Abstract
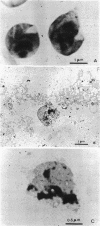
Micrococcus luteus cells cultivated in medium containing lead salts exhibited a sequence of changes in the quantity of total cellular lipids with essentially no changes from normal cellular yields. The lipid composition of cells cultivated one to four times was moderately decreased (phase I) whereas that of cells cultivated five to six times was reduced by as much as 50% (phase II). Cells cultivated more than six times in lead-containing media had progressively greater quantities of lipid (phase III) approaching that found in control cells. These cells with reestablished lipid contents showed no further effects from more prolonged exposure to lead salts. Chromatographic studies of total lipids of cells of each lipid phase revealed relatively complete lipid compositions. These results indicated that lead is apparently affecting a common biochemical parameter in the biosynthesis of lipids of lipid phase II cells. Changes in the relative quantities of individual components were observed in both the nonpolar and polar lipids in each lipid phase. The most notable changes were the decrease in aliphatic hydrocarbons with concomitant increases in the diglycerides and components identified as a complex family of ketones. Microscopy examinations of control and lead-treated cells revealed electron dense inclusion bodies in membrane fragments in only lead-treated cells.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albro P. W., Dittmer J. C. The biochemistry of long-chain, nonisoprenoid hydrocarbons. I. Characterization of the hydrocarbons of Sarcina lutea and the isolation of possible intermediates of biosynthesis. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):394–404. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albro P. W., Dittmer J. C. The biochemistry of long-chain, nonisoprenoid hydrocarbons. IV. Characteristics of synthesis by a cell-free preparation of Sarcina lutea. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3317–3324. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. J. The estimation of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1940 Jun;34(6):858–865. doi: 10.1042/bj0340858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arpin N., Norgård S., Francis G. W., Liaaen-Jensen S. Bacterial carotenoids. XLI. C50-carotenoids. 11. C45- and C50-carotenoids from Sarcina lutea--sarcinaxanthin. Acta Chem Scand. 1973;27(7):2321–2334. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.27-2321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertsch L. L., Bonsen P. P., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germination. XIV. Phospholipids in Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):75–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.75-81.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Siervo A. J., Salton M. R. Changes in phospholipid composition of Micrococcus lysodeikticus during growth. Microbios. 1973 Jun-Aug;8(29):73–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman C. P., West D. Complete separation of lipid classes on a single thin-layer plate. J Lipid Res. 1966 Mar;7(2):324–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUSTON C. K., ALBRO P. W., GRINDEY G. B. LIPIDS OF SARCINA LUTEA. 3. COMPOSITION OF THE COMPLEX LIPIDS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:768–775. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.768-775.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Carotenoid formation by Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):191–198. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.191-198.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATES M. SIMPLIFIED PROCEDURES FOR HYDROLYSIS OR METHANOLYSIS OF LIPIDS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:132–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepage M. Identification and composition of turnip root lipids. Lipids. 1967 May;2(3):244–250. doi: 10.1007/BF02532563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markey S. P., Tornabene T. G. Characterization of branched monounsaturated hydrocarbons of Sarcina lutea and Sarcina flava. Lipids. 1971 Mar;6(3):190–195. doi: 10.1007/BF02533037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews-Roth M. M., Wilson T., Fujimori E., Krinsky N. I. Carotenoid chromophore length and protection against photosensitization. Photochem Photobiol. 1974 Mar;19(3):217–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1974.tb06501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. F., Goyer R. A. Lead-induced inclusion bodies: composition and probable role in lead metabolism. Environ Health Perspect. 1974 May;7:121–127. doi: 10.1289/ehp.747121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison S. J., Tornabene T. G., Kloos W. E. Neutral lipids in the study of relationships of members of the family micrococcaceae. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):353–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.353-358.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Roth C. Plasmid-linked resistance to inorganic salts in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1335–1342. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1335-1342.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R., EHTISHAM-UD-DIN A. F. THE LOCALIZATION OF CYTOCHROMES AND CAROTENOIDS IN ISOLATED BACTERIAL MEMBRANES AND ENVELOPES. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1965 Jun;43:255–264. doi: 10.1038/icb.1965.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salton M. R., Freer J. H. Composition of the membranes isolated from several Gram-positive bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 18;107(3):531–538. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salton M. R., Schmitt M. D. Effects of diphenylamine on carotenoids and menaquinones in bacterial membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 2;135(2):196–207. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short S. A., White D. C., Aleem M. I. Phospholipid metabolism in Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):142–150. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.142-150.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirkell D., Strang R. H., Chapman J. R. The pigments of Sarcina flava: a new series of C50 carotenoids. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Oct;49(1):157–164. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-1-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. D., Ellar D. J. Properties of plasma and mesosomal membranes isolated from Micrococcus lysodeikticus: rates of synthesis and characterisation of lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 23;316(2):180–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornabene T. G., Edwards H. W. Microbial uptake of lead. Science. 1972 Jun 23;176(4041):1334–1335. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4041.1334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornabene T. G., Kates M., Gelpi E., Oro J. Occurrence of squalene, di- and tetrahydrosqualenes, and vitamin MK8 in an extremely halophilic bacterium, Halobacterium cutirubrun. J Lipid Res. 1969 May;10(3):294–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornabene T. G. Lipid composition of selected strains of Yersinia pestis and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 24;306(2):173–185. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90223-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornabene T. G., Morrison S. J., Kloos W. E. Aliphatic hydrocarbon contents of various members of the family Micrococcaceae. Lipids. 1970 Nov;5(11):929–937. doi: 10.1007/BF02531125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornabene T. G., Ogg J. E. Chromatographic studies of the lipid components of Vibrio fetus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 13;239(2):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornabene T. G., Oró J. 14-C incorporation into the fatty acids and aliphatic hydrocarbons of Sarcina lutea. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):349–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.349-358.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornabene T. G., Peterson S. L. Interaction of lead and bacterial lipids. Appl Microbiol. 1975 May;29(5):680–684. doi: 10.1128/am.29.5.680-684.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L., Ulmer D. D. Biochemical effects of mercury, cadmium, and lead. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41(10):91–128. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.000515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C. SYNTHESIS OF 2-DEMETHYL VITAMIN K2 AND THE CYTOCHROME SYSTEM IN HAEMOPHILUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:299–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.299-305.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]