Abstract
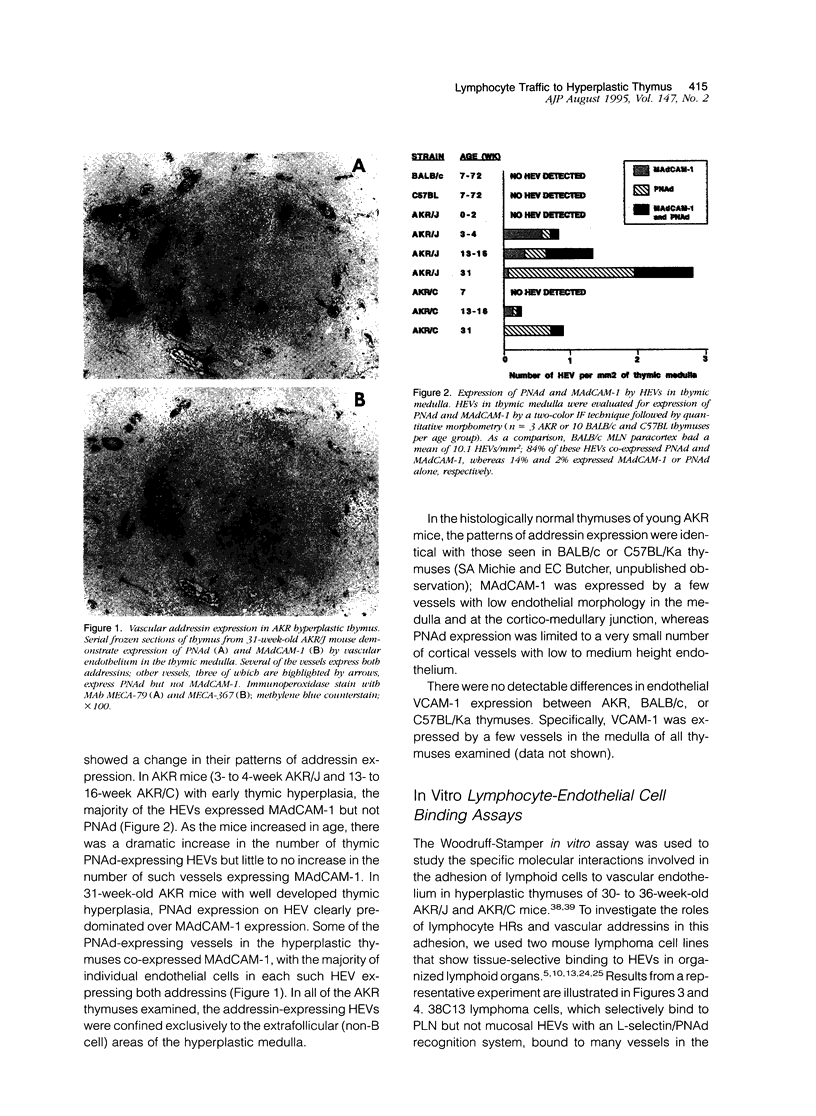
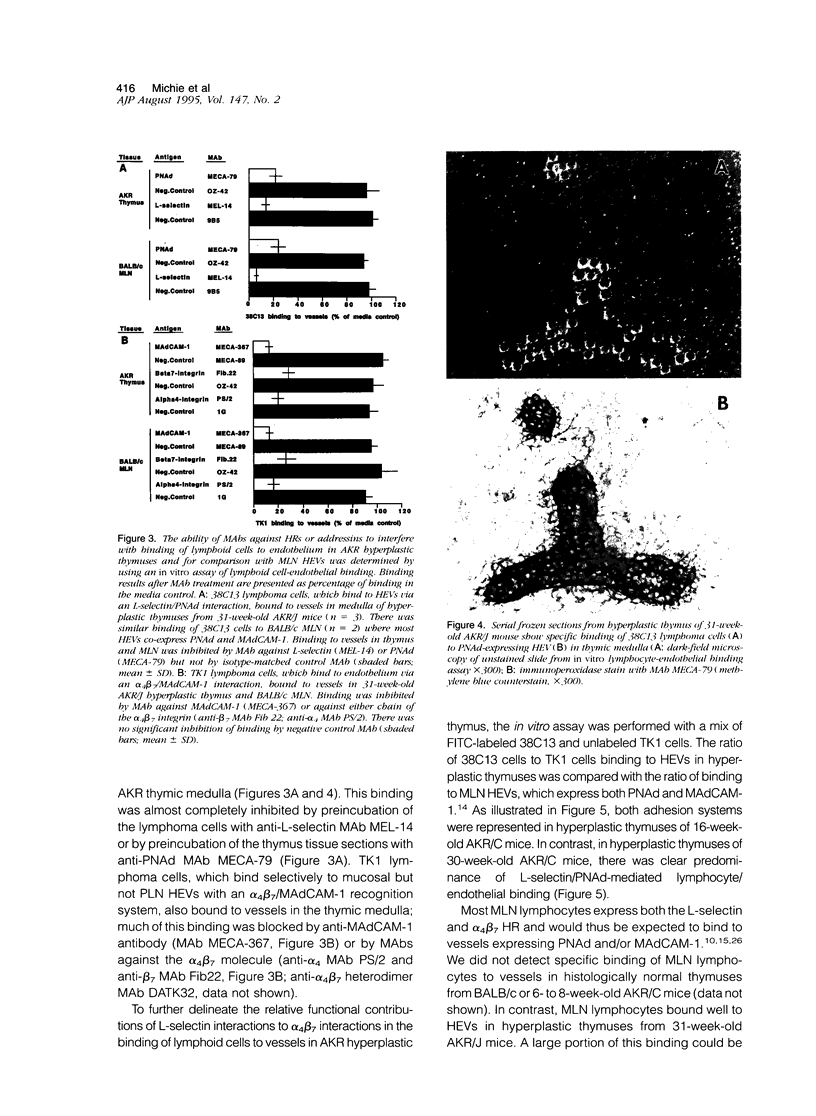
Before the development of thymic lymphoma, AKR mice undergo a striking lymphoid hyperplasia of the thymic medulla. We have previously shown that there is a marked increase in traffic of B and T lymphocytes from the periphery into the preneoplastic, hyperplastic thymuses of these mice, in contrast to the scant traffic of such cells to normal thymuses. The traffic of lymphocytes to lymph nodes and Peyer's patches is controlled in part by the interaction of lymphocyte adhesion molecules called homing receptors with their tissue-selective endothelial ligands known as vascular addressins. We have investigated the roles of homing receptors and vascular addressins in the traffic of lymphocytes to the AKR hyperplastic thymus. We demonstrate that development of hyperplasia is accompanied by an increase in the number of thymic medullary blood vessels with high endothelial venule morphology and expression of the peripheral node addressin (PNAd) and the mucosal addressin (MAdCAM-1). In vitro and in vivo functional assays show that the addressin/homing receptor pairs PNAd/L-selectin and MAdCAM-1/alpha 4 beta 7 are involved in lymphocyte traffic to the hyperplastic thymus. These results indicate that molecular adhesion mechanisms involved in tissue-selective migration of lymphocytes to peripheral lymph node and to mucosal lymphoid tissues play a role in the recruitment of B and T lymphocytes to the AKR thymus and thus in the pathogenesis of thymic hyperplasia.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agus D. B., Surh C. D., Sprent J. Reentry of T cells to the adult thymus is restricted to activated T cells. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1039–1046. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew D. P., Berlin C., Honda S., Yoshino T., Hamann A., Holzmann B., Kilshaw P. J., Butcher E. C. Distinct but overlapping epitopes are involved in alpha 4 beta 7-mediated adhesion to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, mucosal addressin-1, fibronectin, and lymphocyte aggregation. J Immunol. 1994 Nov 1;153(9):3847–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargatze R. F., Streeter P. R., Butcher E. C. Expression of low levels of peripheral lymph node-associated vascular addressin in mucosal lymphoid tissues: possible relevance to the dissemination of passaged AKR lymphomas. J Cell Biochem. 1990 Apr;42(4):219–227. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240420405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumheter S., Singer M. S., Henzel W., Hemmerich S., Renz M., Rosen S. D., Lasky L. A. Binding of L-selectin to the vascular sialomucin CD34. Science. 1993 Oct 15;262(5132):436–438. doi: 10.1126/science.7692600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumhueter S., Dybdal N., Kyle C., Lasky L. A. Global vascular expression of murine CD34, a sialomucin-like endothelial ligand for L-selectin. Blood. 1994 Oct 15;84(8):2554–2565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg E. L., McEvoy L. M., Berlin C., Bargatze R. F., Butcher E. C. L-selectin-mediated lymphocyte rolling on MAdCAM-1. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):695–698. doi: 10.1038/366695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg E. L., Robinson M. K., Warnock R. A., Butcher E. C. The human peripheral lymph node vascular addressin is a ligand for LECAM-1, the peripheral lymph node homing receptor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):343–349. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C. Leukocyte-endothelial cell recognition: three (or more) steps to specificity and diversity. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1033–1036. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C., Scollay R. G., Weissman I. L. Direct fluorescent labeling of cells with fluorescein or rhodamine isothiocyanate. II. Potential application to studies of lymphocyte migration and maturation. J Immunol Methods. 