Abstract
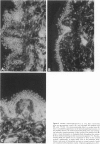
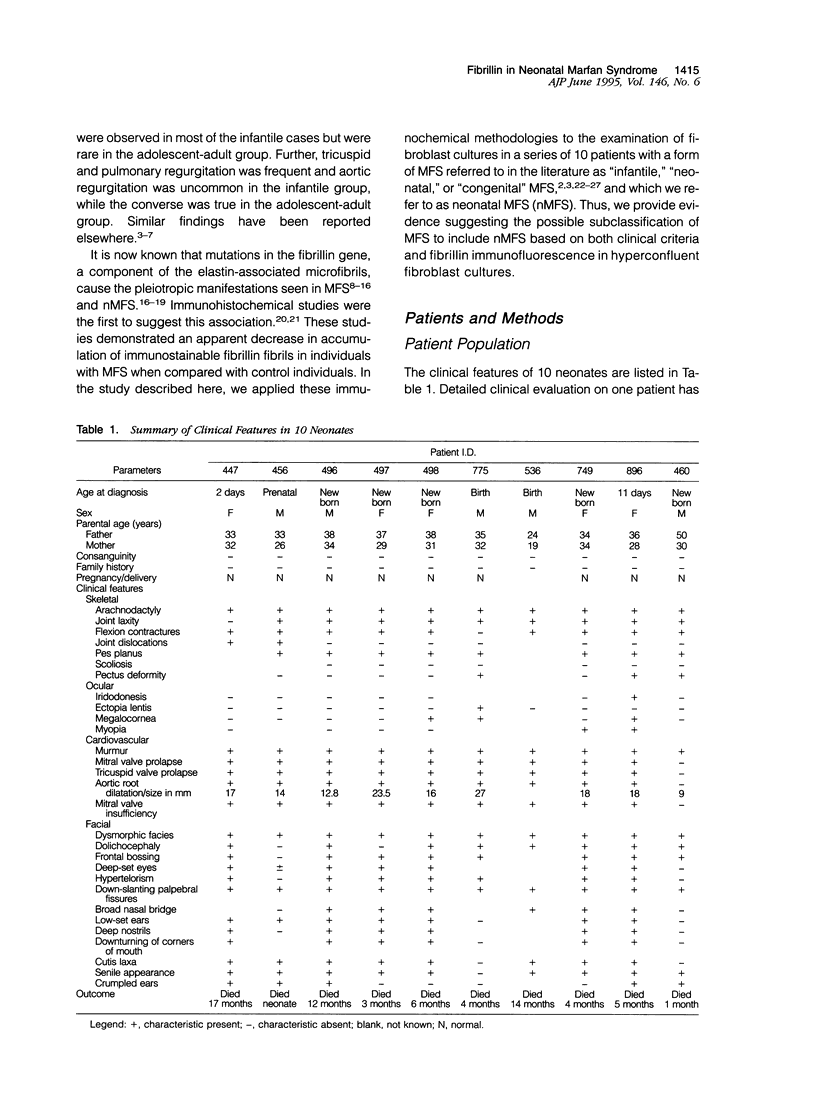
The Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a connective tissue disorder manifested by variable and pleiotropic features in the skeletal, ocular, and cardiovascular systems. The average life span in MFS is about 35 years. A group with much more severe cardiovascular disease and a mean life span of approximately I year also exists. We refer to this latter group as “neonatal Marfan syndrome” (nMFS). Fibrillin defects are now known to be the cause of MFS and nMFS. Immunofluorescence studies were the first to demonstrate this association. Here we describe immunofluorescence studies in a series of 10 neonates and summarize their salient clinical features. In vitro accumulation of fibrillin reactive fibers was assayed using monoclonal antibodies to fibrillin in hyperconfluent fibroblast cultures. As was previously observed in MFS, fibroblast cultures from nMFS patients showed an apparent decrease in accumulation of immunostainable fibrillin. Significantly, however, the morphology of the immunostained fibrils in the nMFS cultures were abnormal and differed not only from control cultures, but also from those seen in cultures of MFS fibroblasts. The nMFS fibrils appeared short, fragmented, and frayed, characteristics that are not seen in MFS. Both the clinical and fibrillin morphology data provide evidence to suggest a useful subclassification of nMFS in the spectrum of MFS.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beals R. K., Hecht F. Congenital contractural arachnodactyly. A heritable disorder of connective tissue. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971 Jul;53(5):987–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buntinx I. M., Willems P. J., Spitaels S. E., Van Reempst P. J., De Paepe A. M., Dumon J. E. Neonatal Marfan syndrome with congenital arachnodactyly, flexion contractures, and severe cardiac valve insufficiency. J Med Genet. 1991 Apr;28(4):267–273. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.4.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Cutting G. R., Pyeritz R. E., Maslen C. L., Sakai L. Y., Corson G. M., Puffenberger E. G., Hamosh A., Nanthakumar E. J., Curristin S. M. Marfan syndrome caused by a recurrent de novo missense mutation in the fibrillin gene. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):337–339. doi: 10.1038/352337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., McIntosh I., Sakai L. Y., Corson G. M., Chalberg S. C., Pyeritz R. E., Francomano C. A. Four novel FBN1 mutations: significance for mutant transcript level and EGF-like domain calcium binding in the pathogenesis of Marfan syndrome. Genomics. 1993 Aug;17(2):468–475. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Pyeritz R. E., Puffenberger E. G., Kendzior R. J., Jr, Corson G. M., Maslen C. L., Sakai L. Y., Francomano C. A., Cutting G. R. Marfan phenotype variability in a family segregating a missense mutation in the epidermal growth factor-like motif of the fibrillin gene. J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1674–1680. doi: 10.1172/JCI115766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Saraiva J. M., Pyeritz R. E., Cutting G. R., Francomano C. A. Clustering of fibrillin (FBN1) missense mutations in Marfan syndrome patients at cysteine residues in EGF-like domains. Hum Mutat. 1992;1(5):366–374. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380010504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Valle D., Francomano C. A., Kendzior R. J., Jr, Pyeritz R. E., Cutting G. R. The skipping of constitutive exons in vivo induced by nonsense mutations. Science. 