Abstract
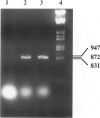
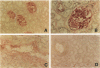
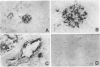
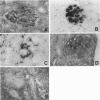
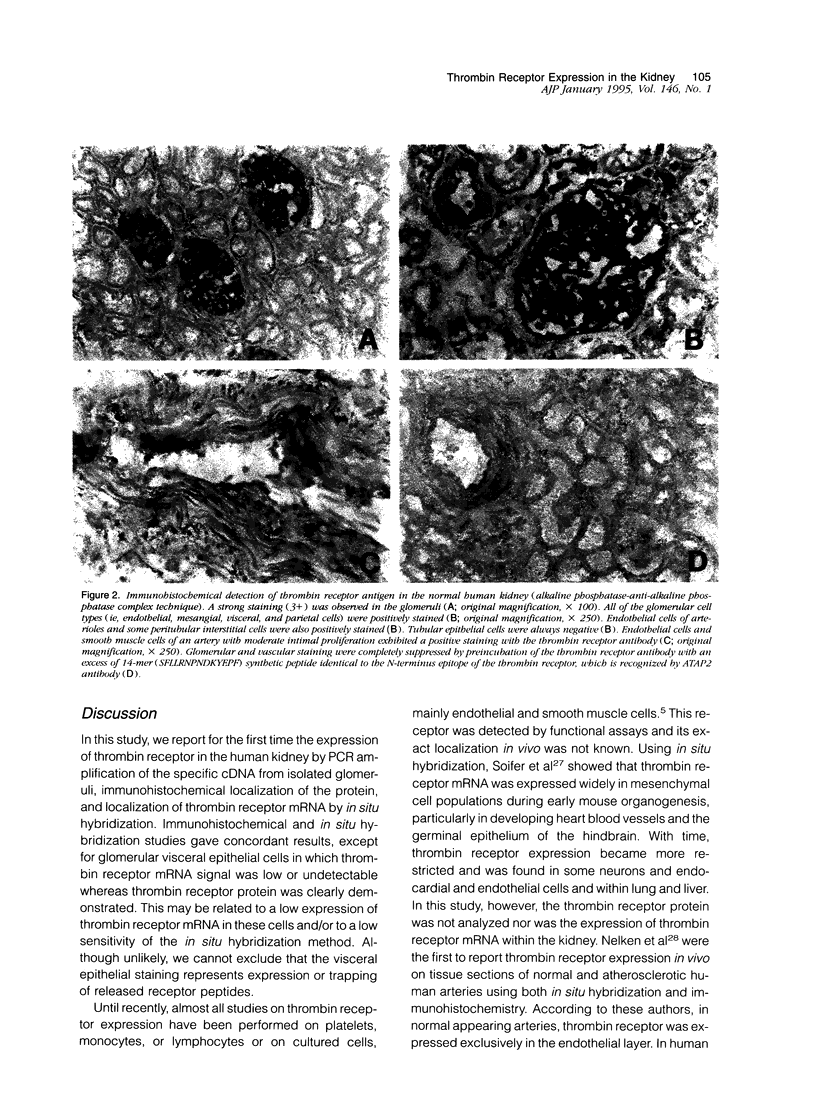
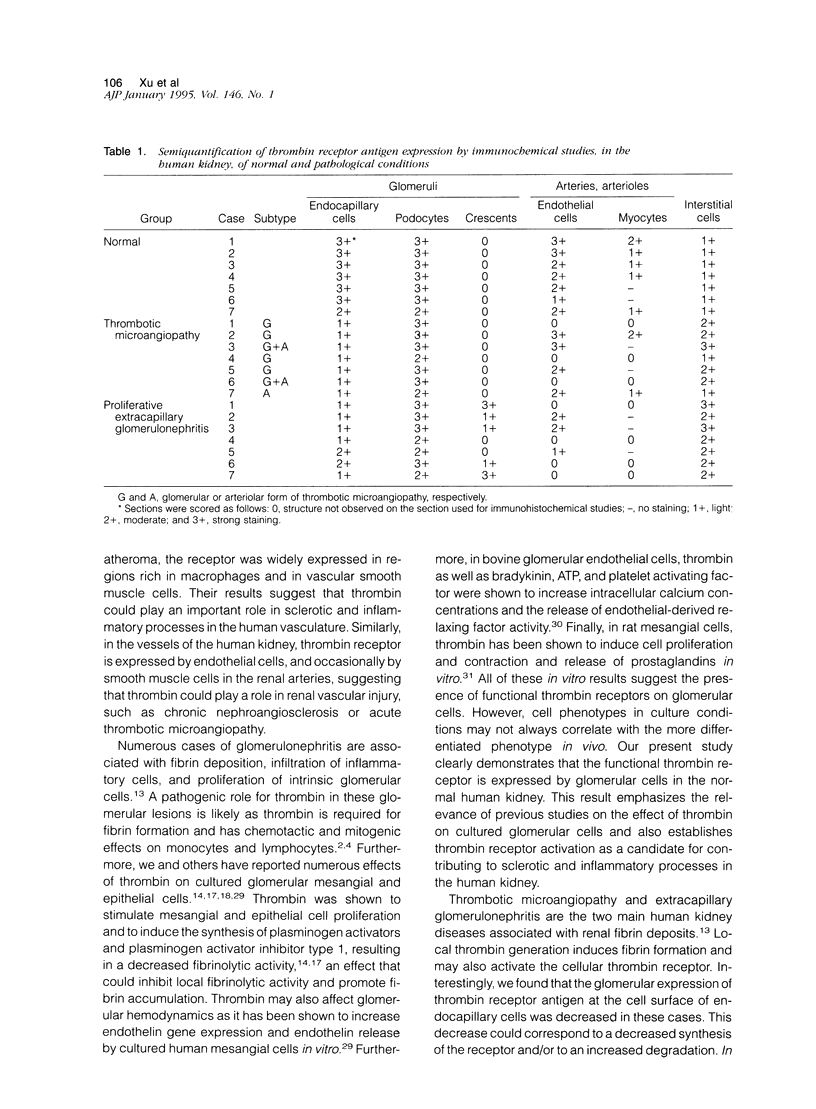
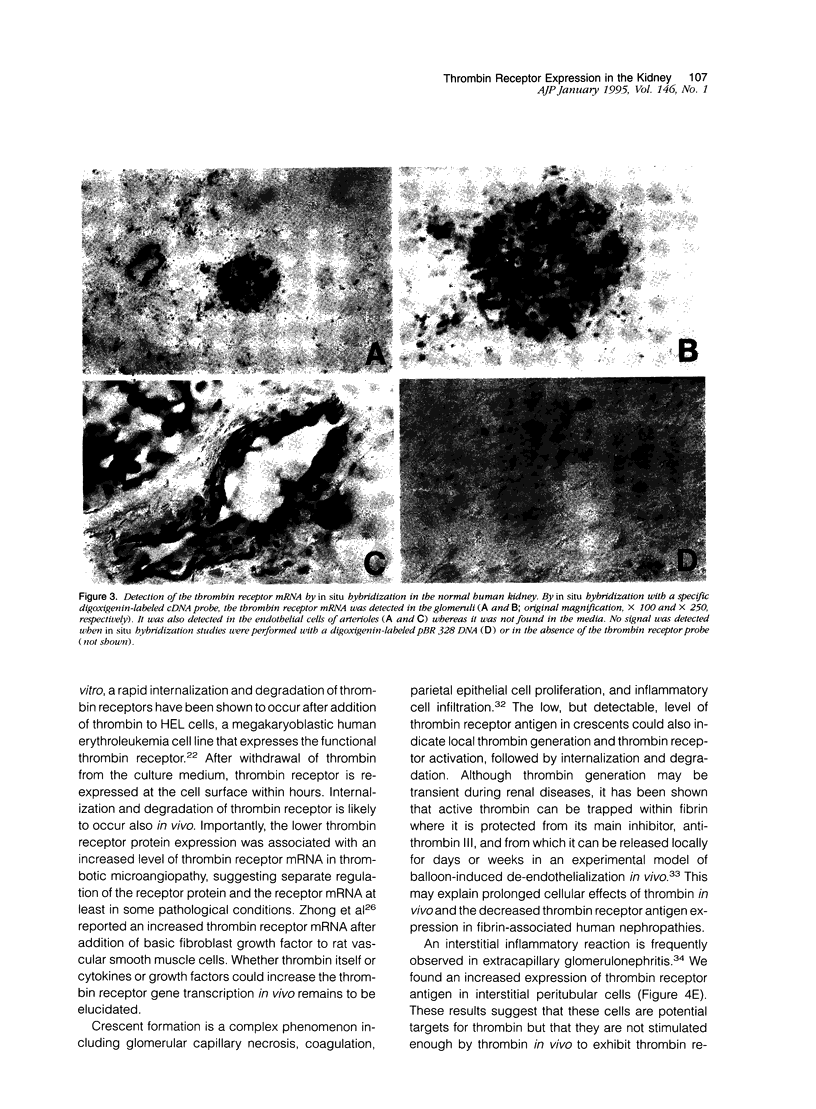
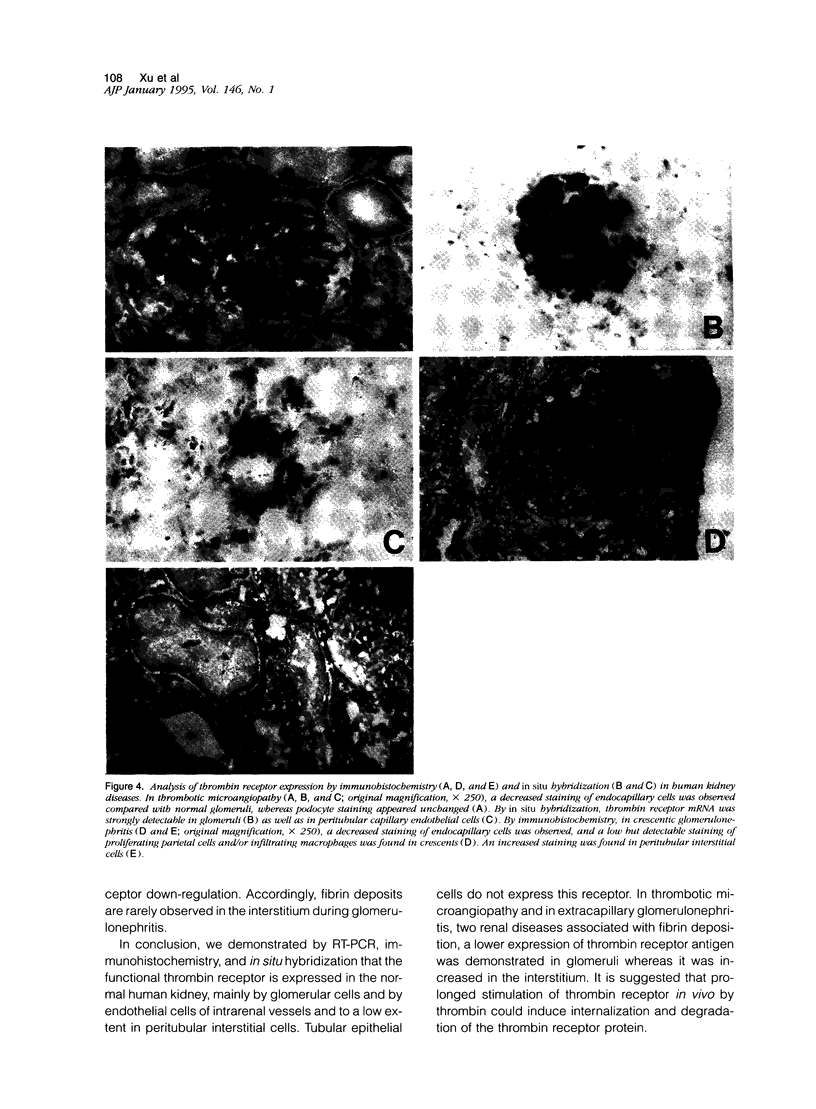
Thrombin exerts procoagulant effects and has also many cellular effects mediated by cell surface receptors. A functional thrombin receptor from human platelets has been cloned and sequenced. In the present study, by reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction, using specific primers designed from the thrombin receptor cDNA sequence, we show that the mRNA encoding for this receptor can be amplified from freshly isolated human glomeruli obtained by microdissection of normal kidney cortex. By immunohistochemistry using a specific monoclonal antibody, ATAP2, directed against the extracellular N-terminus of this receptor, we find that this functional thrombin receptor is constitutively expressed in the normal human kidney. The three glomerular cell types, endothelial, mesangial, and epithelial cells, were positively stained, as were the endothelial cells of renal arteries, arterioles, venules, and peritubular capillaries. Occasionally, interstitial cells and smooth muscle cells in the media of renal arteries were also stained. Proximal and distal tubular cells were not stained. By in situ hybridization, using a digoxigenin-labeled cDNA probe specific for thrombin receptor, the thrombin receptor mRNA was found to have the same distribution as the thrombin receptor protein detected by immunohistochemistry. A lighter staining of glomerular endocapillary cells was observed in cases of thrombotic microangiopathy and extracapillary glomerulonephritis, two renal diseases associated with in situ thrombin generation and fibrin formation. In one case of thrombotic microangiopathy, we observed an increase in thrombin receptor mRNA. This suggests that thrombin receptor protein is not always correlated with thrombin receptor mRNA level. Internalization and degradation of thrombin receptor protein have been demonstrated in vitro and could also occur after activation