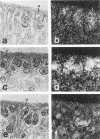
Abstract
Wilms' tumor (WT) is a childhood renal neoplasm with histological features resembling fetal kidney development. Two members of the paired box family of genes, PAX2 and PAX8, are expressed in WT and are potentially involved in its induction. A zinc finger gene, WT1, which is involved in WT induction, encodes a DNA binding protein, and like PAX2 and PAX8 proteins is a transcription factor with an important role in kidney development. We have compared the expression patterns of PAX2, PAX8, and WT1 in fetal kidney and WTs by in situ hybridization. The PAX2, PAX8, and WT1 genes were transcribed in the condensed mesenchyme and early stages of epithelial differentiation in fetal kidney. WT1 gene transcription was observed in the glomeruli of fetal kidney until a later stage in development than PAX genes. In WTs all three genes were expressed in the condensed blastema, but WT1 expression was not detectable in the epithelial structures in two WTs. No evidence of attenuation of PAX gene expression was found in WT. These results suggest that in some WTs the expression of WT1 is attenuated in structures that continued to express PAX genes. It is unlikely that both PAX2 and PAX8 genes would be mutated in WT. However, failure of PAX gene expression to attenuate in WTs may result from mutations involved in the onset of the tumor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Call K. M., Glaser T., Ito C. Y., Buckler A. J., Pelletier J., Haber D. A., Rose E. A., Kral A., Yeger H., Lewis W. H. Isolation and characterization of a zinc finger polypeptide gene at the human chromosome 11 Wilms' tumor locus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):509–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90601-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppes M. J., Campbell C. E., Williams B. R. The role of WT1 in Wilms tumorigenesis. FASEB J. 1993 Jul;7(10):886–895. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.10.8393819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler G. R., Deutsch U., Chowdhury K., Nornes H. O., Gruss P. Pax2, a new murine paired-box-containing gene and its expression in the developing excretory system. Development. 1990 Aug;109(4):787–795. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.4.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler G. R., Douglass E. C. Pax-2 is a DNA-binding protein expressed in embryonic kidney and Wilms tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1179–1183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler G. R., Wilkinson J. E., Rothenpieler U. W., Patterson L. T., Williams-Simons L., Westphal H. Deregulation of Pax-2 expression in transgenic mice generates severe kidney abnormalities. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):65–67. doi: 10.1038/362065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles M. R., Wallis L. J., Fidler A. E., Spurr N. K., Goodfellow P. J., Reeve A. E. Expression of the PAX2 gene in human fetal kidney and Wilms' tumor. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 May;3(5):279–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessler M., Poustka A., Cavenee W., Neve R. L., Orkin S. H., Bruns G. A. Homozygous deletion in Wilms tumours of a zinc-finger gene identified by chromosome jumping. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):774–778. doi: 10.1038/343774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A., Campbell C. E., Bonetta L., McAndrews-Hill M. S., Chilton-MacNeill S., Coppes M. J., Law D. J., Feinberg A. P., Yeger H., Williams B. R. Tissue, developmental, and tumor-specific expression of divergent transcripts in Wilms tumor. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):991–994. doi: 10.1126/science.2173145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreidberg J. A., Sariola H., Loring J. M., Maeda M., Pelletier J., Housman D., Jaenisch R. WT-1 is required for early kidney development. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):679–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90515-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden S. L., Cook D. M., Morris J. F., Gashler A., Sukhatme V. P., Rauscher F. J., 3rd Transcriptional repression mediated by the WT1 Wilms tumor gene product. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1550–1553. doi: 10.1126/science.1654597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poleev A., Fickenscher H., Mundlos S., Winterpacht A., Zabel B., Fidler A., Gruss P., Plachov D. PAX8, a human paired box gene: isolation and expression in developing thyroid, kidney and Wilms' tumors. Development. 1992 Nov;116(3):611–623. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.3.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard-Jones K., Fleming S., Davidson D., Bickmore W., Porteous D., Gosden C., Bard J., Buckler A., Pelletier J., Housman D. The candidate Wilms' tumour gene is involved in genitourinary development. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):194–197. doi: 10.1038/346194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Morris J. F., Tournay O. E., Cook D. M., Curran T. Binding of the Wilms' tumor locus zinc finger protein to the EGR-1 consensus sequence. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1259–1262. doi: 10.1126/science.2244209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenpieler U. W., Dressler G. R. Pax-2 is required for mesenchyme-to-epithelium conversion during kidney development. Development. 1993 Nov;119(3):711–720. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.3.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagge E. P., Hanson P., Re G. G., Othersen H. B., Jr, Smith C. D., Garvin A. J. Paired box gene expression in Wilms' tumor. J Pediatr Surg. 1994 Feb;29(2):134–141. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(94)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman J., Harris E., Desplan C. The paired box encodes a second DNA-binding domain in the paired homeo domain protein. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):594–604. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]