Abstract
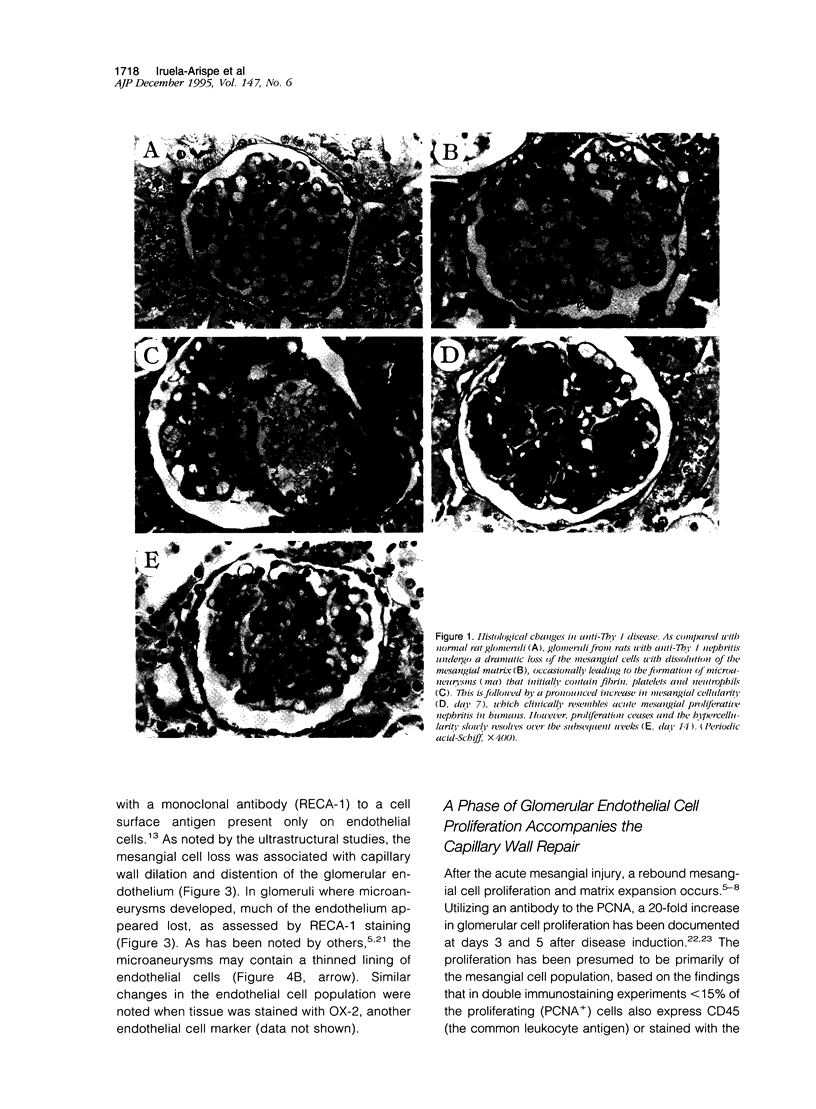
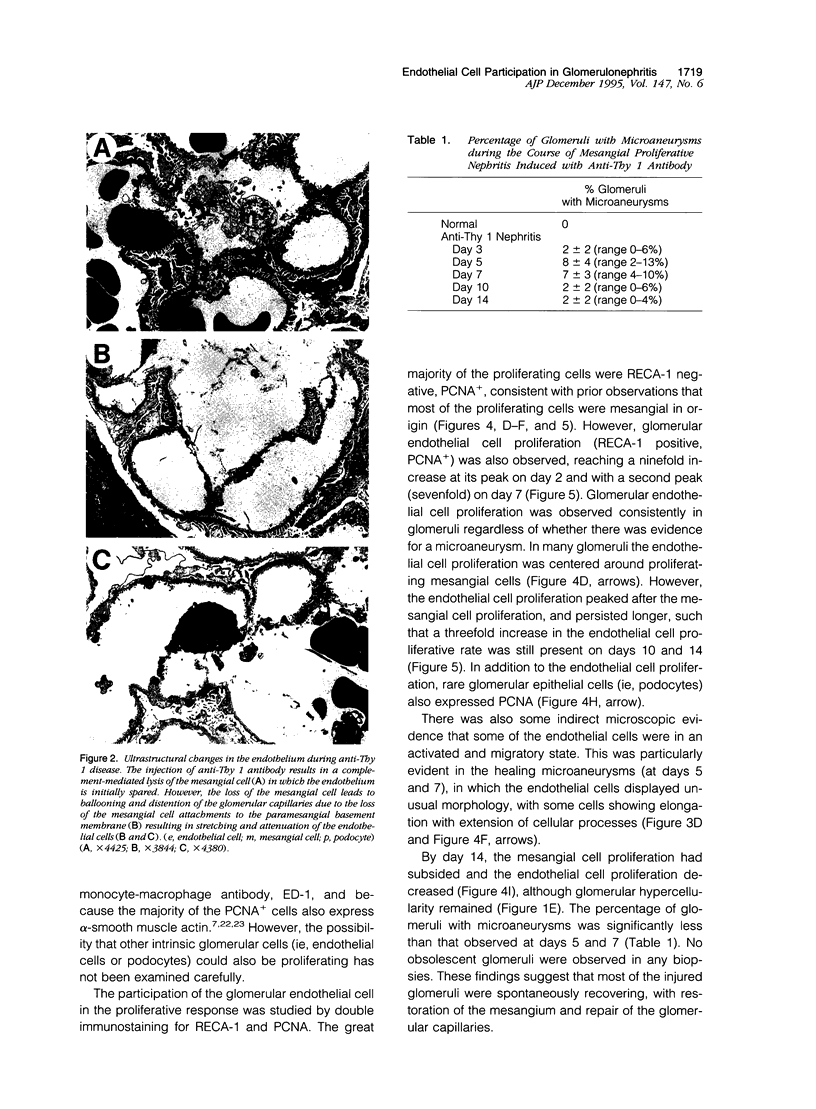
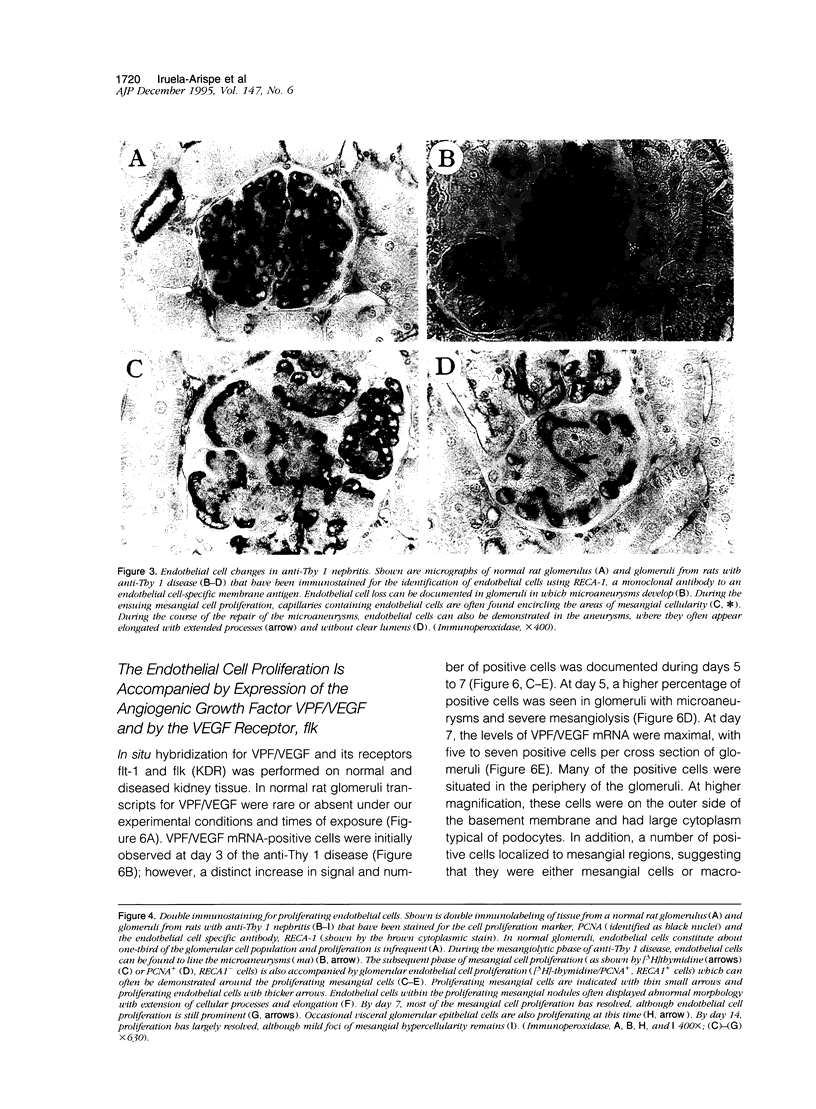
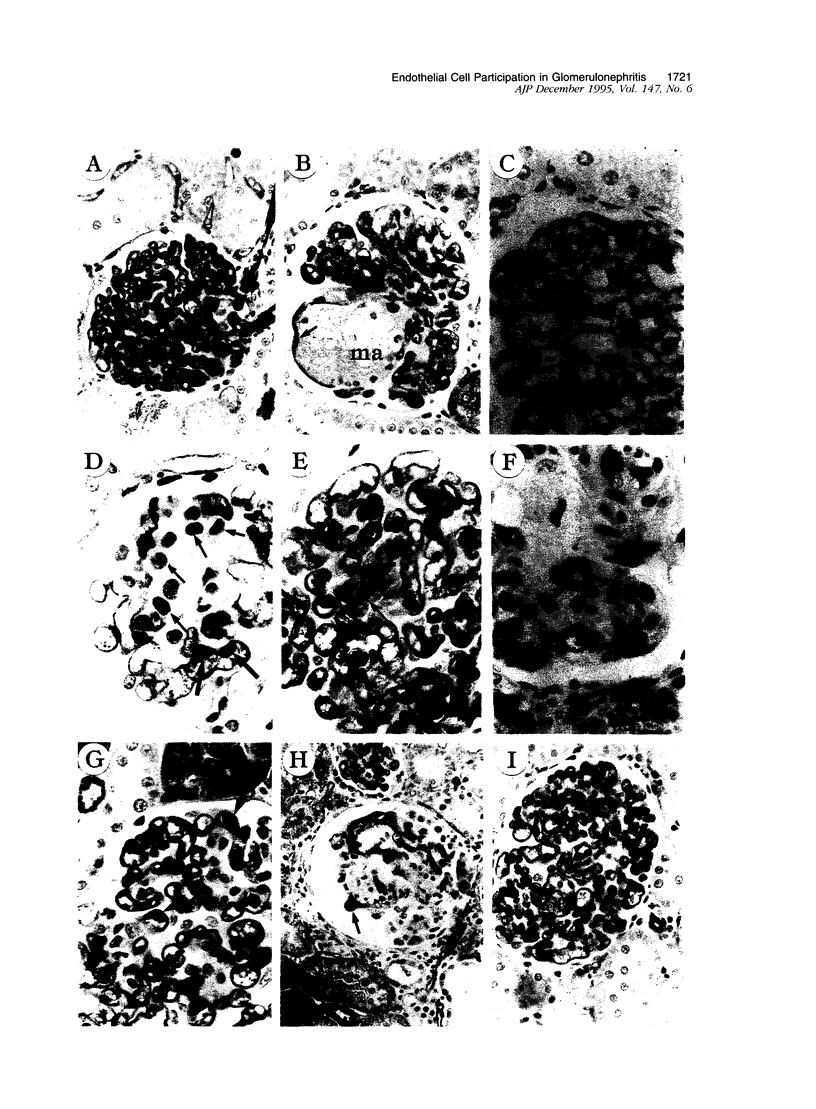
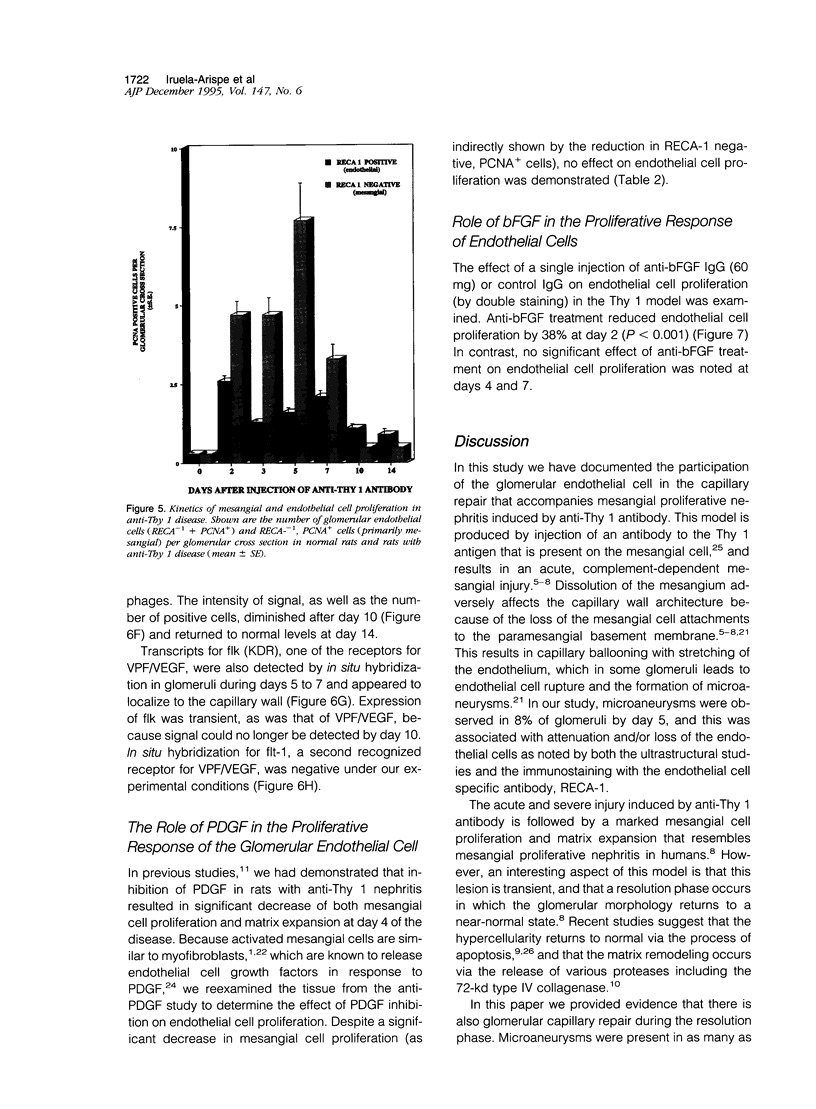
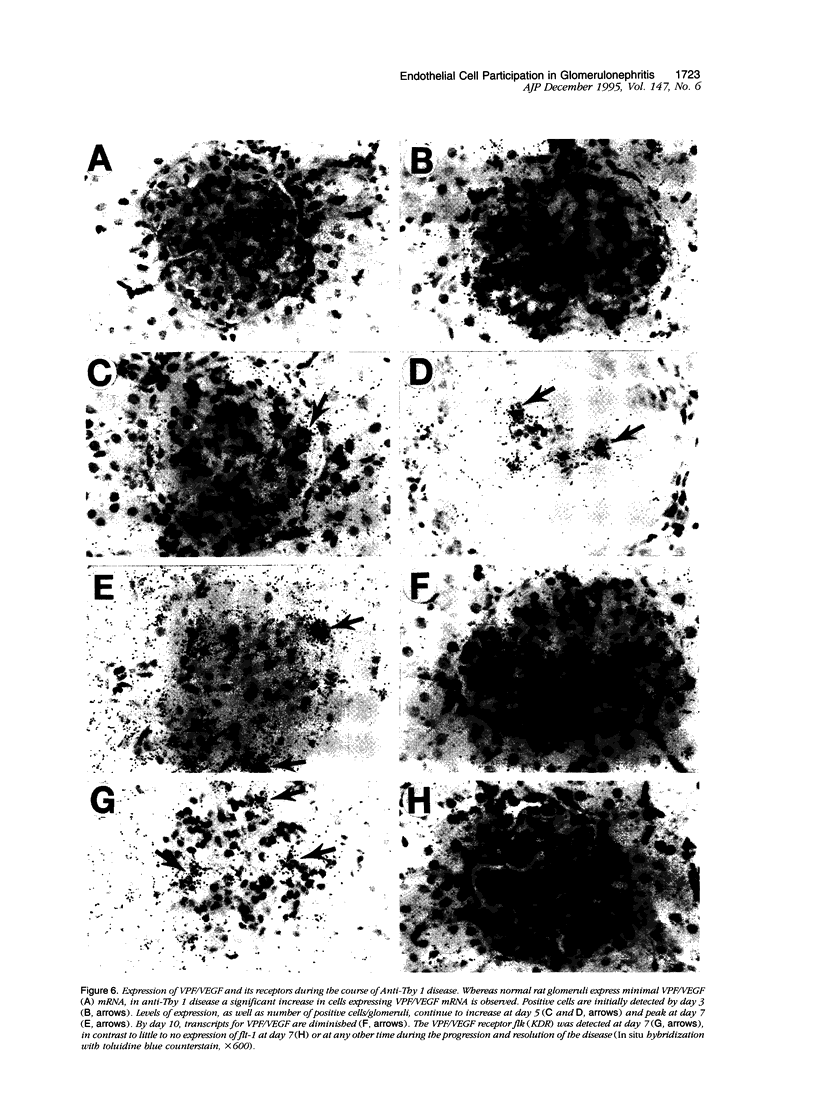
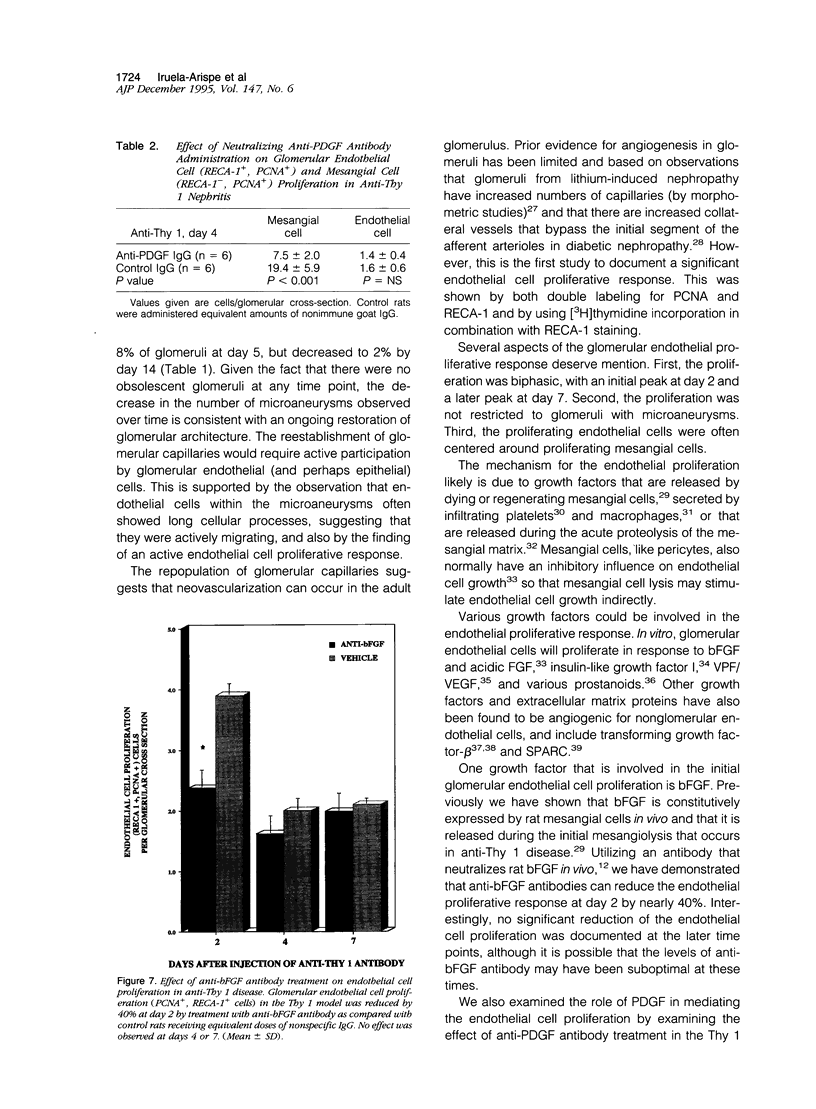
In many glomerular diseases severe injury to the mesangium may occur, leading to matrix dissolution and damage to the glomerular capillaries. Although the destruction of glomerular architecture may lead to permanent injury, in some cases spontaneous recovery occurs. The mechanisms that mediate this recovery are unknown. In this study we provide evidence for glomerular capillary repair (angiogenesis) in the adult injured glomerulus. Injection of anti-Thy 1 antibody into rats results in severe mesangiolysis with capillary ballooning, microaneurysm formation, and loss of endothelial cells in addition to mesangial cells. Although mesangial proliferation is a major response to injury, proliferation of endothelial cells also can be documented from days 2 to 14 in association with repair of the capillaries. The endothelial cell proliferation peaks on days 2 and 7, when it is seven- to ninefold greater than normal. Many of the endothelial cells display morphological features of angiogenesis. The initial wave of endothelial cell proliferation can be reduced by 40% with neutralizing anti-basic fibroblast growth factor antibodies (P < 0.001). The later glomerular endothelial cell proliferation is associated with upregulated expression of vascular permeability factor/endothelial cell growth factor (VPF/VEGF) and an increase of flk, a VPF/VEGF receptor. Although PDGF is expressed in this model, anti-PDGF antibody treatment did not affect the endothelial cell proliferative response. In summary, glomerular endothelial cells have an active role in the glomerular response to injury. Glomeruli are capable of healing microaneurysms, and the mechanism involves basic fibroblast growth factor- and VPF/VEGF-mediated endothelial proliferative responses.