Abstract
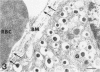
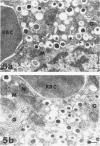
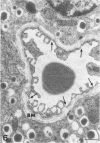
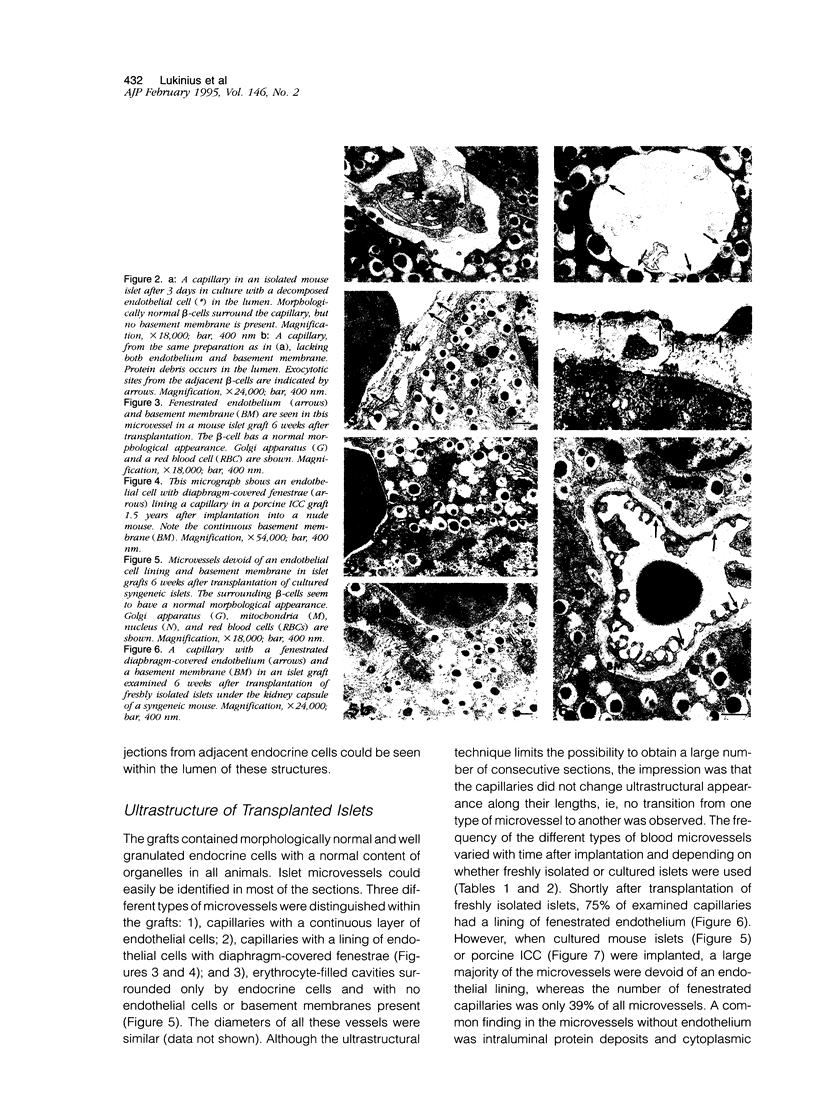
The aim of the present study was to investigate, at the ultrastructural level, the process of revascularization of freshly isolated islets or cultured islets after transplantation under the kidney capsule of syngeneic mice. Native islets in adult pancreases from mice, pigs, and humans contained only capillaries with fenestrated endothelium. However, the endothelial cell lining was disrupted in both freshly isolated and cultured mouse islets. Shortly after transplantation (6 weeks) approximately 80% of graft microvessels contained no endothelial cell lining. Similar data on microvessel morphology were found when fetal porcine islet-like cell clusters were implanted into athymic nude mice. Re-endothelialization was a slow process, with 25% of the microvessels still lacking endothelium 6 months after transplantation of cultured mouse islets or islet-like cell cluster. However, when freshly isolated mouse islets are used only 25% of microvessels within the islet graft lacked endothelium 6 weeks after implantation. We suggest that capillaries damaged during islet isolation may provide a preformed channel, serving as a scaffold for newly formed islet graft blood vessels. The presence of non-endothelialized microvessels, with an associated lack of barrier function, might make transplanted islets more prone to thrombosis or an attack by the immune system. This provides a tentative explanation for the increased vulnerability of islet grafts when compared with whole pancreas transplants.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ausprunk D. H., Folkman J. Migration and proliferation of endothelial cells in preformed and newly formed blood vessels during tumor angiogenesis. Microvasc Res. 1977 Jul;14(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(77)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausprunk D. H., Knighton D. R., Folkman J. Vascularization of normal and neoplastic tissues grafted to the chick chorioallantois. Role of host and preexisting graft blood vessels. Am J Pathol. 1975 Jun;79(3):597–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Aanstoot H. J., Christgau S., Reetz A., Solimena M., Cascalho M., Folli F., Richter-Olesen H., De Camilli P., Camilli P. D. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):151–156. doi: 10.1038/347151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett S. T., Hadley G. A., Dirden B., Schweitzer E. J., Eans S., Pham D., Sheffield C. Composite kidney-islet transplantation prevents recurrent autoimmune beta-cell destruction. Surgery. 1993 Aug;114(2):211–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Mihm M. C., Jr, Dvorak A. M., Barnes B. A., Galli S. J. The microvasculature is the critical target of the immune response in vascularized skin allograft rejection. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 May;74(5):280–284. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12543418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith R. C., Scharp D. W., Hartman B. K., Ballinger W. F., Lacy P. E. A morphologic study of intrahepatic portal-vein islet isografts. Diabetes. 1977 Mar;26(3):201–214. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.3.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart T. K., Pino R. M. Pseudoislet vascularization. Induction of diaphragm-fenestrated endothelia from the hepatic sinusoids. Lab Invest. 1986 Mar;54(3):304–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson J. R., Moss M. C. A morphometric study of the endocrine and exocrine capillaries of the pancreas. Q J Exp Physiol. 1985 Jul;70(3):347–356. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1985.sp002920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs B. B. Ovarian allograft survival. Prolongation after passage in vitro. Transplantation. 1974 Nov;18(5):454–457. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197411000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger M., Haffen K., Grenier J., Eloy R. In vitro culture reduces immunogenicity of pancreatic endocrine islets. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):736–738. doi: 10.1038/270736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., D'Amore P. A. Regulators of angiogenesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:217–239. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Hunt T. K., Scheuenstuhl H., Halliday B. J., Werb Z., Banda M. J. Oxygen tension regulates the expression of angiogenesis factor by macrophages. Science. 1983 Sep 23;221(4617):1283–1285. doi: 10.1126/science.6612342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima T., Leone C. W., Marchildon G. A., Marcum J. A., Rosenberg R. D. Isolation and characterization of heparan sulfate proteoglycans produced by cloned rat microvascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4859–4869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsgren O., Sandler S., Landström A. S., Jansson L., Andersson A. Large-scale production of fetal porcine pancreatic isletlike cell clusters. An experimental tool for studies of islet cell differentiation and xenotransplantation. Transplantation. 1988 Mar;45(3):509–514. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198803000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty K. J., Cooley M. A., Woolnough J., Walker K. Z. Thyroid allograft immunogenicity is reduced after a period in organ culture. Science. 1975 Apr 18;188(4185):259–261. doi: 10.1126/science.1118726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukinius A., Ericsson J. L., Grimelius L., Korsgren O. Ultrastructural studies of the ontogeny of fetal human and porcine endocrine pancreas, with special reference to colocalization of the four major islet hormones. Dev Biol. 1992 Oct;153(2):376–385. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90122-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin M. L., Hardy M. A., Gordon R. E., Reemtsma K., Benvenisty A. I. Induction of Ia antigen expression on endothelium of rat vein allografts: studies by immunogold labeling. Transplant Proc. 1989 Feb;21(1 Pt 1):113–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parr E. L., Bowen K. M., Lafferty K. J. Cellular changes in cultured mouse thyroid glands and islets of Langerhans. Transplantation. 1980 Aug;30(2):135–141. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198008000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P. Pancreas transplantation in humans with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1991 Sep;40(9):1085–1089. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.9.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SJOSTRAND F. S., ELFVIN L. G. The layered, asymmetric structure of the plasma membrane in the exocrine pancreas cells of the cat. J Ultrastruct Res. 1962 Dec;7:504–534. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(62)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samols E., Stagner J. I., Ewart R. B., Marks V. The order of islet microvascular cellular perfusion is B----A----D in the perfused rat pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):350–353. doi: 10.1172/JCI113593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. O., Hughes C. C., McIntyre B. W., Picard J. K., Pober J. S. Human CD4+ T cells proliferate to HLA-DR+ allogeneic vascular endothelium. Identification of accessory interactions. Transplantation. 1993 Jul;56(1):128–134. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199307000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. A., Bicknell R. The isolation and culture of microvascular endothelium. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jun;105(Pt 2):269–273. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theobald V. A., Lauer J. D., Kaplan F. A., Baker K. B., Rosenberg M. "Neutral allografts"--lack of allogeneic stimulation by cultured human cells expressing MHC class I and class II antigens. Transplantation. 1993 Jan;55(1):128–133. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199301000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzakis A. G., Ricordi C., Alejandro R., Zeng Y., Fung J. J., Todo S., Demetris A. J., Mintz D. H., Starzl T. E. Pancreatic islet transplantation after upper abdominal exenteration and liver replacement. Lancet. 1990 Aug 18;336(8712):402–405. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91946-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]