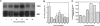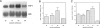Abstract
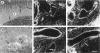
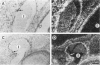
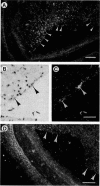
The thrombospondins (TSP-1, -2, and -3) comprise a family of proteins that are homologous at the carboxy terminus but have unique sequences at the amino terminus that might be correlated with the regulation of cell behavior. To investigate the expression of TSP-1, -2, and -3 in endothelial cells, we examined developing murine blood vessels and human atherosclerotic plaques by in situ hybridization. The expression of TSP-1 was also characterized in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Expression of TSP-2 was seen in the dorsal aorta as early as embryonic day 10; TSP-1 was not detected in endothelial cells until later stages, and TSP-3 was not apparent in the vasculature. In atherosclerotic specimens, TSP-1 mRNA was detected in many intraplaque microvessels and in the endothelium lining the atheromatous plaque; TSP-2 was absent from these regions. Cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells did not transcribe TSP-2 mRNA at detectable levels. There were high steady-state levels of TSP-1 mRNA in subconfluent bovine aortic endothelial cells before confluence and at the wound edge after injury of the cell monolayer, with maximal expression of TSP-1 in cultures at a time during which approximately 35% of the cells were in S phase. As the majority of these cells subsequently undergo mitosis, these data are consistent with TSP-1 as an inhibitor of endothelial cell proliferation that functions in G1. These results support the conclusion that, despite sequence homology, the TSPs have distinct functions in vascular biology.
Full text
PDF




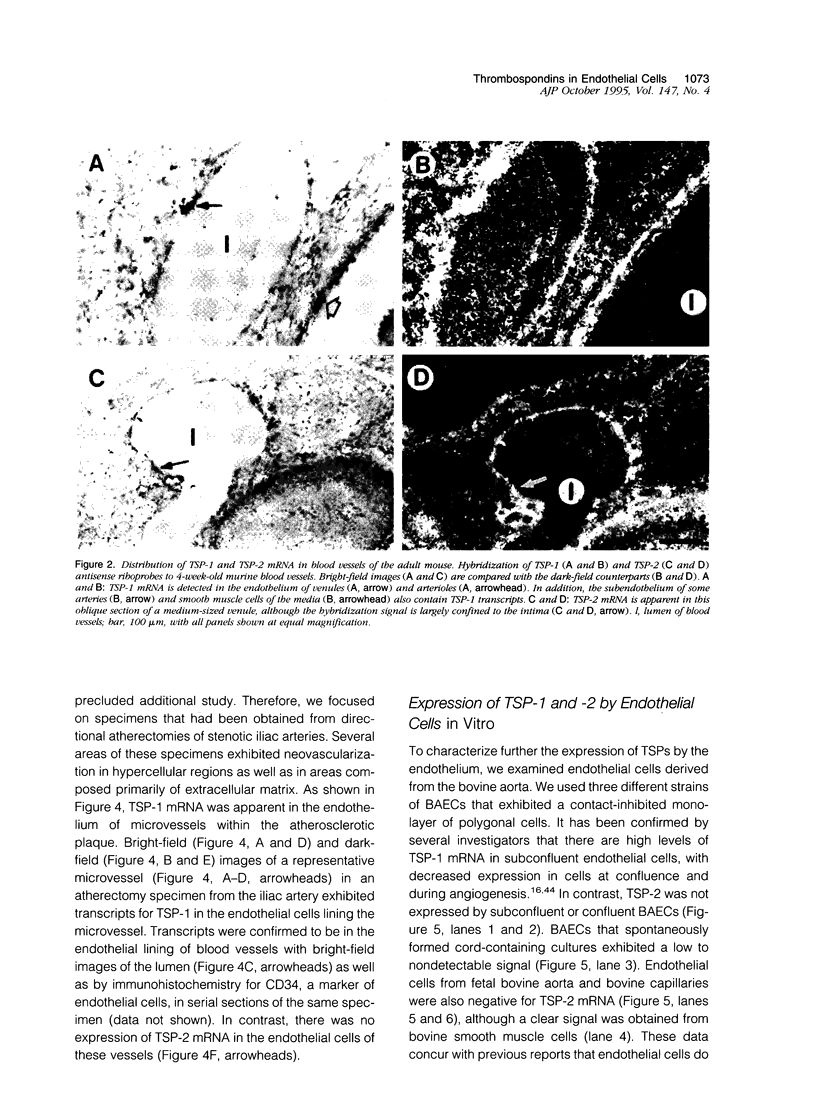
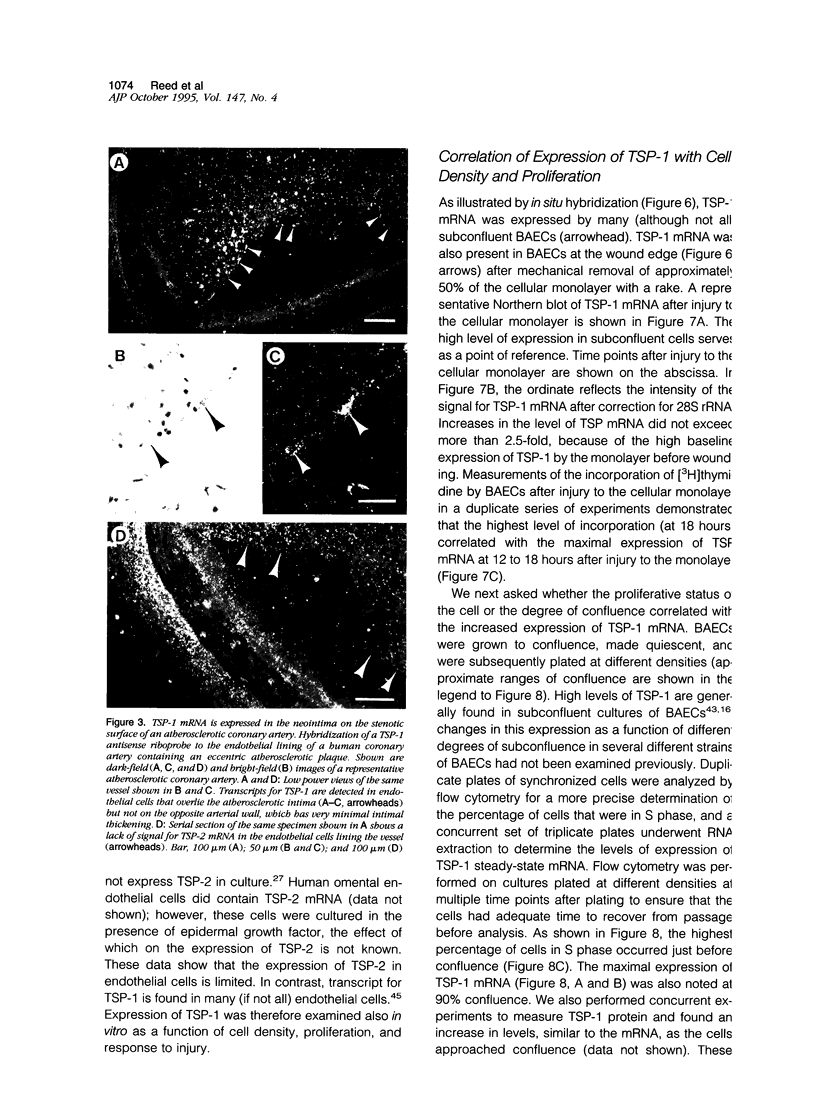
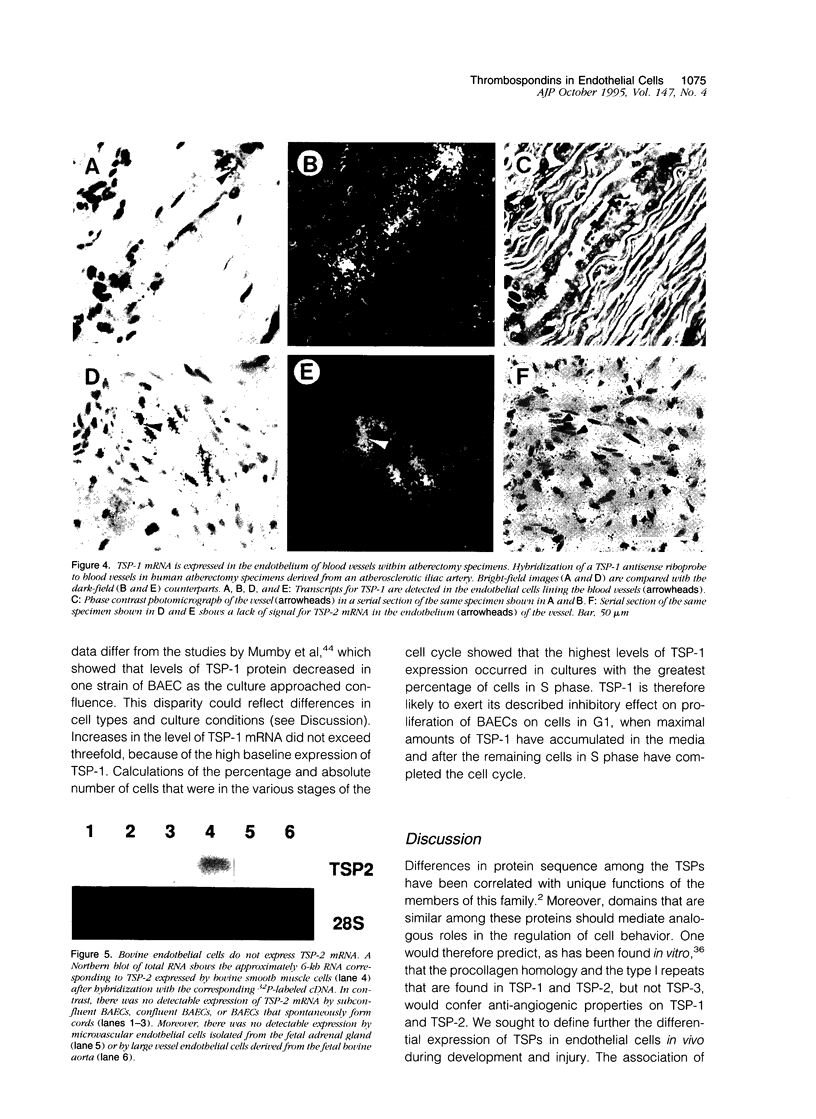
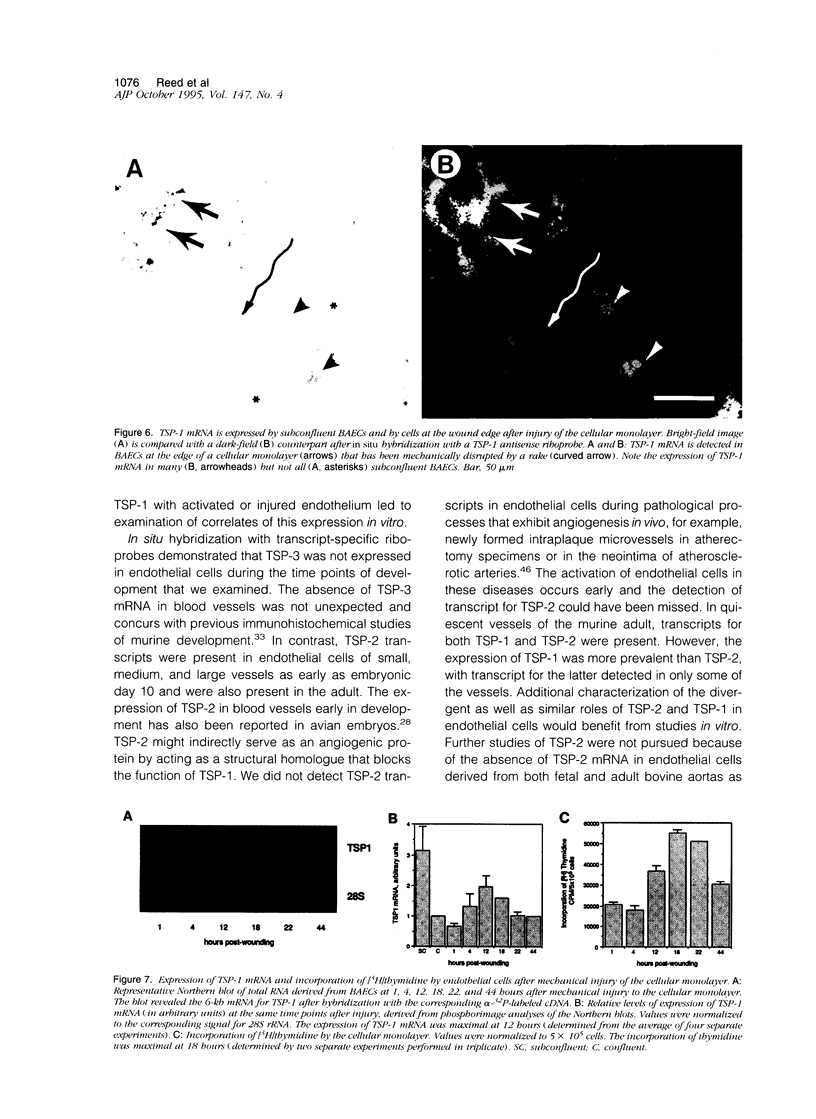
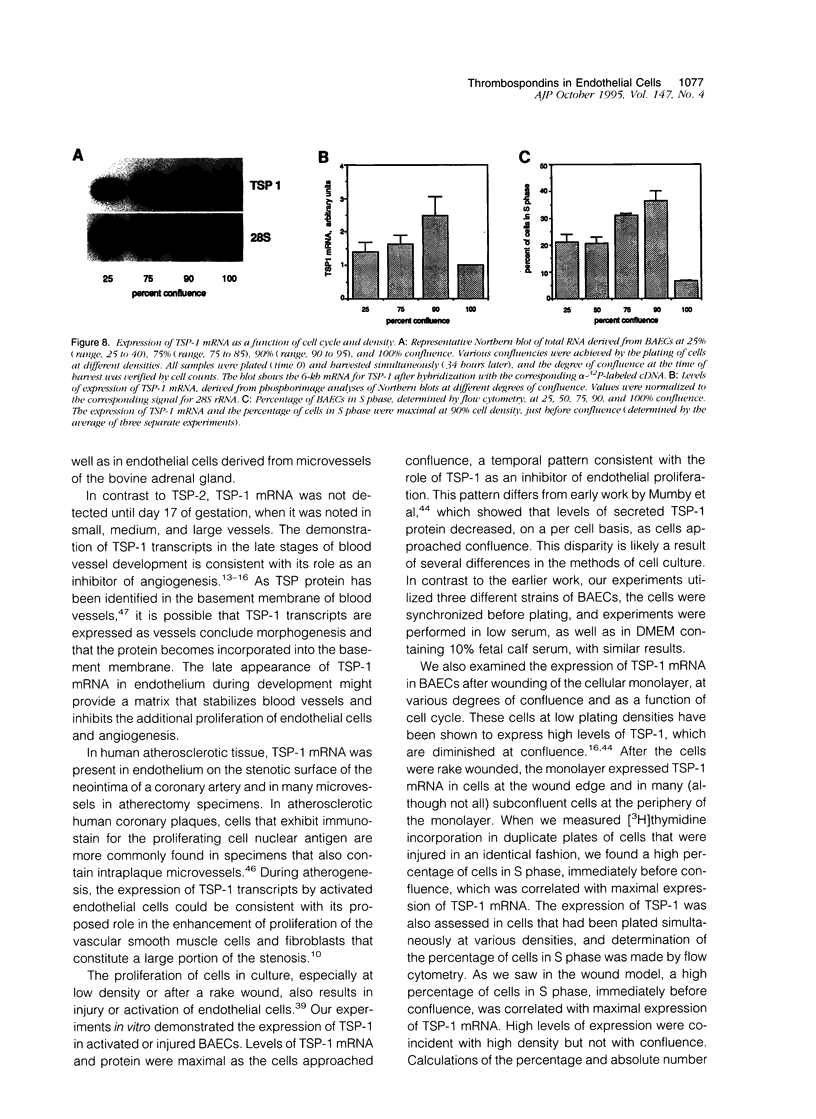



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C., Lawler J. Cell-type specific adhesive interactions of skeletal myoblasts with thrombospondin-1. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Apr;5(4):423–437. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.4.