Abstract
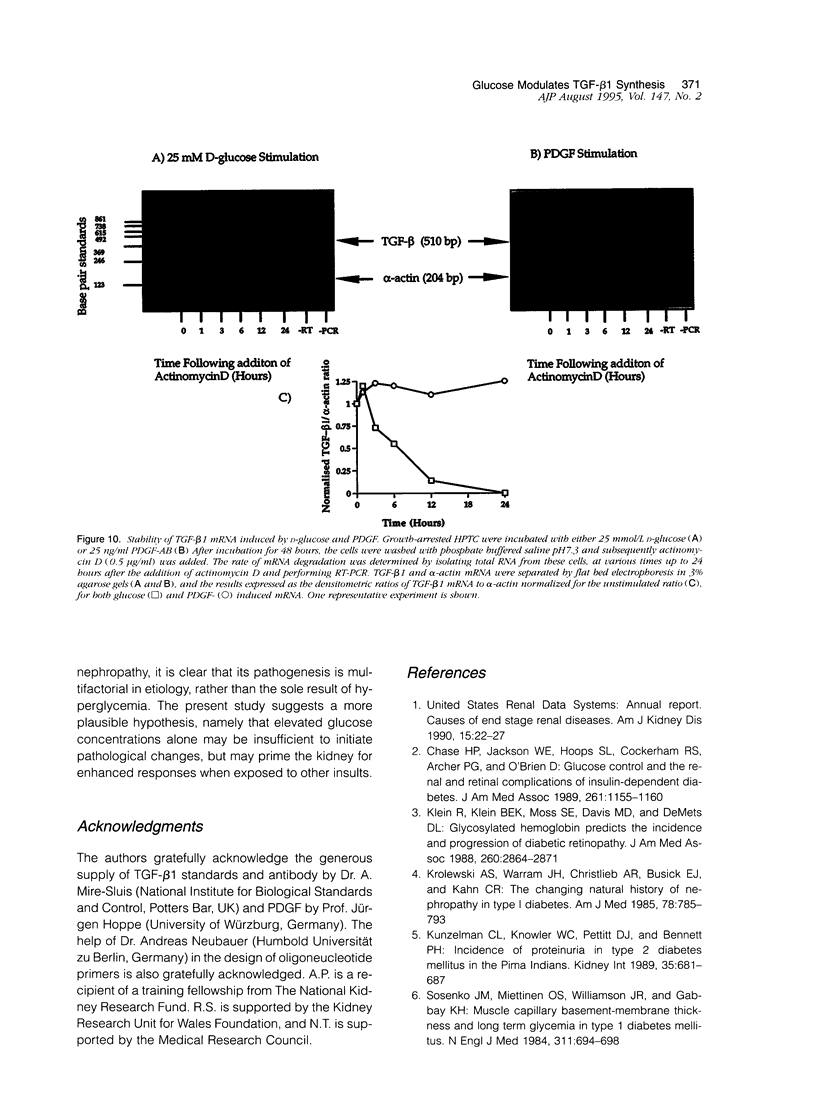
Interstitial fibrosis is a marker of progression of renal impairment in diabetic nephropathy. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta 1 is one of a group of pro-fibrotic cytokines and growth factors that have been associated with the development of interstitial fibrosis. We have examined the modulating influence of glucose on the production of TGF-beta 1 by cultured human proximal tubular cells. Incubation of growth-arrested human proximal tubular cells (HPTC) (72 hours in serum free medium) in 25 mmol/L D-glucose resulted in increased expression of TGF-beta 1 mRNA (as assessed by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction). This was apparent after 6 hours and increased up to 120 hours exposure. TGF-beta 1 secretion, however, as measured by specific enzyme-linked immunoassay, was unaffected by exposure to 25 mmol/L D-glucose. Sequential stimulation of HPTC, first with 25 mmol/L D-glucose for 48 hours and then with platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) isoforms, resulted in a dose-dependent secretion of TGF-beta 1. Pre-exposure to 5 mmol/L D-glucose or 25 mmol/L L-glucose did not prime for TGF-beta 1 release. At 50 ng/ml PDGF this effect was greatest for the AA isoform (AA 31.4 +/- 7.1, AB 20.98 +/- 8.9, BB 7.8 +/- 2.2, P < 0.05 for all versus control, n = 3, mean +/- SEM ng/10(6) cells/24 hours). These effects were blocked by the addition of antibody to the PDGF alpha-receptor. TGF-beta 1 secretion was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by pretreatment with cyclohexamide, but was not affected by pretreatment with actinomycin D. Stimulation of HPTC with a single dose of PDGF induced TGF-beta 1 mRNA; however, only after application of a second dose of PDGF (after TGF-beta 1 mRNA induction) did TGF-beta 1 protein secretion occur. We also demonstrated that PDGF stimulation of HPTC induced an inherently more stable TGF-beta 1 mRNA transcript. These findings demonstrate that elevated D-glucose concentration alone is insufficient to lead to increased TGF-beta 1 secretion by HPTC despite increased mRNA expression. However, application of a second stimulus such as PDGF, when TGF-beta 1 mRNA expression is increased, leads to increased protein synthesis and secretion of TGF-beta 1. This implies that elevated glucose concentrations might prime proximal tubular cells for TGF-beta 1 synthesis and thus contribute to the development of interstitial fibrosis.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assoian R. K., Komoriya A., Meyers C. A., Miller D. M., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor-beta in human platelets. Identification of a major storage site, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7155–7160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader R., Bader H., Grund K. E., Mackensen-Haen S., Christ H., Bohle A. Structure and function of the kidney in diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Correlations between morphological and functional parameters. Pathol Res Pract. 1980;167(2-4):204–216. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(80)80051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassols A., Massagué J. Transforming growth factor beta regulates the expression and structure of extracellular matrix chondroitin/dermatan sulfate proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):3039–3045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battegay E. J., Raines E. W., Seifert R. A., Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. TGF-beta induces bimodal proliferation of connective tissue cells via complex control of an autocrine PDGF loop. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):515–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90448-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohle A., Wehrmann M., Bogenschütz O., Batz C., Müller C. A., Müller G. A. The pathogenesis of chronic renal failure in diabetic nephropathy. Investigation of 488 cases of diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Pathol Res Pract. 1991 Mar;187(2-3):251–259. doi: 10.1016/s0344-0338(11)80780-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Okuda S., Languino L. R., Ruoslahti E. Transforming growth factor-beta regulates production of proteoglycans by mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1990 Feb;37(2):689–695. