Abstract
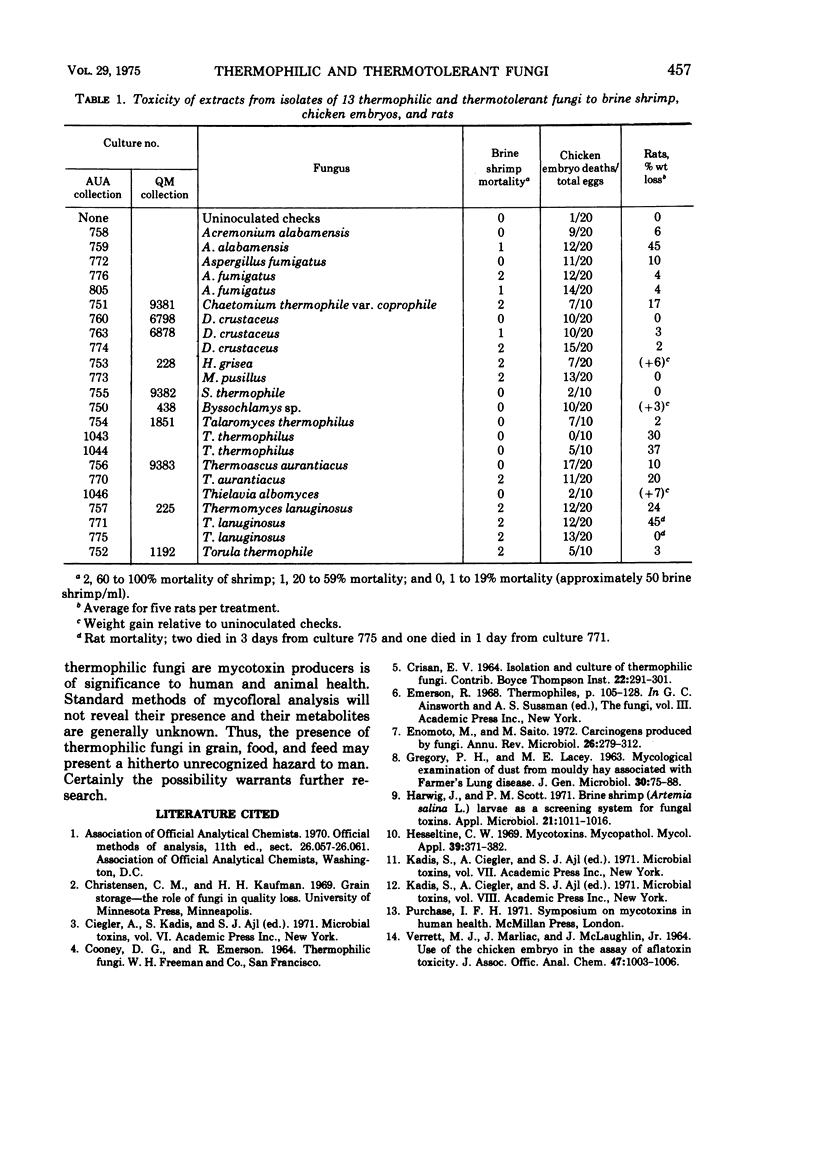
Twenty-three isolates of fungi, representing 13 thermophilic and thermotolerant species, were bioassayed for toxigenicity to brine shrimp, chicken embryos, and rats. Thirteen isolates representing nine genera were highly toxic to at least two of the three systems. Seven additional isolates of five genera were slightly toxic.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Enomoto M., Saito M. Carcinogens produced by fungi. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1972;26:279–312. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.26.100172.001431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGORY P. H., LACEY M. E. Mycological examination of dust from mouldy hay associated with farmer's lung disease. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jan;30:75–88. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-1-75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwig J., Scott P. M. Brine shrimp (Artemia salina L.) larvae as a screening system for fungal toxins. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jun;21(6):1011–1016. doi: 10.1128/am.21.6.1011-1016.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesseltine C. W. Mycotoxins. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1969 Dec 29;39(3):371–383. doi: 10.1007/BF02052805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


