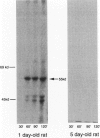
Abstract
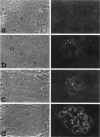
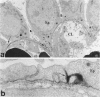
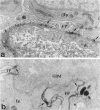
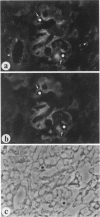
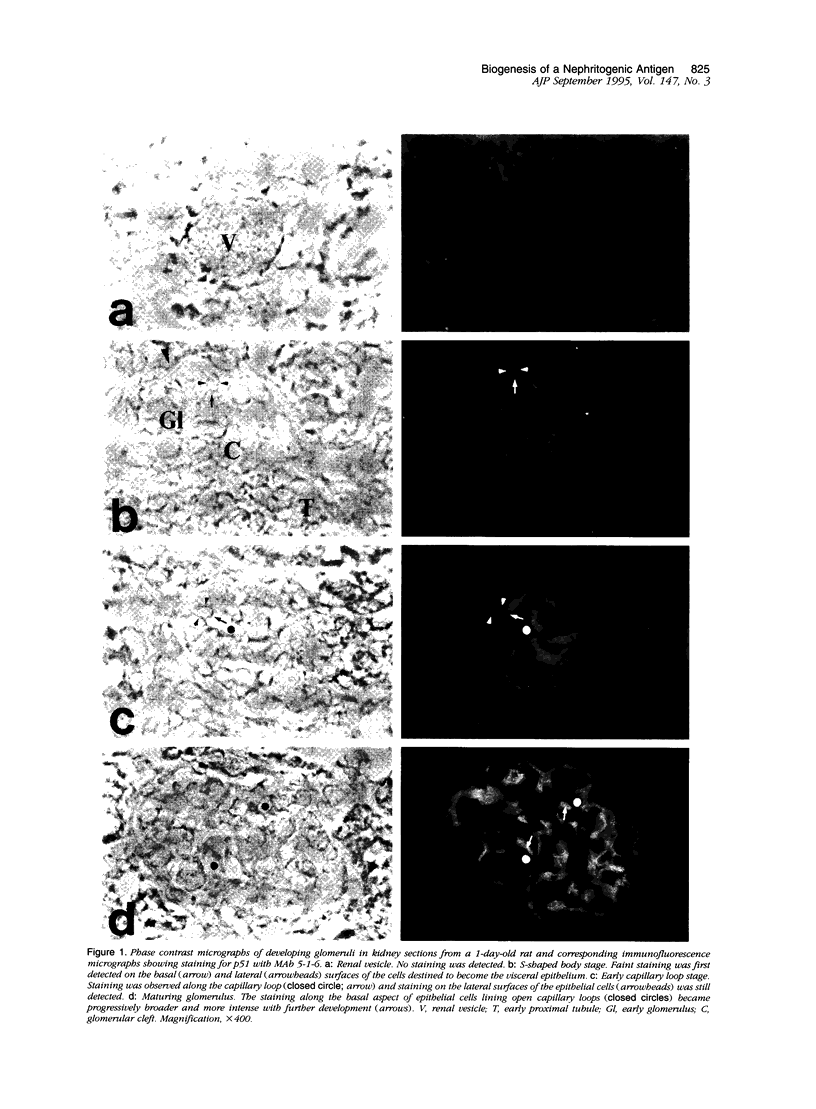
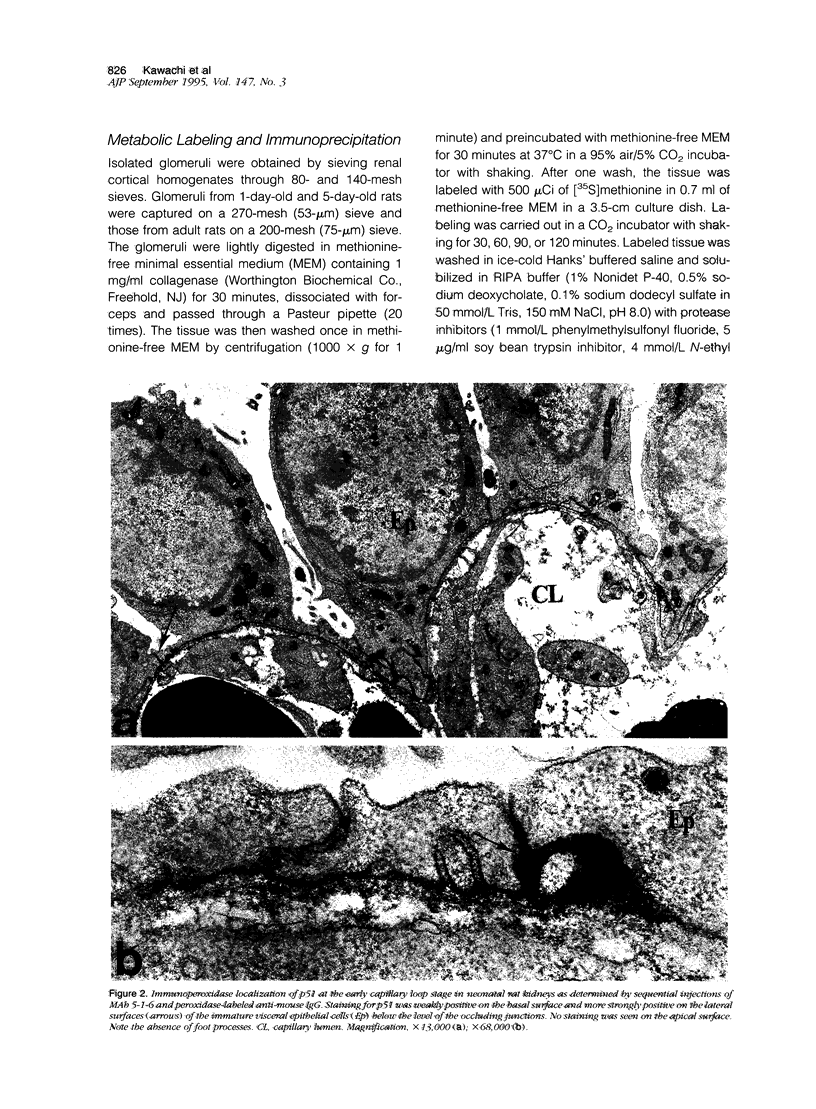
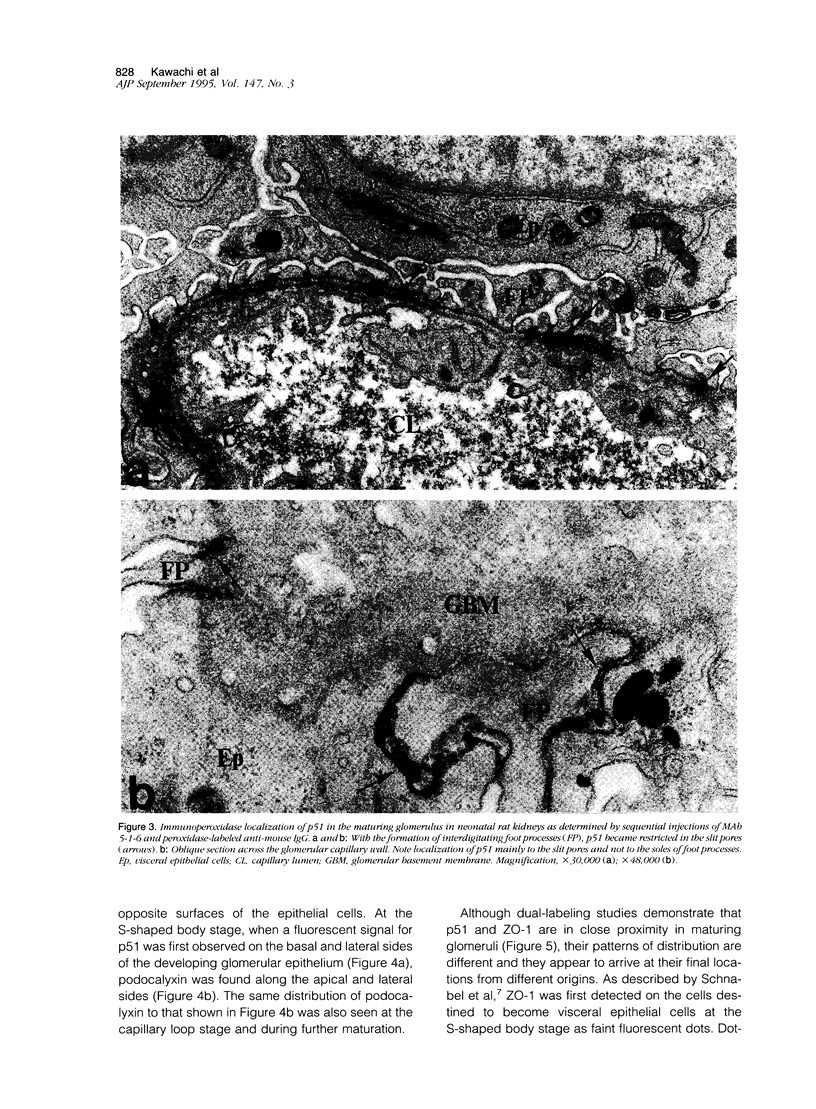
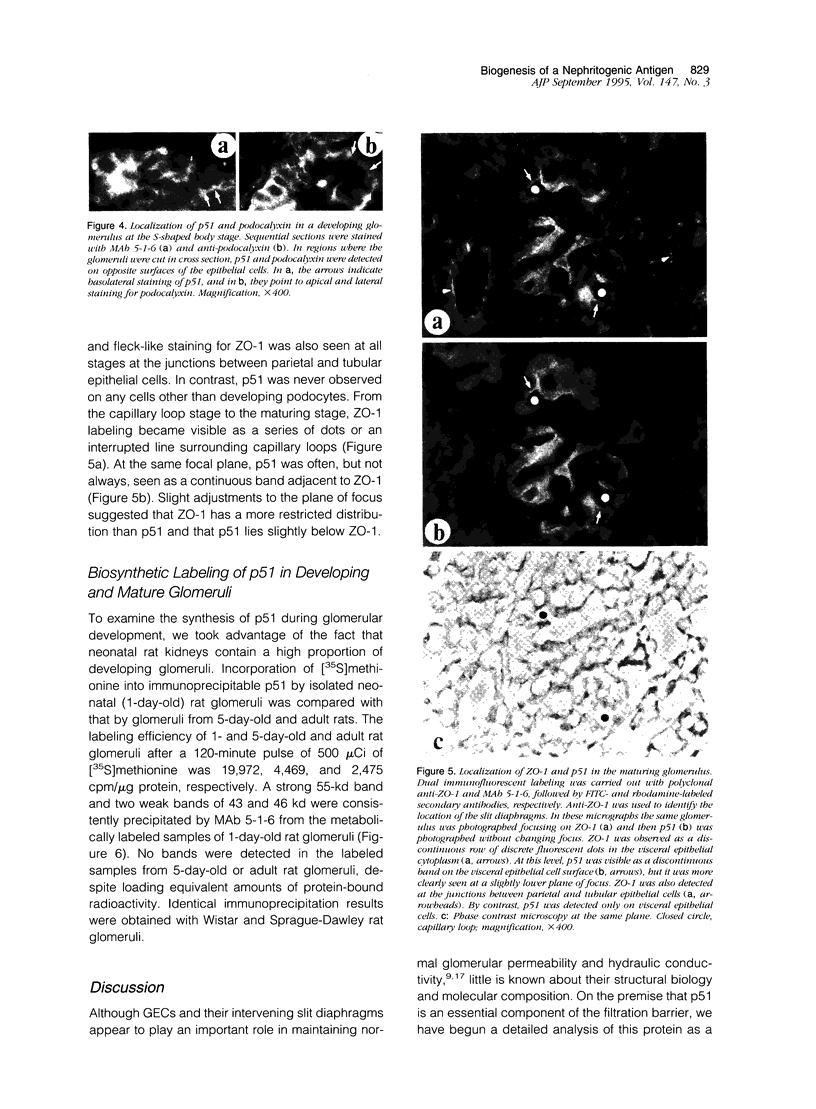
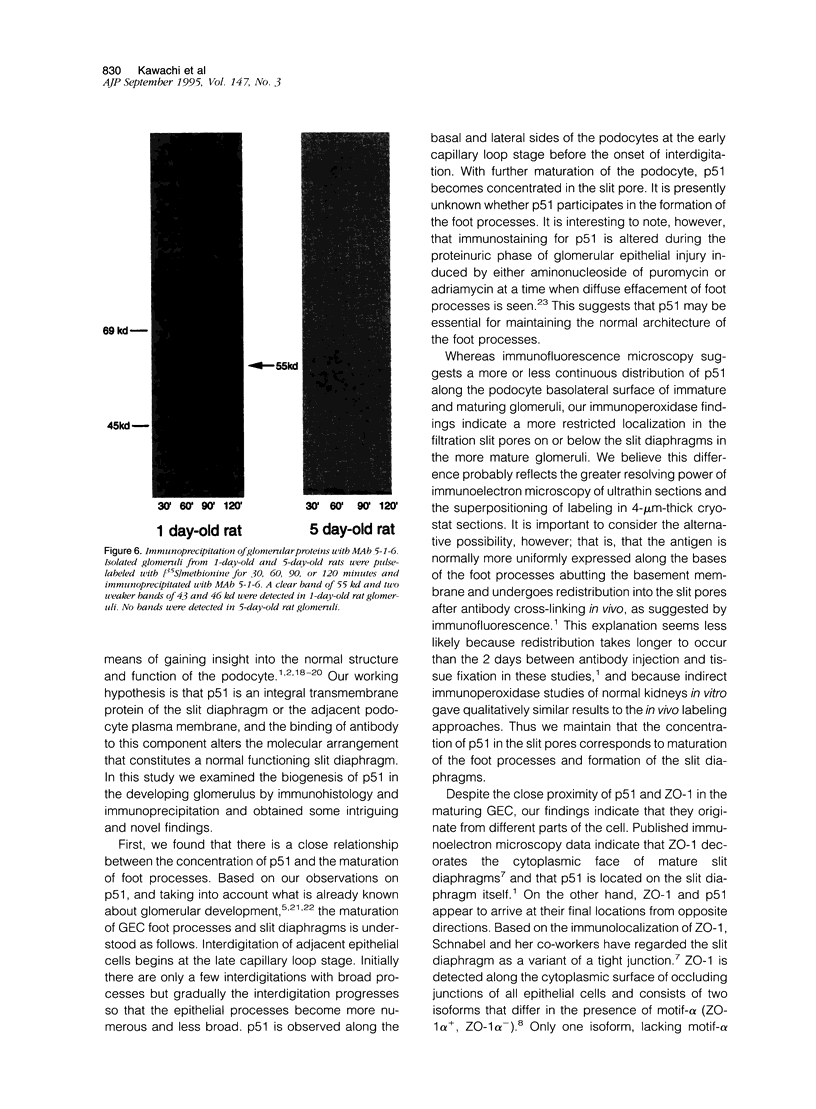
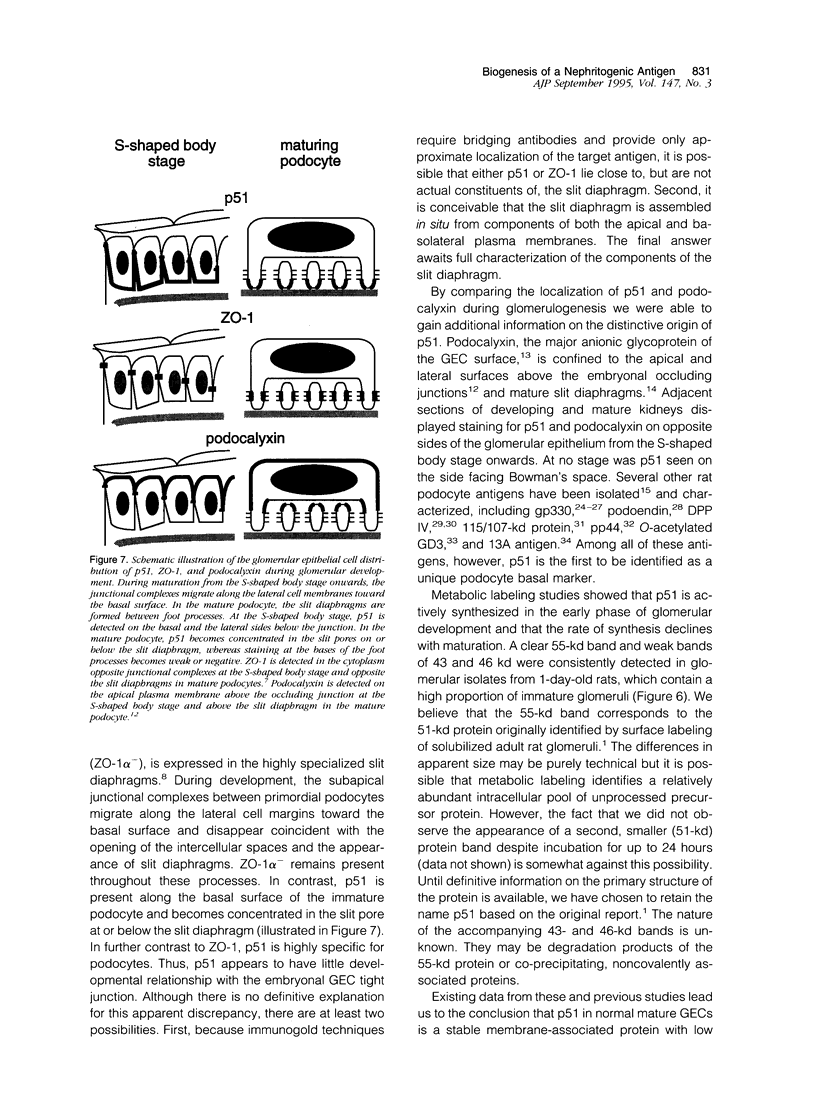
The biogenesis of p51, the target of nephritogenic monoclonal antibody 5-1-6, was studied in the developing glomerulus by immunolocalization and metabolic labeling. The localization of p51 was compared with that of ZO-1, a component of the cytoplasmic face of the epithelial slit diaphragm, and with that of podocalyxin, and apical marker of the podocyte. p51 first became faintly, but clearly, detectable on the basal and lateral sides of the developing podocytes at the S-shaped body stage. Staining intensity increased with further maturation and was restricted to the visceral epithelial cells. On immunoelectron microscopy, the antigen was seen along the basal and lateral surfaces below occluding junction at the early capillary loop stage and later, with the interdigitation of foot processes, became concentrated in the slit pores. At no stage was p51 seen on the apical surface. p51 and ZO-1 were closely localized in the mature glomerulus but arrived at their final positions from opposite directions. p51 was on basal and podocalyxin was on apical sides of the glomerular epithelium from the S-shaped body stage onwards. Metabolic labeling studies showed that p51 is actively synthesized during initial glomerular development and that the rate of synthesis declines