Abstract
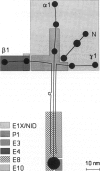
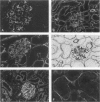
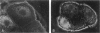
Exposure to mercuric chloride induces the development of a membranous glomerulopathy with high proteinuria in DZB rats, in which immunoglobulin (Ig)G1 and IgG2a bound in the glomeruli were previously found to react with laminin of the EHS tumor and several unidentified glomerular basement membrane components. Monoclonal antibodies were prepared by fusing cervical and mandibular lymph node cells from a HgCl2-treated DZB rat with a nonsecreting mouse myeloma. Monoclonal antibodies were screened for reactivity with collagenase-digested glomerular basement membrane and kidney sections; upon subcloning, eight stable hybridomas were obtained, named MEC1 to MEC8. MEC2 (IgG1, kappa), MEC3 (IgM, kappa), and MEC5 (IgG1, kappa), as well as the polyclonal glomerular eluate, reacted preferentially with the P1 fragment of the laminin-1 (alpha 1 beta 1 gamma 1) isoform. MEC8 (IgM, kappa) reacted with the P1 and the E4 fragment of laminin. Both MEC6 (IgM, kappa) and MEC8 bound to actin and to various other, unidentified cellular antigens, indicating that MEC6 and MEC8 are polyreactive antibodies. MEC7 (IgM, kappa) bound to a cytoskeleton-linked cell membrane antigen, present on various epithelial cells and between heart muscle fibers and associated with small peripheral, intramuscular nerves. Several of the MEC monoclonal antibodies bound in vivo along the glomerular capillary wall. Although discrete electron-dense subepithelial immune aggregates were not detected and proteinuria was not induced, MEC3 localization changed from a continuous pattern into a fine granular pattern along the glomerular basement membrane, and focally along the TBM, upon passive transfer into naive DZB rats. These findings suggest a pathogenetic role for the P1 fragment of laminin either in the induction phase of HgCl2-induced membranous glomerulopathy as an immunogen or in the effector phase as a target antigen.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman L. G., Schneider B. G., Papermaster D. S. Rapid embedding of tissues in Lowicryl K4M for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Nov;32(11):1217–1223. doi: 10.1177/32.11.6436366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aten J., Bosman C. B., Rozing J., Stijnen T., Hoedemaeker P. J., Weening J. J. Mercuric chloride-induced autoimmunity in the brown Norway rat. Cellular kinetics and major histocompatibility complex antigen expression. Am J Pathol. 1988 Oct;133(1):127–138. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aten J., Stet R. J., Wagenaar-Hilbers J. P., Weening J. J., Fleuren G. J., Nieuwenhuis P. Glomerulopathy induced by graft-versus-host reaction in the rat. Requirement of donor CD4+ T lymphocytes and MHC class II incompatibility at the lymphoid compartment. Scand J Immunol. 1992 Jan;35(1):93–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb02838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aten J., Veninga A., Bruijn J. A., Prins F. A., de Heer E., Weening J. J. Antigenic specificities of glomerular-bound autoantibodies in membranous glomerulopathy induced by mercuric chloride. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Apr;63(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(92)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aten J., Veninga A., De Heer E., Rozing J., Nieuwenhuis P., Hoedemaeker P. J., Weening J. J. Susceptibility to the induction of either autoimmunity or immunosuppression by mercuric chloride is related to the major histocompatibility complex class II haplotype. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Mar;21(3):611–616. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck K., Hunter I., Engel J. Structure and function of laminin: anatomy of a multidomain glycoprotein. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):148–160. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.2.2404817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruijn J. A., Hoedemaeker P. J., Fleuren G. J. Pathogenesis of anti-basement membrane glomerulopathy and immune-complex glomerulonephritis: dichotomy dissolved. Lab Invest. 1989 Nov;61(5):480–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgeson R. E., Chiquet M., Deutzmann R., Ekblom P., Engel J., Kleinman H., Martin G. R., Meneguzzi G., Paulsson M., Sanes J. A new nomenclature for the laminins. Matrix Biol. 1994 Apr;14(3):209–211. doi: 10.1016/0945-053x(94)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattell V., Cook H. T. Nitric oxide: role in the physiology and pathology of the glomerulus. Exp Nephrol. 1993 Sep-Oct;1(5):265–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coers W., Huitema S., Smeenk R. J., Salant D. J., Grond J., Weening J. J. Quantification of glomerular epithelial cell adhesion by using anti-DNA antibodies in ELISA. Hybridoma. 1992 Aug;11(4):529–537. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1992.11.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelese-ten Velde I., Prins F. A. New sensitive light microscopical detection of colloidal gold on ultrathin sections by reflection contrast microscopy. Combination of reflection contrast and electron microscopy in post-embedding immunogold histochemistry. Histochemistry. 1990;94(1):61–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00266791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delwel G. O., Hogervorst F., Kuikman I., Paulsson M., Timpl R., Sonnenberg A. Expression and function of the cytoplasmic variants of the integrin alpha 6 subunit in transfected K562 cells. Activation-dependent adhesion and interaction with isoforms of laminin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25865–25875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delwel G. O., de Melker A. A., Hogervorst F., Jaspars L. H., Fles D. L., Kuikman I., Lindblom A., Paulsson M., Timpl R., Sonnenberg A. Distinct and overlapping ligand specificities of the alpha 3A beta 1 and alpha 6A beta 1 integrins: recognition of laminin isoforms. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Feb;5(2):203–215. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom M., Klein G., Mugrauer G., Fecker L., Deutzmann R., Timpl R., Ekblom P. Transient and locally restricted expression of laminin A chain mRNA by developing epithelial cells during kidney organogenesis. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90748-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Earwicker D., Haaparanta T., Ruoslahti E., Sanes J. R. Distribution and isolation of four laminin variants; tissue restricted distribution of heterotrimers assembled from five different subunits. Cell Regul. 1990 Sep;1(10):731–740. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.10.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Krusius T., Wewer U., Ruoslahti E. Laminin from rat yolk sac tumor: isolation, partial characterization, and comparison with mouse laminin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Apr 15;222(2):649–656. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90562-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. W., Mayer U., Nischt R., Aumailley M., Reinhardt D., Wiedemann H., Mann K., Timpl R., Krieg T., Engel J. Recombinant nidogen consists of three globular domains and mediates binding of laminin to collagen type IV. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3137–3146. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04875.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukatsu A., Brentjens J. R., Killen P. D., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R., Andres G. A. Studies on the formation of glomerular immune deposits in brown Norway rats injected with mercuric chloride. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Oct;45(1):35–47. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehlsen K. R., Sriramarao P., Furcht L. T., Skubitz A. P. A synthetic peptide derived from the carboxy terminus of the laminin A chain represents a binding site for the alpha 3 beta 1 integrin. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(2):449–459. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. L., Aumailley M., von der Mark H. Multiple cell surface receptors for the short arms of laminin: alpha 1 beta 1 integrin and RGD-dependent proteins mediate cell attachment only to domains III in murine tumor laminin. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):931–941. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guéry J. C., Druet E., Glotz D., Hirsch F., Mandet C., De Heer E., Druet P. Specificity and cross-reactive idiotypes of anti-glomerular basement membrane autoantibodies in HgCl2-induced autoimmune glomerulonephritis. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jan;20(1):93–100. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall D. E., Reichardt L. F., Crowley E., Holley B., Moezzi H., Sonnenberg A., Damsky C. H. The alpha 1/beta 1 and alpha 6/beta 1 integrin heterodimers mediate cell attachment to distinct sites on laminin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2175–2184. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper P. A., Robinson J. M., Hoover R. L., Wright T. C., Karnovsky M. J. Improved methods for culturing rat glomerular cells. Kidney Int. 1984 Dec;26(6):875–880. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch F., Couderc J., Sapin C., Fournie G., Druet P. Polyclonal effect of HgCl2 in the rat, its possible role in an experimental autoimmune disease. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jul;12(7):620–625. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch F., Druet E., Vendeville B., Cormont F., Bazin H., Druet P. Production of monoclonal anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies during autoimmune glomerulonephritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Dec;33(3):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90313-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst F., Admiraal L. G., Niessen C., Kuikman I., Janssen H., Daams H., Sonnenberg A. Biochemical characterization and tissue distribution of the A and B variants of the integrin alpha 6 subunit. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):179–191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. D., Shah V., Merlie J. P., Sanes J. R. A laminin-like adhesive protein concentrated in the synaptic cleft of the neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):229–234. doi: 10.1038/338229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa I., Kiyama S., Yoshioka T. Renal antioxidant enzymes: their regulation and function. Kidney Int. 1994 Jan;45(1):1–9. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallunki P., Sainio K., Eddy R., Byers M., Kallunki T., Sariola H., Beck K., Hirvonen H., Shows T. B., Tryggvason K. A truncated laminin chain homologous to the B2 chain: structure, spatial expression, and chromosomal assignment. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):679–693. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Miettinen A., Farquhar M. G. Initial events in the formation of immune deposits in passive Heymann nephritis. gp330-anti-gp330 immune complexes form in epithelial coated pits and rapidly become attached to the glomerular basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):109–128. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen M., Ylänne J., Laitinen L., Virtanen I. The alpha 1-alpha 6 subunits of integrins are characteristically expressed in distinct segments of developing and adult human nephron. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1245–1254. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblom A., Marsh T., Fauser C., Engel J., Paulsson M. Characterization of native laminin from bovine kidney and comparison with other laminin variants. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jan 15;219(1-2):383–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb19950.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K., Deutzmann R., Timpl R. Characterization of proteolytic fragments of the laminin-nidogen complex and their activity in ligand-binding assays. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Dec 1;178(1):71–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinkovich M. P., Lunstrum G. P., Keene D. R., Burgeson R. E. The dermal-epidermal junction of human skin contains a novel laminin variant. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):695–703. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer U., Nischt R., Pöschl E., Mann K., Fukuda K., Gerl M., Yamada Y., Timpl R. A single EGF-like motif of laminin is responsible for high affinity nidogen binding. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1879–1885. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin R. W., Gehron P., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R., Valentine T., Swarm R. A murine tumor producing a matrix of basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):204–220. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotou G., End P., Aumailley M., Timpl R., Engel J. Domains of laminin with growth-factor activity. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90987-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Saladin K., Engvall E. Structure of laminin variants. The 300-kDa chains of murine and bovine heart laminin are related to the human placenta merosin heavy chain and replace the a chain in some laminin variants. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17545–17551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier L., Pasquier R., Rossert J., Vial M. C., Mandet C., Druet P. Autoreactive T cells in mercury-induced autoimmunity. Ability to induce the autoimmune disease. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):750–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigg R. J., Cybulsky A. V., Jacobs J. B., Salant D. J. Anti-Fx1A produces complement-dependent cytotoxicity of glomerular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 1988 Jul;34(1):43–52. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco P., Melcion C., Geniteau M., Ronco E., Reininger L., Galceran M., Verroust P. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against rat brush border antigens of the proximal convoluted tubule. Immunology. 1984 Sep;53(1):87–95. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Engvall E., Butkowski R., Hunter D. D. Molecular heterogeneity of basal laminae: isoforms of laminin and collagen IV at the neuromuscular junction and elsewhere. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1685–1699. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapin C., Druet E., Druet P. Induction of anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies in the Brown-Norway rat by mercuric chloride. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Apr;28(1):173–179. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Kleinman H. K., Huber H., Deutzmann R., Yamada Y. Laminin, a multidomain protein. The A chain has a unique globular domain and homology with the basement membrane proteoglycan and the laminin B chains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16536–16544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena R., Bygren P., Cederholm B., Wieslander J. Circulating anti-entactin antibodies in patients with glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1991 May;39(5):996–1004. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon J., Morrison S. L., Kabat E. A. Detection of specific hybridoma clones by replica immunoadsorption of their secreted antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1420–1424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M., Mascelli M., Shan H., Radic M. Z., Pisetsky D., Marshak-Rothstein A., Weigert M. Anti-DNA antibodies from autoimmune mice arise by clonal expansion and somatic mutation. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):265–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. E., McDonald J. A. Extracellular matrix receptors in the kidney cortex. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 2):F783–F792. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.5.F783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Linders C. J., Modderman P. W., Damsky C. H., Aumailley M., Timpl R. Integrin recognition of different cell-binding fragments of laminin (P1, E3, E8) and evidence that alpha 6 beta 1 but not alpha 6 beta 4 functions as a major receptor for fragment E8. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2145–2155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura R. N., Cooper H. M., Collo G., Quaranta V. Cell type-specific integrin variants with alternative alpha chain cytoplasmic domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10183–10187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ternynck T., Avrameas S. Murine natural monoclonal autoantibodies: a study of their polyspecificities and their affinities. Immunol Rev. 1986 Dec;94:99–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R. Structure and biological activity of basement membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 1;180(3):487–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolthuis A., Boes A., Rodemann H. P., Grond J. Vasoactive agents affect growth and protein synthesis of cultured rat mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1992 Jan;41(1):124–131. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Born J., van den Heuvel L. P., Bakker M. A., Veerkamp J. H., Assmann K. J., Berden J. H. A monoclonal antibody against GBM heparan sulfate induces an acute selective proteinuria in rats. Kidney Int. 1992 Jan;41(1):115–123. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]