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abboud H. E. Growth factors in glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1993 Jan;43(1):252–267. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker A. J., Mooney A., Hughes J., Lombardi D., Johnson R. J., Savill J. Mesangial cell apoptosis: the major mechanism for resolution of glomerular hypercellularity in experimental mesangial proliferative nephritis. J Clin Invest. 1994 Nov;94(5):2105–2116. doi: 10.1172/JCI117565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballermann B. J. Regulation of bovine glomerular endothelial cell growth in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 1):C182–C189. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.1.C182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barclay A. N. Different reticular elements in rat lymphoid tissue identified by localization of Ia, Thy-1 and MRC OX 2 antigens. Immunology. 1981 Dec;44(4):727–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beitz J. G., Kim I. S., Calabresi P., Frackelton A. R., Jr Human microvascular endothelial cells express receptors for platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):2021–2025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berse B., Brown L. F., Van de Water L., Dvorak H. F., Senger D. R. Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) gene is expressed differentially in normal tissues, macrophages, and tumors. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Feb;3(2):211–220. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. F., Berse B., Tognazzi K., Manseau E. J., Van de Water L., Senger D. R., Dvorak H. F., Rosen S. Vascular permeability factor mRNA and protein expression in human kidney. Kidney Int. 1992 Dec;42(6):1457–1461. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G., White R. H., Glasgow E. F., Chantler C., Cameron J. S., Gill D., Comley L. A. Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis in children: clinicopathological correlations and long-term prognosis. Pediatr Nephrol. 1988 Oct;2(4):381–388. doi: 10.1007/BF00853424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daemen M. J., Lombardi D. M., Bosman F. T., Schwartz S. M. Angiotensin II induces smooth muscle cell proliferation in the normal and injured rat arterial wall. Circ Res. 1991 Feb;68(2):450–456. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.2.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duijvestijn A. M., van Goor H., Klatter F., Majoor G. D., van Bussel E., van Breda Vriesman P. J. Antibodies defining rat endothelial cells: RECA-1, a pan-endothelial cell-specific monoclonal antibody. Lab Invest. 1992 Apr;66(4):459–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnerty H., Kelleher K., Morris G. E., Bean K., Merberg D. M., Kriz R., Morris J. C., Sookdeo H., Turner K. J., Wood C. R. Molecular cloning of murine FLT and FLT4. Oncogene. 1993 Aug;8(8):2293–2298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floege J., Eng E., Lindner V., Alpers C. E., Young B. A., Reidy M. A., Johnson R. J. Rat glomerular mesangial cells synthesize basic fibroblast growth factor. Release, upregulated synthesis, and mitogenicity in mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1992 Dec;90(6):2362–2369. doi: 10.1172/JCI116126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floege J., Johnson R. J., Gordon K., Iida H., Pritzl P., Yoshimura A., Campbell C., Alpers C. E., Couser W. G. Increased synthesis of extracellular matrix in mesangial proliferative nephritis. Kidney Int. 1991 Sep;40(3):477–488. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida H., Seifert R., Alpers C. E., Gronwald R. G., Phillips P. E., Pritzl P., Gordon K., Gown A. M., Ross R., Bowen-Pope D. F. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and PDGF receptor are induced in mesangial proliferative nephritis in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6560–6564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iruela-Arispe M. L., Liska D. J., Sage E. H., Bornstein P. Differential expression of thrombospondin 1, 2, and 3 during murine development. Dev Dyn. 1993 May;197(1):40–56. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001970105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iruela-Arispe M. L., Sage E. H. Endothelial cells exhibiting angiogenesis in vitro proliferate in response to TGF-beta 1. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Aug;52(4):414–430. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240520406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki M., Masuda Y., Fukuda Y., Sugisaki Y., Yamanaka N., Masugi Y. Experimental mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis in rats induced by intravenous administration of anti-thymocyte serum. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1986 Aug;36(8):1191–1203. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1986.tb02839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. J., Alpers C. E., Pruchno C., Schulze M., Baker P. J., Pritzl P., Couser W. G. Mechanisms and kinetics for platelet and neutrophil localization in immune complex nephritis. Kidney Int. 1989 Nov;36(5):780–789. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. J., Garcia R. L., Pritzl P., Alpers C. E. Platelets mediate glomerular cell proliferation in immune complex nephritis induced by anti-mesangial cell antibodies in the rat. Am J Pathol. 1990 Feb;136(2):369–374. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. J., Iida H., Alpers C. E., Majesky M. W., Schwartz S. M., Pritzi P., Gordon K., Gown A. M. Expression of smooth muscle cell phenotype by rat mesangial cells in immune complex nephritis. Alpha-smooth muscle actin is a marker of mesangial cell proliferation. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):847–858. doi: 10.1172/JCI115089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. J. Platelets in inflammatory glomerular injury. Semin Nephrol. 1991 May;11(3):276–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. J., Raines E. W., Floege J., Yoshimura A., Pritzl P., Alpers C., Ross R. Inhibition of mesangial cell proliferation and matrix expansion in glomerulonephritis in the rat by antibody to platelet-derived growth factor. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1413–1416. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. J. The glomerular response to injury: progression or resolution? Kidney Int. 1994 Jun;45(6):1769–1782. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurki P., Vanderlaan M., Dolbeare F., Gray J., Tan E. M. Expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)/cyclin during the cell cycle. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Sep;166(1):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90520-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemley K. V., Elger M., Koeppen-Hagemann I., Kretzler M., Nagata M., Sakai T., Uiker S., Kriz W. The glomerular mesangium: capillary support function and its failure under experimental conditions. Clin Investig. 