Abstract
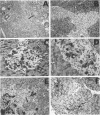
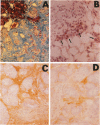
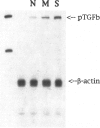
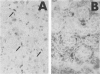
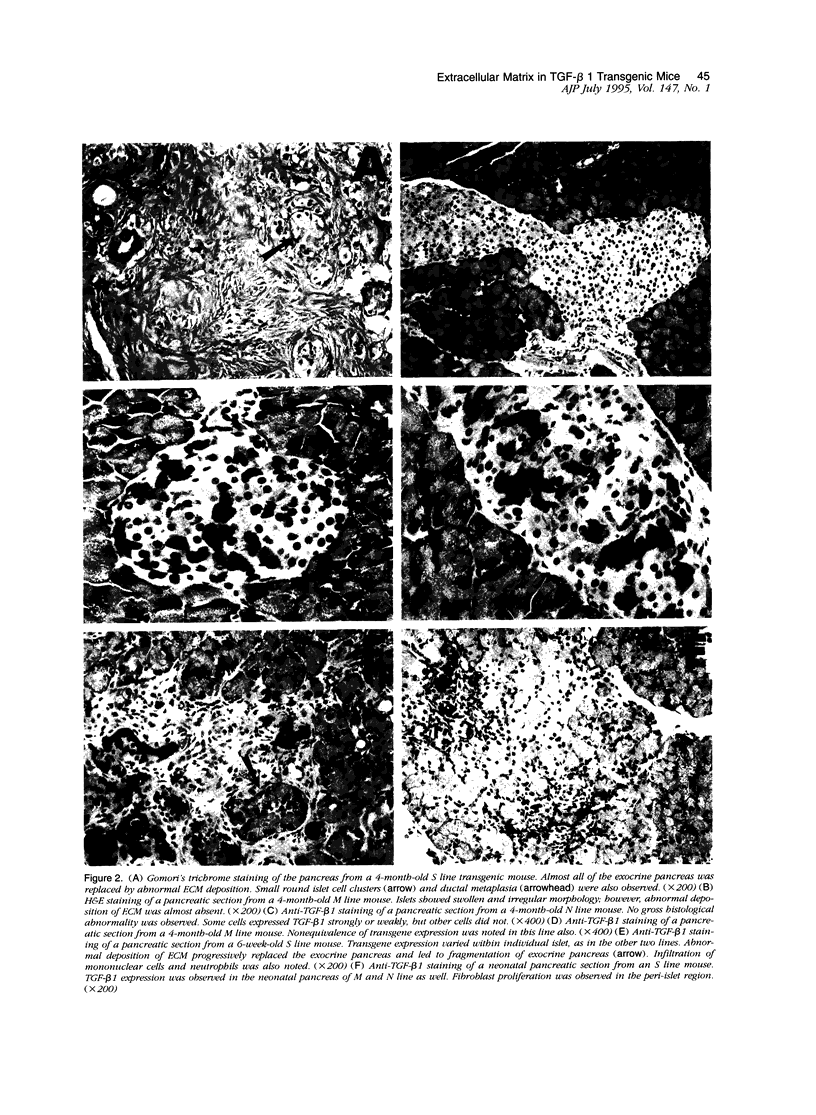
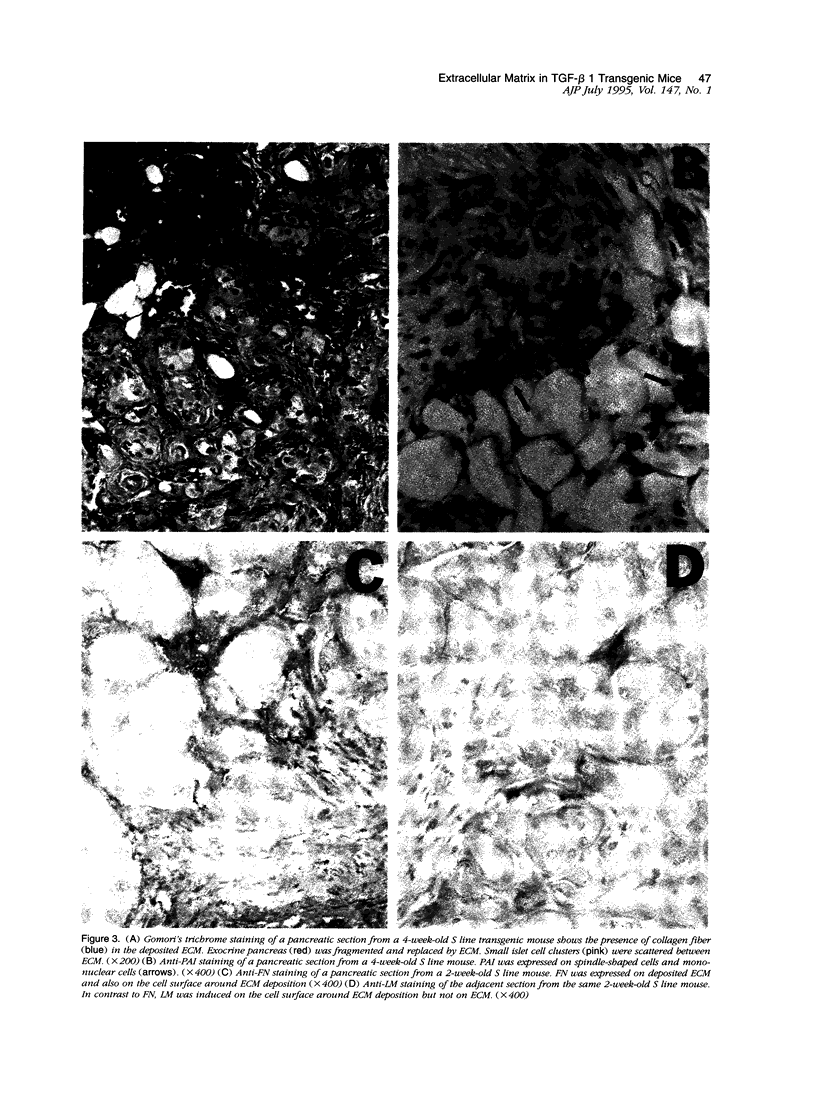
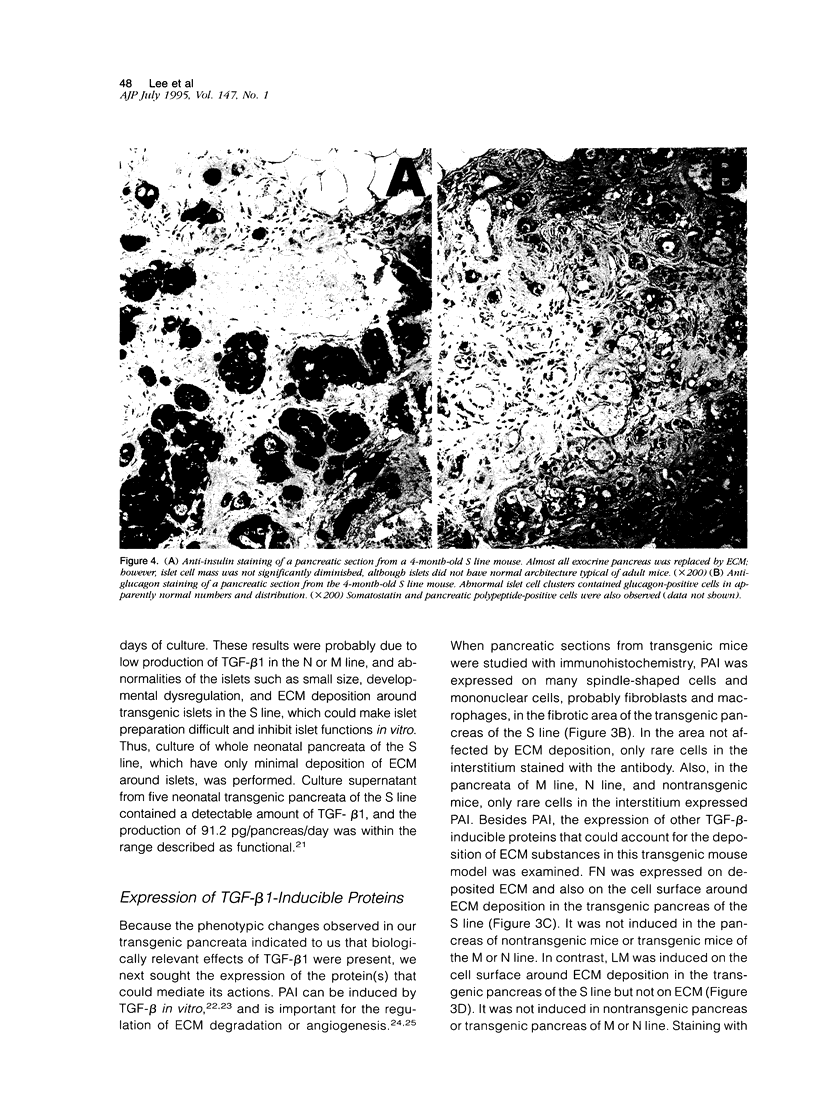
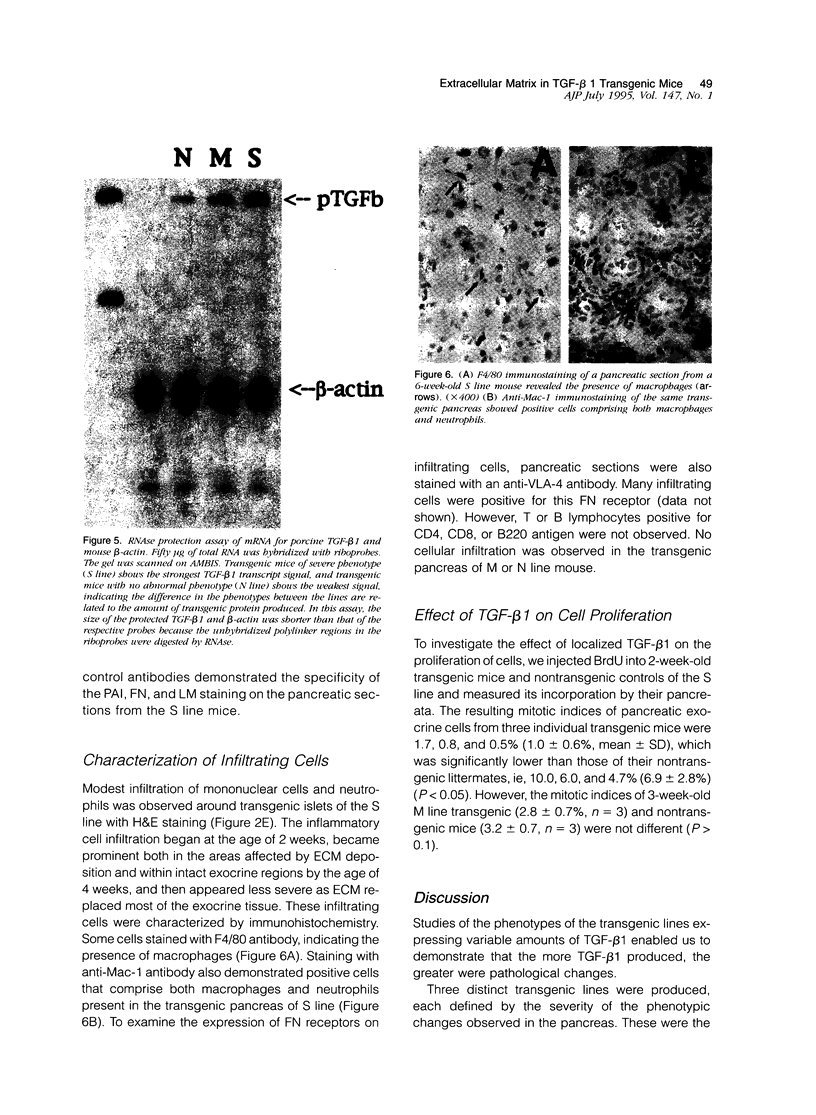
Transgenic mice expressing transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) in the pancreatic β-islet cells directed by human insulin promoter were produced to study in vivo effects of TGF-β1. Fibroblast proliferation and abnormal deposition of extracellular matrix were observed from birth onward, finally replacing almost all the exocrine pancreas. Cellular infiltrates comprising macrophages and neutrophils were also observed. Plasminogen activator inhibitor was induced in the transgenic pancreas as well as fibronectin and laminin, partly explaining accumulation of extracellular matrix. TGF-β1 inhibited proliferation of acinar cells in vivo as evidenced by decreased bromodeoxyuridine incorporation. Development of pancreatic islets was dysregulated, resulting in small islet cell clusters without formation of normal adult islets; however, the overall islet cell mass was not signfifcantly diminished. Additional transgenic lines with less pronounced phenotypes had less expression of TGF-β1 transgene. These findings suggest that TGF-β1 might be a mediator of diseases associated with extracellular matrix deposition such as chronic pancreatitis, and this mouse model will be useful for further analysis of the in vivo effects of TGF-β1, including its potential for immunosuppression.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe M., Harpel J. G., Metz C. N., Nunes I., Loskutoff D. J., Rifkin D. B. An assay for transforming growth factor-beta using cells transfected with a plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 promoter-luciferase construct. Anal Biochem. 1994 Feb 1;216(2):276–284. doi: 10.1006/abio.1994.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Vaheri A. Pericellular matrix in malignant transformation. Adv Cancer Res. 1982;37:111–158. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60883-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Ruoslahti E. Transforming growth factor-beta in disease: the dark side of tissue repair. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):1–7. doi: 10.1172/JCI115821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner A. M., Marquardt H., Malacko A. R., Lioubin M. N., Purchio A. F. Site-directed mutagenesis of cysteine residues in the pro region of the transforming growth factor beta 1 precursor. Expression and characterization of mutant proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13660–13664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. C., Newby R. F., Bourgeois S. Regulation of fibronectin biosynthesis by dexamethasone, transforming growth factor beta, and cAMP in human cell lines. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):2159–2170. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fava R. A., Olsen N. J., Postlethwaite A. E., Broadley K. N., Davidson J. M., Nanney L. B., Lucas C., Townes A. S. Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) induced neutrophil recruitment to synovial tissues: implications for TGF-beta-driven synovial inflammation and hyperplasia. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1121–1132. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng L., Xia Y., Kreisberg J. I., Wilson C. B. Interleukin-1 alpha stimulates KC synthesis in rat mesangial cells: glucocorticoids inhibit KC induction by IL-1. Am J Physiol. 1994 May;266(5 Pt 2):F713–F722. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.266.5.F713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heino J., Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-beta switches the pattern of integrins expressed in MG-63 human osteosarcoma cells and causes a selective loss of cell adhesion to laminin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21806–21811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Chakrabarty S. Regulation of fibronectin and laminin receptor expression, fibronectin and laminin secretion in human colon cancer cells by transforming growth factor-beta 1. Int J Cancer. 1994 Jun 1;57(5):742–746. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910570522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignotz R. A., Massagué J. Cell adhesion protein receptors as targets for transforming growth factor-beta action. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhappan C., Geiser A. G., Kordon E. C., Bagheri D., Hennighausen L., Roberts A. B., Smith G. H., Merlino G. Targeting expression of a transforming growth factor beta 1 transgene to the pregnant mammary gland inhibits alveolar development and lactation. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1835–1845. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05832.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhappan C., Stahle C., Harkins R. N., Fausto N., Smith G. H., Merlino G. T. TGF alpha overexpression in transgenic mice induces liver neoplasia and abnormal development of the mammary gland and pancreas. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1137–1146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90076-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns L. D., Flanders K. C., Ranges G. E., Sriram S. Successful treatment of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with transforming growth factor-beta 1. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1792–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeton M. R., Curriden S. A., van Zonneveld A. J., Loskutoff D. J. Identification of regulatory sequences in the type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene responsive to transforming growth factor beta. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23048–23052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Wakefield L. M., Roberts A. B., Jakowlew S., Alvarez-Mon M., Derynck R., Sporn M. B., Fauci A. S. Production of transforming growth factor beta by human T lymphocytes and its potential role in the regulation of T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1037–1050. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Ohtsuki M., Polyak K., Roberts J. M., Massagué J. Negative regulation of G1 in mammalian cells: inhibition of cyclin E-dependent kinase by TGF-beta. Science. 1993 Apr 23;260(5107):536–539. doi: 10.1126/science.8475385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuruvilla A. P., Shah R., Hochwald G. M., Liggitt H. D., Palladino M. A., Thorbecke G. J. Protective effect of transforming growth factor beta 1 on experimental autoimmune diseases in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2918–2921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Saksela O., Andreasen P. A., Keski-Oja J. Enhanced production and extracellular deposition of the endothelial-type plasminogen activator inhibitor in cultured human lung fibroblasts by transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2403–2410. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund L. R., Riccio A., Andreasen P. A., Nielsen L. S., Kristensen P., Laiho M., Saksela O., Blasi F., Danø K. Transforming growth factor-beta is a strong and fast acting positive regulator of the level of type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor mRNA in WI-38 human lung fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1281–1286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02365.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. M., Moses H. L. Transforming growth factors and the regulation of cell proliferation. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Feb 14;187(3):467–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. The transforming growth factor-beta family. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:597–641. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Pepper M. S., Vassalli J. D., Orci L. Phorbol ester induces cultured endothelial cells to invade a fibrin matrix in the presence of fibrinolytic inhibitors. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Sep;132(3):509–516. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041320313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Rifkin D. B. Membrane and matrix localization of proteinases: a common theme in tumor cell invasion and angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Aug 3;948(1):67–85. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh T., Saxena B., Reibman J., Cronstein B. N., Gold L. I. Neutrophil chemotaxis in response to TGF-beta isoforms (TGF-beta 1, TGF-beta 2, TGF-beta 3) is mediated by fibronectin. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 1;152(5):2456–2466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce D. F., Jr, Johnson M. D., Matsui Y., Robinson S. D., Gold L. I., Purchio A. F., Daniel C. W., Hogan B. L., Moses H. L. Inhibition of mammary duct development but not alveolar outgrowth during pregnancy in transgenic mice expressing active TGF-beta 1. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2308–2317. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G. Heterogeneity in pancreatic beta-cell population. Diabetes. 1992 Jul;41(7):777–781. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.7.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Assoian R. K., Smith J. M., Roche N. S., Wakefield L. M., Heine U. I., Liotta L. A., Falanga V., Kehrl J. H. Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4167–4171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel S. K., Hurta R. A., Kondaiah P., Khalil N., Turley E. A., Wright J. A., Greenberg A. H. Autocrine induction of tumor protease production and invasion by a metallothionein-regulated TGF-beta 1 (Ser223, 225). EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1599–1605. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05205.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandgren E. P., Luetteke N. C., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Lee D. C. Overexpression of TGF alpha in transgenic mice: induction of epithelial hyperplasia, pancreatic metaplasia, and carcinoma of the breast. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1121–1135. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90075-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellheyer K., Bickenbach J. R., Rothnagel J. A., Bundman D., Longley M. A., Krieg T., Roche N. S., Roberts A. B., Roop D. R. Inhibition of skin development by overexpression of transforming growth factor beta 1 in the epidermis of transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5237–5241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Allen J. B., Weeks B. S., Wong H. L., Klotman P. E. Transforming growth factor beta enhances integrin expression and type IV collagenase secretion in human monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4577–4581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Hunt D. A., Wakefield L. M., McCartney-Francis N., Wahl L. M., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor type beta induces monocyte chemotaxis and growth factor production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5788–5792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Hunt D. A., Wong H. L., Dougherty S., McCartney-Francis N., Wahl L. M., Ellingsworth L., Schmidt J. A., Hall G., Roberts A. B. Transforming growth factor-beta is a potent immunosuppressive agent that inhibits IL-1-dependent lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3026–3032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) in inflammation: a cause and a cure. J Clin Immunol. 1992 Mar;12(2):61–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00918135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia Y., Feng L., Yoshimura T., Wilson C. B. LPS-induced MCP-1, IL-1 beta, and TNF-alpha mRNA expression in isolated erythrocyte-perfused rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1993 May;264(5 Pt 2):F774–F780. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.5.F774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]