1980;37(2):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90196-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C., Scollay R. G., Weissman I. L. Lymphocyte adherence to high endothelial venules: characterization of a modified in vitro assay, and examination of the binding of syngeneic and allogeneic lymphocyte populations. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):1996–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C., Scollay R. G., Weissman I. L. Organ specificity of lymphocyte migration: mediation by highly selective lymphocyte interaction with organ-specific determinants on high endothelial venules. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Jul;10(7):556–561. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannella B., Cross A. H., Raine C. S. Adhesion-related molecules in the central nervous system. Upregulation correlates with inflammatory cell influx during relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Lab Invest. 1991 Jul;65(1):23–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhardt B., Conley F. K., Butcher E. C. Cell adhesion molecules on vessels during inflammation in the mouse central nervous system. J Neuroimmunol. 1994 May;51(2):199–208. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(94)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faveeuw C., Gagnerault M. C., Lepault F. Expression of homing and adhesion molecules in infiltrated islets of Langerhans and salivary glands of nonobese diabetic mice. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 15;152(12):5969–5978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. J., Bevan M. J., Weissman I. L. Thymic cytotoxic T lymphocytes are primed in vivo to minor histocompatibility antigens. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):436–451. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOWANS J. L., KNIGHT E. J. THE ROUTE OF RE-CIRCULATION OF LYMPHOCYTES IN THE RAT. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Jan 14;159:257–282. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallatin W. M., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. A cell-surface molecule involved in organ-specific homing of lymphocytes. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):30–34. doi: 10.1038/304030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamann A., Andrew D. P., Jablonski-Westrich D., Holzmann B., Butcher E. C. Role of alpha 4-integrins in lymphocyte homing to mucosal tissues in vivo. J Immunol. 1994 Apr 1;152(7):3282–3293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmerich S., Rosen S. D. 6'-sulfated sialyl Lewis x is a major capping group of GlyCAM-1. Biochemistry. 1994 Apr 26;33(16):4830–4835. doi: 10.1021/bi00182a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks H. R., Eestermans I. L. Disappearance and reappearance of high endothelial venules and immigrating lymphocytes in lymph nodes deprived of afferent lymphatic vessels: a possible regulatory role of macrophages in lymphocyte migration. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Aug;13(8):663–669. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzmann B., McIntyre B. W., Weissman I. L. Identification of a murine Peyer's patch--specific lymphocyte homing receptor as an integrin molecule with an alpha chain homologous to human VLA-4 alpha. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90981-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Crowe D. T., Weissman I. L., Holzmann B. Cloning and expression of mouse integrin beta p(beta 7): a functional role in Peyer's patch-specific lymphocyte homing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8254–8258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänninen A., Taylor C., Streeter P. R., Stark L. S., Sarte J. M., Shizuru J. A., Simell O., Michie S. A. Vascular addressins are induced on islet vessels during insulitis in nonobese diabetic mice and are involved in lymphoid cell binding to islet endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2509–2515. doi: 10.1172/JCI116859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai Y., Singer M. S., Fennie C., Lasky L. A., Rosen S. D. Identification of a carbohydrate-based endothelial ligand for a lymphocyte homing receptor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1213–1221. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung T. M., Gallatin W. M., Weissman I. L., Dailey M. O. Down-regulation of homing receptors after T cell activation. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4110–4117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. Y., Evans L. H., Malik F. G., Rouse R. V. Macrophages are the first thymic cells to express polytropic retrovirus in AKR mouse leukemogenesis. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6238–6241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6238-6241.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Singer M. S., Dowbenko D., Imai Y., Henzel W. J., Grimley C., Fennie C., Gillett N., Watson S. R., Rosen S. D. An endothelial ligand for L-selectin is a novel mucin-like molecule. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):927–938. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90612-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Sarvetnick N. Induction of vascular addressins and adhesion molecules in the pancreas of IFN-gamma transgenic mice. J Immunol. 1994 May 1;152(9):4597–4603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCHESI V. T., GOWANS J. L. THE MIGRATION OF LYMPHOCYTES THROUGH THE ENDOTHELIUM OF VENULES IN LYMPH NODES: AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Jan 14;159:283–290. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R. Homing of naive, memory and effector lymphocytes. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Jun;5(3):423–427. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90063-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebius R. E., Brevé J., Kraal G., Streeter P. R. Developmental regulation of vascular addressin expression: a possible role for site-associated environments. Int Immunol. 1993 May;5(5):443–449. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.5.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebius R. E., Streeter P. R., Brevé J., Duijvestijn A. M., Kraal G. The influence of afferent lymphatic vessel interruption on vascular addressin expression. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):85–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie S. A., Kirkpatrick E. A., Rouse R. V. Rare peripheral T cells migrate to and persist in normal mouse thymus. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1929–1934. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie S. A., Rouse R. V. Study of murine T cell migration using the Thy-1 allotypic marker. Demonstration of antigen-specific homing to lymph node germinal centers. Transplantation. 1988 Jul;46(1):98–104. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198807000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie S. A., Rouse R. V. Traffic of mature lymphocytes into the mouse thymus. Thymus. 1989;13(3-4):141–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie S. A., Rouse R. V. Traffic of peripheral B and T lymphocytes to hyperplastic, preneoplastic thymuses of AKR mice. Am J Pathol. 1991 Apr;138(4):1015–1025. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie S. A., Streeter P. R., Bolt P. A., Butcher E. C., Picker L. J. The human peripheral lymph node vascular addressin. An inducible endothelial antigen involved in lymphocyte homing. Am J Pathol. 1993 Dec;143(6):1688–1698. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake K., Medina K., Ishihara K., Kimoto M., Auerbach R., Kincade P. W. A VCAM-like adhesion molecule on murine bone marrow stromal cells mediates binding of lymphocyte precursors in culture. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):557–565. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake K., Weissman I. L., Greenberger J. S., Kincade P. W. Evidence for a role of the integrin VLA-4 in lympho-hemopoiesis. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):599–607. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naparstek Y., Holoshitz J., Eisenstein S., Reshef T., Rappaport S., Chemke J., Ben-Nun A., Cohen I. R. Effector T lymphocyte line cells migrate to the thymus and persist there. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):262–264. doi: 10.1038/300262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill J. K., Butter C., Baker D., Gschmeissner S. E., Kraal G., Butcher E. C., Turk J. L. Expression of vascular addressins and ICAM-1 by endothelial cells in the spinal cord during chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the Biozzi AB/H mouse. Immunology. 1991 Apr;72(4):520–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Butcher E. C. Physiological and molecular mechanisms of lymphocyte homing. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:561–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.003021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüegg C., Postigo A. A., Sikorski E. E., Butcher E. C., Pytela R., Erle D. J. Role of integrin alpha 4 beta 7/alpha 4 beta P in lymphocyte adherence to fibronectin and VCAM-1 and in homotypic cell clustering. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):179–189. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmi M., Granfors K., MacDermott R., Jalkanen S. Aberrant binding of lamina propria lymphocytes to vascular endothelium in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. 1994 Mar;106(3):596–605. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90691-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Newman W., Tanaka Y., Shaw S. Lymphocyte interactions with endothelial cells. Immunol Today. 1992 Mar;13(3):106–112. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90151-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski E. E., Hallmann R., Berg E. L., Butcher E. C. The Peyer's patch high endothelial receptor for lymphocytes, the mucosal vascular addressin, is induced on a murine endothelial cell line by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IL-1. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 15;151(10):5239–5250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamper H. B., Jr, Woodruff J. J. Lymphocyte homing into lymph nodes: in vitro demonstration of the selective affinity of recirculating lymphocytes for high-endothelial venules. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):828–833. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen B. J., Butcher E. C., Engelhardt B. Evidence for involvement of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in lymphocyte interaction with endothelium in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the central nervous system in the SJL/J mouse. Am J Pathol. 1994 Jul;145(1):189–201. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeter P. R., Berg E. L., Rouse B. T., Bargatze R. F., Butcher E. C. A tissue-specific endothelial cell molecule involved in lymphocyte homing. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):41–46. doi: 10.1038/331041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeter P. R., Rouse B. T., Butcher E. C. Immunohistologic and functional characterization of a vascular addressin involved in lymphocyte homing into peripheral lymph nodes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1853–1862. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wogensen L., Huang X., Sarvetnick N. Leukocyte extravasation into the pancreatic tissue in transgenic mice expressing interleukin 10 in the islets of Langerhans. J Exp Med. 1993 Jul 1;178(1):175–185. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu N. W., Jalkanen S., Streeter P. R., Butcher E. C. Evolutionary conservation of tissue-specific lymphocyte-endothelial cell recognition mechanisms involved in lymphocyte homing. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1845–1851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]