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase H. P., Jackson W. E., Hoops S. L., Cockerham R. S., Archer P. G., O'Brien D. Glucose control and the renal and retinal complications of insulin-dependent diabetes. JAMA. 1989 Feb 24;261(8):1155–1160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl-Jørgensen K., Brinchmann-Hansen O., Hanssen K. F., Ganes T., Kierulf P., Smeland E., Sandvik L., Aagenaes O. Effect of near normoglycaemia for two years on progression of early diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy: the Oslo study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Nov 8;293(6556):1195–1199. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6556.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detrisac C. J., Sens M. A., Garvin A. J., Spicer S. S., Sens D. A. Tissue culture of human kidney epithelial cells of proximal tubule origin. Kidney Int. 1984 Feb;25(2):383–390. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis E. N., Steffes M. W., Goetz F. C., Sutherland D. E., Mauer S. M. Glomerular filtration surface in type I diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int. 1986 Apr;29(4):889–894. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldt-Rasmussen B., Mathiesen E. R., Deckert T. Effect of two years of strict metabolic control on progression of incipient nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1986 Dec 6;2(8519):1300–1304. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine A., Goldstein R. H. The effect of transforming growth factor-beta on cell proliferation and collagen formation by lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3897–3902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floege J., Topley N., Wessel K., Kaever V., Radeke H., Hoppe J., Kishimoto T., Resch K. Monokines and platelet-derived growth factor modulate prostanoid production in growth arrested, human mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1990 Mar;37(3):859–869. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillausseau P. J., Dupuy E., Bryckaert M. C., Timsit J., Chanson P., Tobelem G., Caen J. P., Lubetzki J. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;19(2):172–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1989.tb00213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberstroh U., Zahner G., Disser M., Thaiss F., Wolf G., Stahl R. A. TGF-beta stimulates rat mesangial cell proliferation in culture: role of PDGF beta-receptor expression. Am J Physiol. 1993 Feb;264(2 Pt 2):F199–F205. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.2.F199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignotz R. A., Endo T., Massagué J. Regulation of fibronectin and type I collagen mRNA levels by transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6443–6446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignotz R. A., Massagué J. Cell adhesion protein receptors as targets for transforming growth factor-beta action. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignotz R. A., Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates the expression of fibronectin and collagen and their incorporation into the extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4337–4345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa O., LeRoy E. C., Trojanowska M. Mitogenic effect of transforming growth factor beta 1 on human fibroblasts involves the induction of platelet-derived growth factor alpha receptors. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Oct;145(1):181–186. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041450124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakowlew S. B., Cubert J., Danielpour D., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Differential regulation of the expression of transforming growth factor-beta mRNAs by growth factors and retinoic acid in chicken embryo chondrocytes, myocytes, and fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Feb;150(2):377–385. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagami S., Border W. A., Ruoslahti E., Noble N. A. Coordinated expression of beta 1 integrins and transforming growth factor-beta-induced matrix proteins in glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1993 Jul;69(1):68–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Klein B. E., Moss S. E., Davis M. D., DeMets D. L. Glycosylated hemoglobin predicts the incidence and progression of diabetic retinopathy. JAMA. 1988 Nov 18;260(19):2864–2871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krolewski A. S., Warram J. H., Christlieb A. R., Busick E. J., Kahn C. R. The changing natural history of nephropathy in type I diabetes. Am J Med. 1985 May;78(5):785–794. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90284-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunzelman C. L., Knowler W. C., Pettitt D. J., Bennett P. H. Incidence of proteinuria in type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Pima Indians. Kidney Int. 1989 Feb;35(2):681–687. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane P. H., Steffes M. W., Fioretto P., Mauer S. M. Renal interstitial expansion in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int. 1993 Mar;43(3):661–667. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauer S. M., Steffes M. W., Ellis E. N., Sutherland D. E., Brown D. M., Goetz F. C. Structural-functional relationships in diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1143–1155. doi: 10.1172/JCI111523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani M., Okuda Y., Yamaoka T., Tsukahara K., Isaka M., Bannai C., Yamashita K. High glucose and hyperosmolarity increase platelet-derived growth factor mRNA levels in cultured human vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Sep 16;187(2):664–669. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91246-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Fukui M., Ebihara I., Osada S., Nagaoka I., Tomino Y., Koide H. mRNA expression of growth factors in glomeruli from diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1993 Mar;42(3):450–456. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.3.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Miller D., Ruoslahti E., Border W. A. Production of extracellular matrix by glomerular epithelial cells is regulated by transforming growth factor-beta 1. Kidney Int. 1992 May;41(5):1213–1221. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubauer A., Neubauer B., Liu E. Polymerase chain reaction based assay to detect allelic loss in human DNA: loss of beta-interferon gene in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):993–998. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Bryan J. P., Frye R. A., Cogswell P. C., Neubauer A., Kitch B., Prokop C., Espinosa R., 3rd, Le Beau M. M., Earp H. S., Liu E. T. axl, a transforming gene isolated from primary human myeloid leukemia cells, encodes a novel receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5016–5031. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overall C. M., Wrana J. L., Sodek J. Independent regulation of collagenase, 72-kDa progelatinase, and metalloendoproteinase inhibitor expression in human fibroblasts by transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1860–1869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. O., Steadman R., Donovan K. D., Williams J. D. A new antibody capture enzyme linked immunoassay specific for transforming growth factor beta 1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;27(2):207–213. doi: 10.1016/1357-2725(94)00077-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce G. F., Mustoe T. A., Lingelbach J., Masakowski V. R., Griffin G. L., Senior R. M., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta enhance tissue repair activities by unique mechanisms. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):429–440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce G. F., Vande Berg J., Rudolph R., Tarpley J., Mustoe T. A. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB and transforming growth factor beta 1 selectively modulate glycosaminoglycans, collagen, and myofibroblasts in excisional wounds. Am J Pathol. 1991 Mar;138(3):629–646. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redinbaugh M. G., Campbell W. H. Adaptation of the dye-binding protein assay to microtiter plates. Anal Biochem. 1985 May 15;147(1):144–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichard P., Nilsson B. Y., Rosenqvist U. The effect of long-term intensified insulin treatment on the development of microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jul 29;329(5):304–309. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307293290502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Anzano M. A., Meyers C. A., Wideman J., Blacher R., Pan Y. C., Stein S., Lehrman S. R., Smith J. M., Lamb L. C. Purification and properties of a type beta transforming growth factor from bovine kidney. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 6;22(25):5692–5698. doi: 10.1021/bi00294a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Lamb L. C., Newton D. L., Sporn M. B., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Transforming growth factors: isolation of polypeptides from virally and chemically transformed cells by acid/ethanol extraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3494–3498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor beta. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;51:107–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocco M. V., Chen Y., Goldfarb S., Ziyadeh F. N. Elevated glucose stimulates TGF-beta gene expression and bioactivity in proximal tubule. Kidney Int. 1992 Jan;41(1):107–114. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Raines E. W., Bowen-Pope D. F. The biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90733-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankland S. J., Scholey J. W., Ly H., Thai K. Expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 during diabetic renal hypertrophy. Kidney Int. 1994 Aug;46(2):430–442. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soma Y., Grotendorst G. R. TGF-beta stimulates primary human skin fibroblast DNA synthesis via an autocrine production of PDGF-related peptides. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Aug;140(2):246–253. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosenko J. M., Miettinen O. S., Williamson J. R., Gabbay K. H. Muscle capillary basement-membrane thickness and long-term glycemia in type I diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1984 Sep 13;311(11):694–698. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198409133111102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Roche N. S., Flanders K. C., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Transforming growth factor beta 1 positively regulates its own expression in normal and transformed cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7741–7746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villiger P. M., Lotz M. Differential expression of TGF beta isoforms by human articular chondrocytes in response to growth factors. J Cell Physiol. 1992 May;151(2):318–325. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041510213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlassara H. Receptor-mediated interactions of advanced glycosylation end products with cellular components within diabetic tissues. Diabetes. 1992 Oct;41 (Suppl 2):52–56. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.2.s52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P. H., Lau J., Chalmers T. C. Meta-analysis of effects of intensive blood-glucose control on late complications of type I diabetes. Lancet. 1993 May 22;341(8856):1306–1309. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90816-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witowski J., Topley N., Jörres A., Liberek T., Coles G. A., Williams J. D. Effect of lactate-buffered peritoneal dialysis fluids on human peritoneal mesothelial cell interleukin-6 and prostaglandin synthesis. Kidney Int. 1995 Jan;47(1):282–293. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf G., Sharma K., Chen Y., Ericksen M., Ziyadeh F. N. High glucose-induced proliferation in mesangial cells is reversed by autocrine TGF-beta. Kidney Int. 1992 Sep;42(3):647–656. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Nakamura T., Noble N. A., Ruoslahti E., Border W. A. Expression of transforming growth factor beta is elevated in human and experimental diabetic nephropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1814–1818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y., Lin G., Baarsch M. J., Scamurra R. W., Murtaugh M. P. Interleukin-4 suppresses inflammatory cytokine gene transcription in porcine macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1994 Oct;56(4):507–513. doi: 10.1002/jlb.56.4.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziyadeh F. N., Sharma K., Ericksen M., Wolf G. Stimulation of collagen gene expression and protein synthesis in murine mesangial cells by high glucose is mediated by autocrine activation of transforming growth factor-beta. J Clin Invest. 1994 Feb;93(2):536–542. doi: 10.1172/JCI117004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziyadeh F. N., Simmons D. A., Snipes E. R., Goldfarb S. Effect of myo-inositol on cell proliferation and collagen transcription and secretion in proximal tubule cells cultured in elevated glucose. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1991 May;1(11):1220–1229. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V1111220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziyadeh F. N., Snipes E. R., Watanabe M., Alvarez R. J., Goldfarb S., Haverty T. P. High glucose induces cell hypertrophy and stimulates collagen gene transcription in proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 2):F704–F714. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.4.F704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]