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagavandoss P., Wilks J. W. Specific inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation by thrombospondin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 31;170(2):867–872. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92171-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Devarayalu S., Li P., Disteche C. M., Framson P. A second thrombospondin gene in the mouse is similar in organization to thrombospondin 1 but does not respond to serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8636–8640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Sage E. H. Thrombospondins. Methods Enzymol. 1994;245:62–85. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)45006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle V. P., Ou X., O'Rourke K., Dixit V. M. High level thrombospondin 1 expression in two NIH 3T3 cloned lines confers serum- and anchorage-independent growth. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2899–2903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoviel D. B., Amacher S. L., Judge K. W., Bornstein P. Thrombospondin gene expression is associated with mitogenesis in 3T3 cells: induction by basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Oct;145(1):16–23. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041450104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Framson P., Bornstein P. A serum response element and a binding site for NF-Y mediate the serum response of the human thrombospondin 1 gene. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4989–4996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. J., Polverini P. J., Rastinejad F., Le Beau M. M., Lemons R. S., Frazier W. A., Bouck N. P. A tumor suppressor-dependent inhibitor of angiogenesis is immunologically and functionally indistinguishable from a fragment of thrombospondin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6624–6628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo N. H., Krutzsch H. C., Nègre E., Zabrenetzky V. S., Roberts D. D. Heparin-binding peptides from the type I repeats of thrombospondin. Structural requirements for heparin binding and promotion of melanoma cell adhesion and chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19349–19355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimark R. L., Twardzik D. R., Schwartz S. M. Inhibition of endothelial regeneration by type-beta transforming growth factor from platelets. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1078–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.3461562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P. W., Harper S. J., McVey J. H., Hogan B. L. In vivo expression of mRNA for the Ca++-binding protein SPARC (osteonectin) revealed by in situ hybridization. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):473–482. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iruela-Arispe M. L., Bornstein P., Sage H. Thrombospondin exerts an antiangiogenic effect on cord formation by endothelial cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):5026–5030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.5026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iruela-Arispe M. L., Liska D. J., Sage E. H., Bornstein P. Differential expression of thrombospondin 1, 2, and 3 during murine development. Dev Dyn. 1993 May;197(1):40–56. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001970105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Ruggiero J. T., Falcone D. J. Monocytes and macrophages synthesize and secrete thrombospondin. Blood. 1985 Jan;65(1):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Ruggiero J. T., Leung L. K., Doyle M. J., McKeown-Longo P. J., Mosher D. F. Cultured human fibroblasts synthesize and secrete thrombospondin and incorporate it into extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):998–1002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella M. G., Wight T. N. Modulation of sulfated proteoglycan synthesis by bovine aortic endothelial cells during migration. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):679–687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosfeld M. D., Frazier W. A. Identification of active peptide sequences in the carboxyl-terminal cell binding domain of human thrombospondin-1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16230–16236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosfeld M. D., Pavlopoulos T. V., Frazier W. A. Cell attachment activity of the carboxyl-terminal domain of human thrombospondin expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24257–24259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBell T. L., Milewicz D. J., Disteche C. M., Byers P. H. Thrombospondin II: partial cDNA sequence, chromosome location, and expression of a second member of the thrombospondin gene family in humans. Genomics. 