Abstract
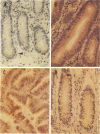
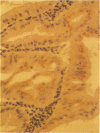
We report overexpression of the proto-oncogene bcl-2 in gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma and its precursor lesions. The bcl-2 proto-oncogene is centrally involved in the oncogenesis of human follicular lymphoma via a chromosomal translocation t(14;18)(q32;q21) and is also expressed in the epithelial regenerative compartment or the basal crypts of the normal colon and small intestine. We describe an immunohistochemical analysis of fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue using both a polyclonal rabbit and a monoclonal mouse antibody to the Bcl-2 protein. In addition to confirming bcl-2 expression in normal colonic and small intestinal crypts, we also observed expression in the gastric epithelial regenerative compartment, the mucous neck region. No increased expression was found in nonneoplastic or inflammatory gastrointestinal conditions, including ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, or inflammatory or hamartomatous polyps. Increased bcl-2 expression, however, was present in hyperplastic colonic polyps and in the majority of dysplastic lesions, from the earliest precursors through large adenomas, high grade flat dysplasia, and adenocarcinoma, all in comparison with adjacent internal control normal epithelium. Increased expression was present in dysplastic glandular lesions from all gastrointestinal sites, including colon, small bowel, and stomach. Furthermore, bcl-2 expression was frequently abnormal in nondysplastic epithelium surrounding dysplastic lesions, suggesting that altered expression occurred before the development of morphological dysplasia. Specifically, directly contiguous morphologically nondysplastic epithelium often showed abnormal bcl-2 expression throughout the full length of the crypt-villus axis. This expression pattern gradually diminished to involve only the crypt base (the normal pattern of expression), proceeding away from malignant or dysplastic lesions. Abnormal bcl-2 immunoreactivity in 1), the earliest precursor dysplastic lesions and its persistence throughout neoplastic progression and 2), contiguous morphologically unaltered nondysplastic epithelium suggests that bcl-2 alterations occur early during the morphological and molecular sequence of events leading to gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasia.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark W. H. Tumour progression and the nature of cancer. Br J Cancer. 1991 Oct;64(4):631–644. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombel M., Symmans F., Gil S., O'Toole K. M., Chopin D., Benson M., Olsson C. A., Korsmeyer S., Buttyan R. Detection of the apoptosis-suppressing oncoprotein bc1-2 in hormone-refractory human prostate cancers. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):390–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOULDS L. The natural history of cancer. J Chronic Dis. 1958 Jul;8(1):2–37. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(58)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenoglio C. M., Lane N. The anatomical precursor of colorectal carcinoma. Cancer. 1974 Sep;34(3):suppl–suppl:823. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197409)34:3+<819::aid-cncr2820340706>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R. L., Coltrera M. D., Gown A. M. Analysis of proliferative grade using anti-PCNA/cyclin monoclonal antibodies in fixed, embedded tissues. Comparison with flow cytometric analysis. Am J Pathol. 1989 Apr;134(4):733–739. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauwerky C. E., Hoxie J., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Pre-B-cell leukemia with a t(8; 14) and a t(14; 18) translocation is preceded by follicular lymphoma. Oncogene. 1988 May;2(5):431–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D. M., Zutter M., Hickey W., Nahm M., Korsmeyer S. J. BCL2 protein is topographically restricted in tissues characterized by apoptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6961–6965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D., Nuñez G., Milliman C., Schreiber R. D., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):334–336. doi: 10.1038/348334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsumata M., Siegel R. M., Louie D. C., Miyashita T., Tsujimoto Y., Nowell P. C., Greene M. I., Reed J. C. Differential effects of Bcl-2 on T and B cells in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11376–11380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 initiates a new category of oncogenes: regulators of cell death. Blood. 1992 Aug 15;80(4):879–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajewski S., Tanaka S., Takayama S., Schibler M. J., Fenton W., Reed J. C. Investigation of the subcellular distribution of the bcl-2 oncoprotein: residence in the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, and outer mitochondrial membranes. Cancer Res. 1993 Oct 1;53(19):4701–4714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBrun D. P., Warnke R. A., Cleary M. L. Expression of bcl-2 in fetal tissues suggests a role in morphogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1993 Mar;142(3):743–753. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louie D. C., Kant J. A., Brooks J. J., Reed J. C. Absence of t(14;18) major and minor breakpoints and of Bcl-2 protein overproduction in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1991 Dec;139(6):1231–1237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Q. L., Elia G., Lucas S., Thomas J. A. Bcl-2 proto-oncogene expression in Epstein-Barr-virus-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1993 Jan 2;53(1):29–35. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910530107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Q. L., Poulsom R., Wong L., Hanby A. M. Bcl-2 expression in adult and embryonic non-haematopoietic tissues. J Pathol. 1993 Apr;169(4):431–437. doi: 10.1002/path.1711690408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Harte P., Deasy J., Ross D., Lahey S., Steele G., Jr Evidence for an adenoma-carcinoma sequence in dimethylhydrazine-induced neoplasms of rat intestinal epithelium. Am J Pathol. 1983 Feb;110(2):230–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Deane N., Platt F. M., Nunez G., Jaeger U., McKearn J. P., Korsmeyer S. J. bcl-2-immunoglobulin transgenic mice demonstrate extended B cell survival and follicular lymphoproliferation. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Korsmeyer S. J. Progression from lymphoid hyperplasia to high-grade malignant lymphoma in mice transgenic for the t(14; 18). Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):254–256. doi: 10.1038/349254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Nunez G., Platt F. M., Hockenberry D., London L., McKearn J. P., Korsmeyer S. J. Deregulated Bcl-2-immunoglobulin transgene expands a resting but responsive immunoglobulin M and D-expressing B-cell population. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1901–1907. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Troncoso P., Brisbay S. M., Logothetis C., Chung L. W., Hsieh J. T., Tu S. M., Campbell M. L. Expression of the protooncogene bcl-2 in the prostate and its association with emergence of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6940–6944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto T., Bussey H. J., Morson B. C. The evolution of cancer of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1975 Dec;36(6):2251–2270. doi: 10.1002/cncr.2820360944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell P. C. The clonal evolution of tumor cell populations. Science. 1976 Oct 1;194(4260):23–28. doi: 10.1126/science.959840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C. Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Meister L., Tanaka S., Cuddy M., Yum S., Geyer C., Pleasure D. Differential expression of bcl2 protooncogene in neuroblastoma and other human tumor cell lines of neural origin. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 15;51(24):6529–6538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. E., Haggitt R. C., Burmer G. C., Brentnall T. A., Stevens A. C., Levine D. S., Dean P. J., Kimmey M., Perera D. R., Rabinovitch P. S. DNA aneuploidy in colonic biopsies predicts future development of dysplasia in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1992 Nov;103(5):1611–1620. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. Analysis of the structure, transcripts, and protein products of bcl-2, the gene involved in human follicular lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5214–5218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L. Toward an understanding of the molecular mechanisms of physiological cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):786–789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]