in vivo. This is the first demonstration of the constitutive expression of the functional thrombin receptor in the human kidney. These results suggest that thrombin may exert glomerular and vascular effects within the kidney in normal and in pathological conditions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrightson C. R., Nambi P., Zabko-Potapovich B., Dytko G., Groom T. Effect of thrombin on proliferation, contraction and prostaglandin production of rat glomerular mesangial cells in culture. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Oct;263(1):404–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit R., Kahn A., Wilner G. D., Fenton J. W., 2nd Monocyte chemotaxis: stimulation by specific exosite region in thrombin. Science. 1983 May 13;220(4598):728–731. doi: 10.1126/science.6836310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland Y. S., Critchlow M. A., Ashhurst D. E. Digoxigenin as a probe label for in situ hybridization on skeletal tissues. Histochem J. 1991 Sep;23(9):415–418. doi: 10.1007/BF01042298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Vassallo R. R., Jr, Belmonte E., Ahuja M., Cichowski K., Hoxie J. A. Structure and function of the human platelet thrombin receptor. Studies using monoclonal antibodies directed against a defined domain within the receptor N terminus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13795–13798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B., Buchanan J. M. Mitogenic activity of blood components. I. Thrombin and prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):131–135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I. Characterization of a functional thrombin receptor. Issues and opportunities. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):351–355. doi: 10.1172/JCI115592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. G., Lüscher E. F. Actions of thrombin and other coagulant and proteolytic enzymes on blood platelets. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):857–858. doi: 10.1038/216857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelehrter T. D., Sznycer-Laszuk R. Thrombin induction of plasminogen activator-inhibitor in cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):165–169. doi: 10.1172/JCI112271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton M. W., Moar S. L., Richardson M. Deendothelialization in vivo initiates a thrombogenic reaction at the rabbit aorta surface. Correlation of uptake of fibrinogen and antithrombin III with thrombin generation by the exposed subendothelium. Am J Pathol. 1989 Sep;135(3):499–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He C. J., Peraldi M. N., Adida C., Rebibou J. M., Meulders Q., Sraer J. D., Rondeau E. Thrombin signal transduction mechanisms in human glomerular epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Mar;150(3):475–483. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He C. J., Rondeau E., Medcalf R. L., Lacave R., Schleuning W. D., Sraer J. D. Thrombin increases proliferation and decreases fibrinolytic activity of kidney glomerular epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Jan;146(1):131–140. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041460117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzman L. B., Wiggins R. C. Consequences of glomerular injury. Glomerular crescent formation. Semin Nephrol. 1991 May;11(3):346–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins W. E., Fujii S., Sobel B. E. Synergistic induction of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 in HEP G2 cells by thrombin and transforming growth factor-beta. Blood. 1992 Jan 1;79(1):75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoxie J. A., Ahuja M., Belmonte E., Pizarro S., Parton R., Brass L. F. Internalization and recycling of activated thrombin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13756–13763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggiano N., Larocca L. M., Piantelli M., Ranelletti F. O., Lauriola L., Ricci R., Capelli A. Detection of mRNA and hnRNA using a digoxigenin labelled cDNA probe by in situ hybridization on frozen tissue sections. Histochem J. 1991 Feb;23(2):69–74. doi: 10.1007/BF01047110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden P. A., Brock T. A., Ballermann B. J. Glomerular endothelial cells respond to calcium-mobilizing agonists with release of EDRF. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1295–F1303. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara C. A., Sarembock I. J., Gimple L. W., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Coughlin S. R., Owens G. K. Thrombin stimulates proliferation of cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells by a proteolytically activated receptor. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):94–98. doi: 10.1172/JCI116206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelken N. A., Soifer S. J., O'Keefe J., Vu T. K., Charo I. F., Coughlin S. R. Thrombin receptor expression in normal and atherosclerotic human arteries. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1614–1621. doi: 10.1172/JCI116031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peten E. P., Striker L. J., Carome M. A., Elliott S. J., Yang C. W., Striker G. E. The contribution of increased collagen synthesis to human glomerulosclerosis: a quantitative analysis of alpha 2IV collagen mRNA expression by competitive polymerase chain reaction. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1571–1576. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M. Human endothelial cells in culture produce platelet-activating factor (1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) when stimulated with thrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3534–3538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough R. M., Naughton M. A., Teng W., Hung D. T., Rose J., Vu T. K., Wheaton V. I., Turck C. W., Coughlin S. R. Tethered ligand agonist peptides. Structural requirements for thrombin receptor activation reveal mechanism of proteolytic unmasking of agonist function. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13146–13149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soifer S. J., Peters K. G., O'Keefe J., Coughlin S. R. Disparate temporal expression of the prothrombin and thrombin receptor genes during mouse development. Am J Pathol. 1994 Jan;144(1):60–69. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troyer D., Padilla R., Smith T., Kreisberg J., Glass W., 2nd Stimulation of the thrombin receptor of human glomerular mesangial cells by Ser-Phe-Leu-Leu-Arg-Asn-Pro-Asn-Asp-Lys-Tyr-Glu-Pro-Phe peptide. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20126–20131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villamediana L. M., Rondeau E., He C. J., Medcalf R. L., Peraldi M. N., Lacave R., Delarue F., Sraer J. D. Thrombin regulates components of the fibrinolytic system in human mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1990 Nov;38(5):956–961. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I., Coughlin S. R. Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1057–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90261-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Wheaton V. I., Hung D. T., Charo I., Coughlin S. R. Domains specifying thrombin-receptor interaction. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):674–677. doi: 10.1038/353674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler B. B., Ley C. W., Jaffe E. A. Stimulation of endothelial cell prostacyclin production by thrombin, trypsin, and the ionophore A 23187. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):923–930. doi: 10.1172/JCI109220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee J., Kuncio G. S., Neilson E. G. Tubulointerstitial injury following glomerulonephritis. Semin Nephrol. 1991 May;11(3):361–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharias U., He C. J., Nguyen G., Sraer J. D., Rondeau E. Long-term effects of thrombin require sustained activation of the functional thrombin receptor. FEBS Lett. 1993 Nov 15;334(2):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81716-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong C., Hayzer D. J., Corson M. A., Runge M. S. Molecular cloning of the rat vascular smooth muscle thrombin receptor. Evidence for in vitro regulation by basic fibroblast growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16975–16979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoja C., Orisio S., Perico N., Benigni A., Morigi M., Benatti L., Rambaldi A., Remuzzi G. Constitutive expression of endothelin gene in cultured human mesangial cells and its modulation by transforming growth factor-beta, thrombin, and a thromboxane A2 analogue. Lab Invest. 1991 Jan;64(1):16–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]