1993 Jan 29;259(5095):680–683. doi: 10.1126/science.8430317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. H. Congenital Marfan syndrome. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(2):329–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geva T., Sanders S. P., Diogenes M. S., Rockenmacher S., Van Praagh R. Two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiographic and pathologic characteristics of the infantile Marfan syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1990 May 15;65(18):1230–1237. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(90)90979-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey M., Menashe V., Weleber R. G., Koler R. D., Bigley R. H., Lovrien E., Zonana J., Hollister D. W. Cosegregation of elastin-associated microfibrillar abnormalities with the Marfan phenotype in families. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):652–660. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey M., Vandemark N., Wang M., Velinov M., Wargowski D., Tsipouras P., Han J., Becker J., Robertson W., Droste S. Prenatal diagnosis and a donor splice site mutation in fibrillin in a family with Marfan syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Aug;53(2):472–480. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. M., Robinson L. K., Smith L. T., Glass N., Rosenberg H., Duvic M. Severe perinatal Marfan syndrome. Pediatrics. 1989 Jul;84(1):83–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber M. A., Graham T. P., Jr, Engel E., Smith C. Marfan syndrome with contractural arachnodactyly and severe mitral regurgitation in a premature infant. J Pediatr. 1978 Jul;93(1):80–82. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80608-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister D. W., Godfrey M., Sakai L. Y., Pyeritz R. E. Immunohistologic abnormalities of the microfibrillar-fiber system in the Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 19;323(3):152–159. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007193230303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalaguier J., Montoya F., Sarda P., Teot L., Bonnet H. Syndrome de Marfan mortel en période néonatale. J Genet Hum. 1985 Dec;33(5):435–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kainulainen K., Karttunen L., Puhakka L., Sakai L., Peltonen L. Mutations in the fibrillin gene responsible for dominant ectopia lentis and neonatal Marfan syndrome. Nat Genet. 1994 Jan;6(1):64–69. doi: 10.1038/ng0194-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kainulainen K., Sakai L. Y., Child A., Pope F. M., Puhakka L., Ryhänen L., Palotie A., Kaitila I., Peltonen L. Two mutations in Marfan syndrome resulting in truncated fibrillin polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5917–5921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lababidi Z., Monzon C. Early cardiac manifestations of Marfan's syndrome in the newborn. Am Heart J. 1981 Nov;102(5):943–945. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(81)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Godfrey M., Vitale E., Hori H., Mattei M. G., Sarfarazi M., Tsipouras P., Ramirez F., Hollister D. W. Linkage of Marfan syndrome and a phenotypically related disorder to two different fibrillin genes. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):330–334. doi: 10.1038/352330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milewicz D. M., Duvic M. Severe neonatal Marfan syndrome resulting from a de novo 3-bp insertion into the fibrillin gene on chromosome 15. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Mar;54(3):447–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse R. P., Rockenmacher S., Pyeritz R. E., Sanders S. P., Bieber F. R., Lin A., MacLeod P., Hall B., Graham J. M., Jr Diagnosis and management of infantile marfan syndrome. Pediatrics. 1990 Dec;86(6):888–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., D'Alessio M., Ramirez F., Lynch J. R., Sykes B., Pangilinan T., Bonadio J. Genomic organization of the sequence coding for fibrillin, the defective gene product in Marfan syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):961–968. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phornphutkul C., Rosenthal A., Nadas A. S. Cardiac manifestations of Marfan syndrome in infancy and childhood. Circulation. 1973 Mar;47(3):587–596. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.47.3.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulkkinen L., Kainulainen K., Krusius T., Mäkinen P., Schollin J., Gustavsson K. H., Peltonen L. Deficient expression of the gene coding for decorin in a lethal form of Marfan syndrome. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17780–17785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghunath M., Superti-Furga A., Godfrey M., Steinmann B. Decreased extracellular deposition of fibrillin and decorin in neonatal Marfan syndrome fibroblasts. Hum Genet. 1993 Jan;90(5):511–515. doi: 10.1007/BF00217450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankar K. R., Hultgren M. K., Lauer R. M., Diehl A. M. Lethal tricuspid and mitral regurgitation in Marfan's syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1967 Jul;20(1):122–127. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(67)90117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillence D. O., Senn A., Danks D. M. Genetic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet. 1979 Apr;16(2):101–116. doi: 10.1136/jmg.16.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisk H. E., Zahka K. G., Pyeritz R. E. The Marfan syndrome in early childhood: analysis of 15 patients diagnosed at less than 4 years of age. Am J Cardiol. 1983 Aug;52(3):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(83)90138-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Superti-Furga A., Raghunath M., Willems P. J. Deficiencies of fibrillin and decorin in fibroblast cultures of a patient with neonatal Marfan syndrome. J Med Genet. 1992 Dec;29(12):875–878. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.12.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsipouras P., Del Mastro R., Sarfarazi M., Lee B., Vitale E., Child A. H., Godfrey M., Devereux R. B., Hewett D., Steinmann B. Genetic linkage of the Marfan syndrome, ectopia lentis, and congenital contractural arachnodactyly to the fibrillin genes on chromosomes 15 and 5. The International Marfan Syndrome Collaborative Study. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 2;326(14):905–909. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199204023261401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M., Price C., Han J., Cisler J., Imaizumi K., Van Thienen M. N., DePaepe A., Godfrey M. Recurrent mis-splicing of fibrillin exon 32 in two patients with neonatal Marfan syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Apr;4(4):607–613. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.4.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]