substantially with maturation. We conclude that p51 is primarily synthesized during the initial glomerular development, becomes concentrated in the slit pores of mature podocytes, and serves as a basal differentiation marker for podocytes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamson D. R. Glomerulogenesis in the developing kidney. Semin Nephrol. 1991 Jul;11(4):375–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamson D. R., Irwin M. H., St John P. L., Perry E. W., Accavitti M. A., Heck L. W., Couchman J. R. Selective immunoreactivities of kidney basement membranes to monoclonal antibodies against laminin: localization of the end of the long arm and the short arms to discrete microdomains. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3477–3491. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamson D. R. Structure and development of the glomerular capillary wall and basement membrane. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 2):F783–F794. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.5.F783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhan A. K., Schneeberger E. E., Baird L. G., Collins A. B., Kamata K., Bradford D., Erikson M. E., McCluskey R. T. Studies with monoclonal antibodies against brush border antigens in Heymann nephritis. Lab Invest. 1985 Oct;53(4):421–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G., WISSIG S. L., PALADE G. E. Glomerular permeability. I. Ferritin transfer across the normal glomerular capillary wall. J Exp Med. 1961 Jan 1;113:47–66. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. W., Langlois J. C. Podoendin. A new cell surface protein of the podocyte and endothelium. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):245–267. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawachi H., Matsui K., Orikasa M., Morioka T., Oite T., Shimizu F. Quantitative studies of monoclonal antibody 5-1-6-induced proteinuric state in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Feb;87(2):215–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb02977.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. Immunocytochemical localization of the Heymann nephritis antigen (GP330) in glomerular epithelial cells of normal Lewis rats. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):667–686. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. The pathogenic antigen of Heymann nephritis is a membrane glycoprotein of the renal proximal tubule brush border. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5557–5561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Sharkey D. J., Farquhar M. G. Identification and characterization of podocalyxin--the major sialoprotein of the renal glomerular epithelial cell. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1591–1596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurihara H., Anderson J. M., Farquhar M. G. Diversity among tight junctions in rat kidney: glomerular slit diaphragms and endothelial junctions express only one isoform of the tight junction protein ZO-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7075–7079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendrick D. L., Rennke H. G. Induction of proteinuria in the rat by a monoclonal antibody against SGP-115/107. Kidney Int. 1988 Apr;33(4):818–830. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen A., Dekan G., Farquhar M. G. Monoclonal antibodies against membrane proteins of the rat glomerulus. Immunochemical specificity and immunofluorescence distribution of the antigens. Am J Pathol. 1990 Oct;137(4):929–944. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundel P., Gilbert P., Kriz W. Podocytes in glomerulus of rat kidney express a characteristic 44 KD protein. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Aug;39(8):1047–1056. doi: 10.1177/39.8.1856454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narisawa M., Kawachi H., Oite T., Shimizu F. Divalency of the monoclonal antibody 5-1-6 is required for induction of proteinuria in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Jun;92(3):522–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb03431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natori Y., Hayakawa I., Shibata S. Identification of gp108, a pathogenic antigen of passive Heymann nephritis, as dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Nov;70(2):434–439. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okasora T., Nagase M., Kawachi H., Matsui K., Orikasa M., Morioka T., Yamazaki I., Oite T., Shimizu F. Altered localization of antigen recognized by proteinuria-inducing monoclonal antibody in experimental nephrosis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1991;60(1):41–46. doi: 10.1007/BF02899526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Singh A., Amherdt M., Brown D., Perrelet A. Microheterogeneity of protein and sterol content in kidney podocyte membrane. Nature. 1981 Oct 22;293(5834):646–647. doi: 10.1038/293646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orikasa M., Matsui K., Oite T., Shimizu F. Massive proteinuria induced in rats by a single intravenous injection of a monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):807–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. H., Kanwar Y. S., Farquhar M. G. Assembly of the glomerular filtration surface. Differentiation of anionic sites in glomerular capillaries of newborn rat kidney. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):735–753. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reivinen J., Holthöfer H., Miettinen A. A cell-type specific ganglioside of glomerular podocytes in rat kidney: an O-acetylated GD3. Kidney Int. 1992 Sep;42(3):624–631. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodewald R., Karnovsky M. J. Porous substructure of the glomerular slit diaphragm in the rat and mouse. J Cell Biol. 1974 Feb;60(2):423–433. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco P., Melcion C., Geniteau M., Ronco E., Reininger L., Galceran M., Verroust P. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against rat brush border antigens of the proximal convoluted tubule. Immunology. 1984 Sep;53(1):87–95. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salant D. J. The structural biology of glomerular epithelial cells in proteinuric diseases. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 1994 Nov;3(6):569–574. doi: 10.1097/00041552-199411000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada H., Stukenbrok H., Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. Epithelial polyanion (podocalyxin) is found on the sides but not the soles of the foot processes of the glomerular epithelium. Am J Pathol. 1986 Nov;125(2):309–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel E., Anderson J. M., Farquhar M. G. The tight junction protein ZO-1 is concentrated along slit diaphragms of the glomerular epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1255–1263. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel E., Dekan G., Miettinen A., Farquhar M. G. Biogenesis of podocalyxin--the major glomerular sialoglycoprotein--in the newborn rat kidney. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;48(2):313–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. R., Siliciano J. D., Mooseker M. S., Goodenough D. A. Identification of ZO-1: a high molecular weight polypeptide associated with the tight junction (zonula occludens) in a variety of epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):755–766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima N., Kawachi H., Oite T., Nishi S., Arakawa M., Shimizu F. Effect of chlorpromazine on kinetics of injected monoclonal antibody in MoAb-induced glomerular injury. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Jan;91(1):135–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb03368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting R. H., Kristal B., Myers B. D. The biophysical basis of hypofiltration in nephrotic humans with membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1994 Feb;45(2):390–397. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissari J., Holthöfer H., Miettinen A. Novel 13A antigen is an integral protein of the basolateral membrane of rat glomerular podocytes. Lab Invest. 1994 Oct;71(4):519–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verroust P., Ronco P., Chatelet F. Antigenic targets in membranous glomerulonephritis. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1987;9(4):341–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00197213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]