Abstract
Allogeneic graft-versus-host disease is characterized by skin, gut, and bile duct destruction by relatively few donor type lymphocytes. In contrast, we can now show that human-to-mouse xenogeneic graft-versus-host disease is characterized by vasculitis and tumor-like infiltrations of the murine lymphohemopoietic organs with many human CD25+, HLA-DR+, CD4+ lymphoblasts. Using the technique of serial transplantation, it appears that at least 90% of the human lymphoblasts were unreactive to murine tissues. It is demonstrated consistently that the donor type lymphoblasts induced typical allogeneic rejection of distantly located full thickness human unmatched fetal skin grafts. The fact that the human grafts show primary immune responses in vivo indicates that the graft-versus-host disease murine model may be suitable for vaccination studies.
Full text
PDF

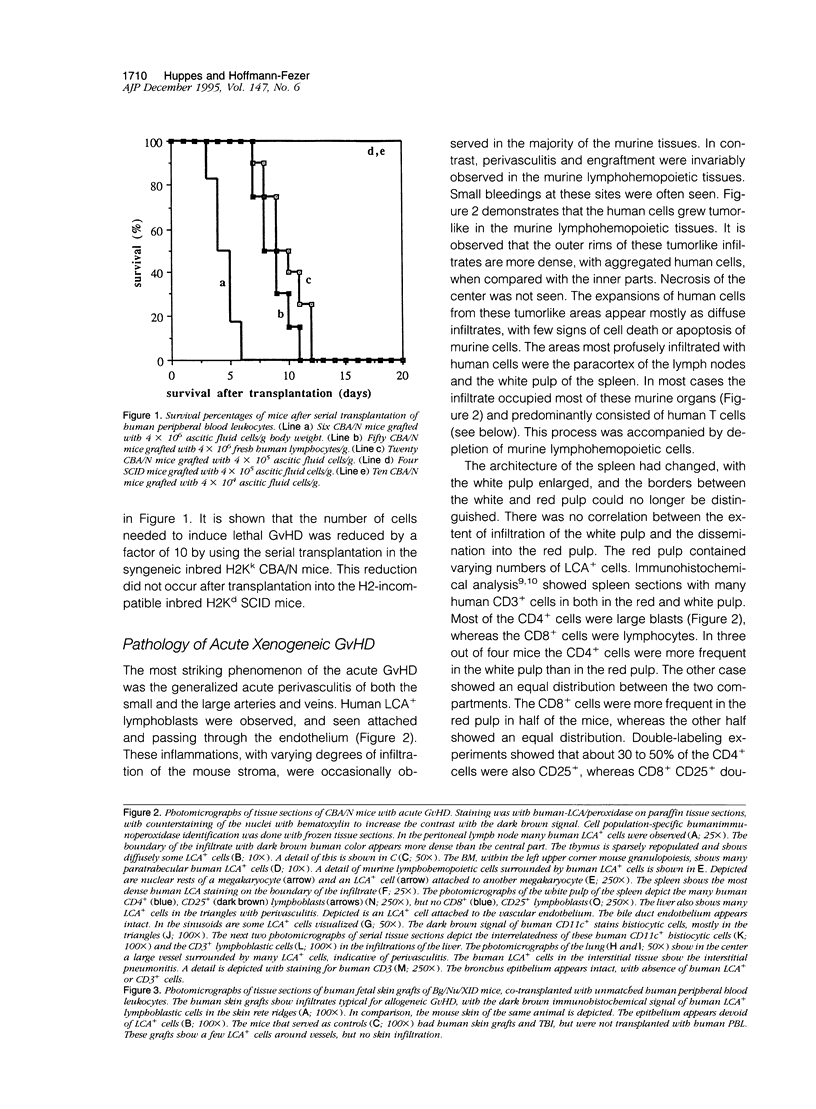
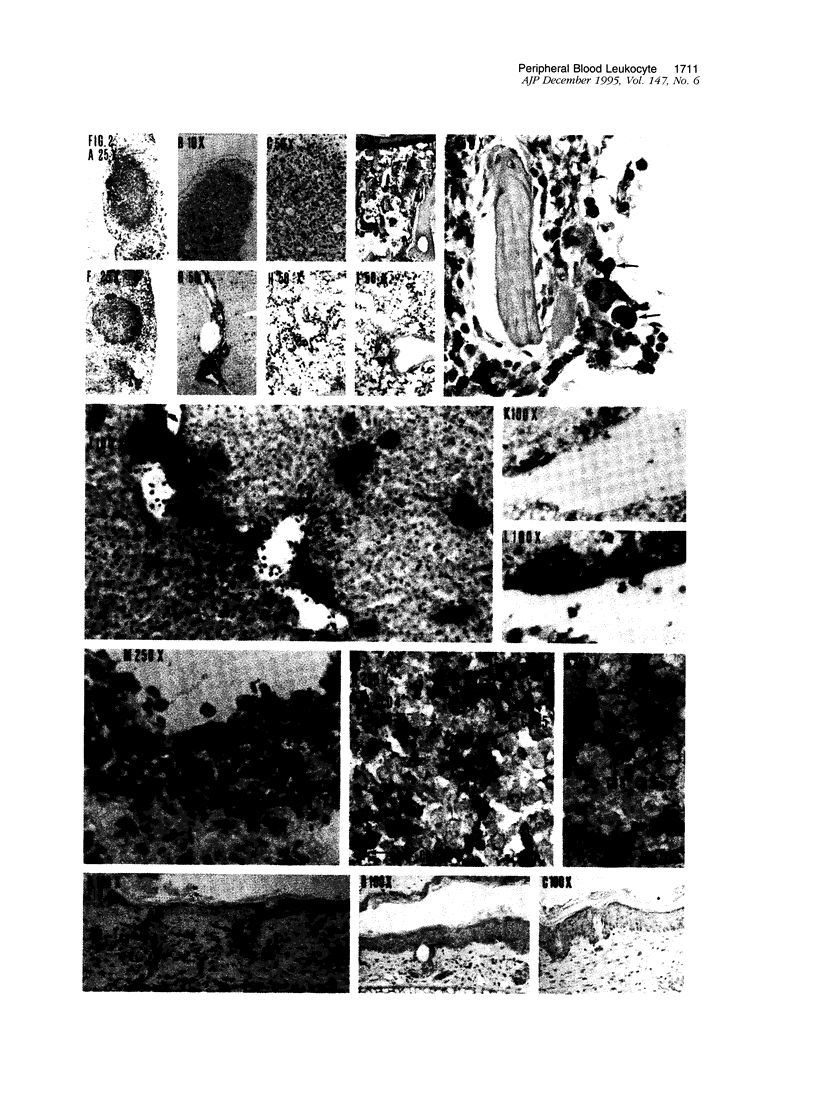



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biedermann K. A., Sun J. R., Giaccia A. J., Tosto L. M., Brown J. M. scid mutation in mice confers hypersensitivity to ionizing radiation and a deficiency in DNA double-strand break repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1394–1397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann-Fezer G., Gall C., Zengerle U., Kranz B., Thierfelder S. Immunohistology and immunocytology of human T-cell chimerism and graft-versus-host disease in SCID mice. Blood. 1993 Jun 15;81(12):3440–3448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann-Fezer G., Kranz B., Gall C., Thierfelder S. Peritoneal sanctuary for human lymphopoiesis in SCID mice injected with human peripheral blood lymphocytes from Epstein-Barr virus-negative donors. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Dec;22(12):3161–3166. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppes W., De Geus B., Zurcher C., Van Bekkum D. W. Acute human vs. mouse graft vs. host disease in normal and immunodeficient mice. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jan;22(1):197–206. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppes W., Fickenscher H., 'tHart B. A., Fleckenstein B. Cytokine dependence of human to mouse graft-versus-host disease. Scand J Immunol. 