1992 Mar;12(3):421–429. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90430-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J. W., Slayter H. S., Coligan J. E. Isolation and characterization of a high molecular weight glycoprotein from human blood platelets. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8609–8616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J., Weinstein R., Hynes R. O. Cell attachment to thrombospondin: the role of ARG-GLY-ASP, calcium, and integrin receptors. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2351–2361. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majack R. A., Cook S. C., Bornstein P. Control of smooth muscle cell growth by components of the extracellular matrix: autocrine role for thrombospondin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9050–9054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majack R. A., Cook S. C., Bornstein P. Platelet-derived growth factor and heparin-like glycosaminoglycans regulate thrombospondin synthesis and deposition in the matrix by smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1059–1070. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majack R. A., Goodman L. V., Dixit V. M. Cell surface thrombospondin is functionally essential for vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):415–422. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majack R. A., Mildbrandt J., Dixit V. M. Induction of thrombospondin messenger RNA levels occurs as an immediate primary response to platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8821–8825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson J., Sage H., Bornstein P. Isolation and characterization of a glycoprotein secreted by aortic endothelial cells in culture. Apparent identity with platelet thrombospondin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11330–11336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Abbott-Brown D., Raugi G. J., Bornstein P. Regulation of thrombospondin secretion by cells in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Sep;120(3):280–288. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041200304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy-Ullrich J. E., Hök M. Thrombospondin modulates focal adhesions in endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1309–1319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy-Ullrich J. E., Schultz-Cherry S., Hök M. Transforming growth factor-beta complexes with thrombospondin. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Feb;3(2):181–188. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien E. R., Garvin M. R., Dev R., Stewart D. K., Hinohara T., Simpson J. B., Schwartz S. M. Angiogenesis in human coronary atherosclerotic plaques. Am J Pathol. 1994 Oct;145(4):883–894. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea K. S., Dixit V. M. Unique distribution of the extracellular matrix component thrombospondin in the developing mouse embryo. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2737–2748. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phan S. H., Dillon R. G., McGarry B. M., Dixit V. M. Stimulation of fibroblast proliferation by thrombospondin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):56–63. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qabar A. N., Lin Z., Wolf F. W., O'Shea K. S., Lawler J., Dixit V. M. Thrombospondin 3 is a developmentally regulated heparin binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1262–1269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastinejad F., Polverini P. J., Bouck N. P. Regulation of the activity of a new inhibitor of angiogenesis by a cancer suppressor gene. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):345–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raugi G. J., Mumby S. M., Abbott-Brown D., Bornstein P. Thrombospondin: synthesis and secretion by cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):351–354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RayChaudhury A., Frazier W. A., D'Amore P. A. Comparison of normal and tumorigenic endothelial cells: differences in thrombospondin production and responses to transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jan;107(Pt 1):39–46. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed M. J., Puolakkainen P., Lane T. F., Dickerson D., Bornstein P., Sage E. H. Differential expression of SPARC and thrombospondin 1 in wound repair: immunolocalization and in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Oct;41(10):1467–1477. doi: 10.1177/41.10.8245406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. D., Sherwood J. A., Ginsburg V. Platelet thrombospondin mediates attachment and spreading of human melanoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;104(1):131–139. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Crouch E., Bornstein P. Collagen synthesis by bovine aortic endothelial cells in culture. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5433–5442. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz-Cherry S., Lawler J., Murphy-Ullrich J. E. The type 1 repeats of thrombospondin 1 activate latent transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):26783–26788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz-Cherry S., Murphy-Ullrich J. E. Thrombospondin causes activation of latent transforming growth factor-beta secreted by endothelial cells by a novel mechanism. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):923–932. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottile J., Mosher D. F., Fullenweider J., George J. N. Human platelets contain mRNA transcripts for platelet factor 4 and actin. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Dec 29;62(4):1100–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraboletti G., Roberts D., Liotta L. A., Giavazzi R. Platelet thrombospondin modulates endothelial cell adhesion, motility, and growth: a potential angiogenesis regulatory factor. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):765–772. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolsma S. S., Volpert O. V., Good D. J., Frazier W. A., Polverini P. J., Bouck N. Peptides derived from two separate domains of the matrix protein thrombospondin-1 have anti-angiogenic activity. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(2):497–511. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. P. The in situ localization of tenascin splice variants and thrombospondin 2 mRNA in the avian embryo. Development. 1993 Jan;117(1):347–358. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.1.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos H. L., Devarayalu S., de Vries Y., Bornstein P. Thrombospondin 3 (Thbs3), a new member of the thrombospondin gene family. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12192–12196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wight T. N., Raugi G. J., Mumby S. M., Bornstein P. Light microscopic immunolocation of thrombospondin in human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Apr;33(4):295–302. doi: 10.1177/33.4.3884704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]