G. Widespread serum amyloid P immunoreactivity in cortical amyloid deposits and the neurofibrillary pathology of Alzheimer's disease and other degenerative disorders. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1991 Jun;17(3):189–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1991.tb00714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuentzel S. L., Ali S. M., Altman R. A., Greenberg B. D., Raub T. J. The Alzheimer beta-amyloid protein precursor/protease nexin-II is cleaved by secretase in a trans-Golgi secretory compartment in human neuroglioma cells. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 15;295(Pt 2):367–378. doi: 10.1042/bj2950367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majocha R. E., Benes F. M., Reifel J. L., Rodenrys A. M., Marotta C. A. Laminar-specific distribution and infrastructural detail of amyloid in the Alzheimer disease cortex visualized by computer-enhanced imaging of epitopes recognized by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6182–6186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Brown A., Prinja D., Davies C. A., Landon M., Masters C. L., Beyreuthers K. An analysis of the morphology of senile plaques in Down's syndrome patients of different ages using immunocytochemical and lectin histochemical techniques. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1989 Jul-Aug;15(4):317–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1989.tb01232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Esiri M. M. The pattern of acquisition of plaques and tangles in the brains of patients under 50 years of age with Down's syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 1989 Feb;89(2-3):169–179. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(89)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Terakado K., Usami M., Yoshikawa K. Formation of amyloid-like fibrils in COS cells overexpressing part of the Alzheimer amyloid protein precursor. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):566–569. doi: 10.1038/347566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Takio K., Ogawara M., Selkoe D. J. Mass spectrometry of purified amyloid beta protein in Alzheimer's disease. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17082–17086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motte J., Williams R. S. Age-related changes in the density and morphology of plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in Down syndrome brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;77(5):535–546. doi: 10.1007/BF00687256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohgami T., Kitamoto T., Shin R. W., Kaneko Y., Ogomori K., Tateishi J. Increased senile plaques without microglia in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;81(3):242–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00305864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappolla M. A., Omar R. A., Sambamurti K., Anderson J. P., Robakis N. K. The genesis of the senile plaque. Further evidence in support of its neuronal origin. Am J Pathol. 1992 Nov;141(5):1151–1159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappolla M. A., Omar R. A., Vinters H. V. Image analysis microspectroscopy shows that neurons participate in the genesis of a subset of early primitive (diffuse) senile plaques. Am J Pathol. 1991 Sep;139(3):599–607. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambamurti K., Shioi J., Anderson J. P., Pappolla M. A., Robakis N. K. Evidence for intracellular cleavage of the Alzheimer's amyloid precursor in PC12 cells. J Neurosci Res. 1992 Oct;33(2):319–329. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490330216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. L., DiDario A. G., Lee V. M., Trojanowski J. Q. An extensive network of PHF tau-rich dystrophic neurites permeates neocortex and nearly all neuritic and diffuse amyloid plaques in Alzheimer disease. FEBS Lett. 1994 May 9;344(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00259-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. L., DiDario A. G., Otvos L., Jr, Hoshi N., Kant J. A., Lee V. M., Trojanowski J. Q. Plaque-associated neuronal proteins: a recurrent motif in neuritic amyloid deposits throughout diverse cortical areas of the Alzheimer's disease brain. Exp Neurol. 1994 Dec;130(2):311–322. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1994.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J. Physiological production of the beta-amyloid protein and the mechanism of Alzheimer's disease. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Oct;16(10):403–409. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90008-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji M., Golde T. E., Ghiso J., Cheung T. T., Estus S., Shaffer L. M., Cai X. D., McKay D. M., Tintner R., Frangione B. Production of the Alzheimer amyloid beta protein by normal proteolytic processing. Science. 1992 Oct 2;258(5079):126–129. doi: 10.1126/science.1439760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman H., Murray J. M., DiLullo C. Confocal microscopy: an overview. Biotechniques. 1989 Feb;7(2):154–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow A. D., Sekiguchi R., Nochlin D., Fraser P., Kimata K., Mizutani A., Arai M., Schreier W. A., Morgan D. G. An important role of heparan sulfate proteoglycan (Perlecan) in a model system for the deposition and persistence of fibrillar A beta-amyloid in rat brain. Neuron. 1994 Jan;12(1):219–234. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90165-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Iwatsubo T., Odaka A., Ishibashi Y., Kitada C., Ihara Y. High tissue content of soluble beta 1-40 is linked to cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Am J Pathol. 1994 Aug;145(2):452–460. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trojanowski J. Q., Shin R. W., Schmidt M. L., Lee V. M. Relationship between plaques, tangles, and dystrophic processes in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1995 May-Jun;16(3):335–345. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(94)00176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verga L., Frangione B., Tagliavini F., Giaccone G., Migheli A., Bugiani O. Alzheimer patients and Down patients: cerebral preamyloid deposits differ ultrastructurally and histochemically from the amyloid of senile plaques. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Nov 6;105(3):294–299. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90636-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegiel J., Wisniewski H. M. The complex of microglial cells and amyloid star in three-dimensional reconstruction. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;81(2):116–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00334499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertkin A. M., Turner R. S., Pleasure S. J., Golde T. E., Younkin S. G., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M. Human neurons derived from a teratocarcinoma cell line express solely the 695-amino acid amyloid precursor protein and produce intracellular beta-amyloid or A4 peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9513–9517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Bancher C., Barcikowska M., Wen G. Y., Currie J. Spectrum of morphological appearance of amyloid deposits in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;78(4):337–347. doi: 10.1007/BF00688170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Vorbrodt A. W., Wegiel J., Morys J., Lossinsky A. S. Ultrastructure of the cells forming amyloid fibers in Alzheimer disease and scrapie. Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1990;7:287–297. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320370757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Wegiel J. Spatial relationships between astrocytes and classical plaque components. Neurobiol Aging. 1991 Sep-Oct;12(5):593–600. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(91)90091-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Wegiel J., Wang K. C., Kujawa M., Lach B. Ultrastructural studies of the cells forming amyloid fibers in classical plaques. Can J Neurol Sci. 1989 Nov;16(4 Suppl):535–542. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100029887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Hirai S., Morimatsu M., Shoji M., Ihara Y. A variety of cerebral amyloid deposits in the brains of the Alzheimer-type dementia demonstrated by beta protein immunostaining. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;76(6):541–549. doi: 10.1007/BF00689591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Hachimi K. H., Foncin J. F. Do microglial cells phagocyte the beta/A4-amyloid senile plaque core of Alzheimer disease? C R Acad Sci III. 1994 May;317(5):445–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]