1994 Jul;40(1):26–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1994.tb03429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martino G., Anastasi J., Feng J., Mc Shan C., DeGroot L., Quintans J., Grimaldi L. M. The fate of human peripheral blood lymphocytes after transplantation into SCID mice. Eur J Immunol. 1993 May;23(5):1023–1028. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzinger P., Bevan M. J. Hypothesis: why do so many lymphocytes respond to major histocompatibility antigens? Cell Immunol. 1977 Mar 1;29(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Gulizia R. J., Baird S. M., Wilson D. B. Transfer of a functional human immune system to mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):256–259. doi: 10.1038/335256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Gulizia R. J., MacIsaac P. D., Corey L., Greenberg P. D. Resistance to human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection of SCID mice reconstituted with peripheral blood leukocytes from donors vaccinated with vaccinia gp160 and recombinant gp160. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2443–2447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. A., Spaner D. E. The scid mouse: mutation in a DNA repair gene creates recipients useful for studies on stem cells, lymphocyte development and graft-versus-host disease. Immunol Rev. 1991 Dec;124:63–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E., Farrant J., Chandler P. Phenotypic and functional studies of human peripheral blood lymphocytes engrafted in scid mice. Immunol Rev. 1991 Dec;124:97–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tary-Lehmann M., Saxon A. Human mature T cells that are anergic in vivo prevail in SCID mice reconstituted with human peripheral blood. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):503–516. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torbett B. E., Picchio G., Mosier D. E. hu-PBL-SCID mice: a model for human immune function, AIDS, and lymphomagenesis. Immunol Rev. 1991 Dec;124:139–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bekkum D. W., Knaan S. Role of bacterial microflora in development of intestinal lesions from graft-versus-host reaction. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Mar;58(3):787–790. doi: 10.1093/jnci/58.3.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