1992 Sep;70(9):843–856. doi: 10.1007/BF00180755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner V., Reidy M. A. Proliferation of smooth muscle cells after vascular injury is inhibited by an antibody against basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3739–3743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett D. H., Johnson R. J., Marti H. P., Martin J., Davies M., Couser W. G. Structural characterization of the mesangial cell type IV collagenase and enhanced expression in a model of immune complex-mediated glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol. 1992 Jul;141(1):85–98. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcussen N., Nyengaard J. R., Christensen S. Compensatory growth of glomeruli is accomplished by an increased number of glomerular capillaries. Lab Invest. 1994 Jun;70(6):868–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster W. R., Williams A. F. Identification of Ia glycoproteins in rat thymus and purification from rat spleen. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jun;9(6):426–433. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min W., Yamanaka N. Three-dimensional analysis of increased vasculature around the glomerular vascular pole in diabetic nephropathy. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1993;423(3):201–207. doi: 10.1007/BF01614771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitta K., Simonson M. S., Dunn M. J. The regulation and role of prostaglandin biosynthesis in cultured bovine glomerular endothelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1991 Aug;2(2):156–163. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V22156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi H., Rosen K. M., Smith F. E., Villa-Komaroff L., Nayak R. C., King G. L. Characterization of type I IGF receptor and IGF-I mRNA expression in cultured human and bovine glomerular cells. Regul Pept. 1993 Oct 20;48(1-2):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(93)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda S., Languino L. R., Ruoslahti E., Border W. A. Elevated expression of transforming growth factor-beta and proteoglycan production in experimental glomerulonephritis. Possible role in expansion of the mesangial extracellular matrix. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):453–462. doi: 10.1172/JCI114731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlidge A., D'Amore P. A. Inhibition of capillary endothelial cell growth by pericytes and smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1455–1462. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popović-Rolović M., Kostić M., Antić-Peco A., Jovanović O., Popović D. Medium- and long-term prognosis of patients with acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Nephron. 1991;58(4):393–399. doi: 10.1159/000186469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Assoian R. K., Smith J. M., Roche N. S., Wakefield L. M., Heine U. I., Liotta L. A., Falanga V., Kehrl J. H. Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4167–4171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato N., Beitz J. G., Kato J., Yamamoto M., Clark J. W., Calabresi P., Raymond A., Frackelton A. R., Jr Platelet-derived growth factor indirectly stimulates angiogenesis in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1993 Apr;142(4):1119–1130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Kitamura H., Masuda Y., Ishizaki M., Sugisaki Y., Yamanaka N. Apoptosis in the repair process of experimental proliferative glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1995 Jan;47(1):114–121. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida K., Uchida S., Nitta K., Yumura W., Marumo F., Nihei H. Glomerular endothelial cells in culture express and secrete vascular endothelial growth factor. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jan;266(1 Pt 2):F81–F88. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.266.1.F81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Fuks Z., Ishai-Michaeli R., Bashkin P., Levi E., Korner G., Bar-Shavit R., Klagsbrun M. Extracellular matrix-resident basic fibroblast growth factor: implication for the control of angiogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Feb;45(2):167–176. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240450208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Wilson C. B. Complement dependence of antibody-induced mesangial cell injury in the rat. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3758–3765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yamamoto K., Kawasaki K., Yaoita E., Shimizu F., Kihara I. Immunoelectron microscopic demonstration of Thy-1 antigen on the surfaces of mesangial cells in the rat glomerulus. Nephron. 1986;43(4):293–298. doi: 10.1159/000183857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura A., Gordon K., Alpers C. E., Floege J., Pritzl P., Ross R., Couser W. G., Bowen-Pope D. F., Johnson R. J. Demonstration of PDGF B-chain mRNA in glomeruli in mesangial proliferative nephritis by in situ hybridization. Kidney Int. 1991 Sep;40(3):470–476. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








