Abstract
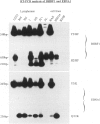
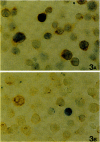
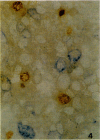
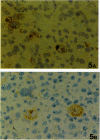
Using RT-PCR analysis of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent gene transcription in EBV-harboring cell lines (JY and RAJI) and in post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders (PT-LPDs), we detected transcription of all tested latent genes (EBNA1, EBNA2, LMP1, LMP2A, and BARF0) in all cases, suggesting the presence of similar EBV expression patterns in both PT-LPDs and cell lines. In addition, the detection of immediate early (ZEBRA) and early gene (BHRF1) transcripts in cell lines and PT-LPDs indicates that activation of the virus lytic cycle occurs. To investigate EBV expression patterns at the single-cell level, a combination of immunohistochemistry and RNA in situ hybridization (including double-staining procedures) was used. In the JY and RAJI cell lines, the latency type 3 expression pattern was detected in 80 to 90% of the cells as shown by the co-expression of EBNA2 and LMP1. In contrast, in the three PT-LPDs that could be analyzed by double staining, cells expressing both EBNA2 and LMP1 were rarely detected. A mixture of at least three different cell populations were identified: (1) cells exclusively expressing EBER1/2 and EBNA1 (latency type 1); (2) cells expressing EBER1/2, EBNA1, and LMP1 (latency type 2); and (3) cells expressing EBER1/2, EBNA1, and EBNA2 in the absence of LMP1. Activation of the lytic cycle was observed in a small minority of cells, as demonstrated by detection of ZEBRA and EA-D in all cases and GP350/220 in two cases. Thus, in contrast to EBV-transformed cell lines, the observed EBV gene expression pattern in PT-LPDs reflects a mixture of multiple EBV-harboring subpopulations expressing different subsets of EBV-encoded proteins. These data indicate that the operational definitions of EBV latencies in vitro cannot easily be applied to PT-LPDs but that a continuum of different latency expression patterns can be detected at the single cell level in these lymphomas with, in a small minority of cells, progression to the virus lytic cycle.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin P. J., Flemington E., Yandava C. N., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Complex transcription of the Epstein-Barr virus BamHI fragment H rightward open reading frame 1 (BHRF1) in latently and lytically infected B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3678–3682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks L. A., Lear A. L., Young L. S., Rickinson A. B. Transcripts from the Epstein-Barr virus BamHI A fragment are detectable in all three forms of virus latency. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3182–3190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3182-3190.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. L., Sadler R. H., Walling D. M., Su I. J., Hsieh H. C., Raab-Traub N. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) gene expression in EBV-positive peripheral T-cell lymphomas. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6303–6308. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6303-6308.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen F., Zou J. Z., di Renzo L., Winberg G., Hu L. F., Klein E., Klein G., Ernberg I. A subpopulation of normal B cells latently infected with Epstein-Barr virus resembles Burkitt lymphoma cells in expressing EBNA-1 but not EBNA-2 or LMP1. J Virol. 1995 Jun;69(6):3752–3758. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.6.3752-3758.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deacon E. M., Pallesen G., Niedobitek G., Crocker J., Brooks L., Rickinson A. B., Young L. S. Epstein-Barr virus and Hodgkin's disease: transcriptional analysis of virus latency in the malignant cells. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):339–349. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratama J. W., Zutter M. M., Minarovits J., Oosterveer M. A., Thomas E. D., Klein G., Ernberg I. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded growth-transformation-associated proteins in lymphoproliferations of bone-marrow transplant recipients. Int J Cancer. 1991 Jan 21;47(2):188–192. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B. Different Epstein-Barr virus-B cell interactions in phenotypically distinct clones of a Burkitt's lymphoma cell line. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jul;71(Pt 7):1481–1495. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-7-1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grässer F. A., Murray P. G., Kremmer E., Klein K., Remberger K., Feiden W., Reynolds G., Niedobitek G., Young L. S., Mueller-Lantzsch N. Monoclonal antibodies directed against the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1): immunohistologic detection of EBNA1 in the malignant cells of Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1994 Dec 1;84(11):3792–3798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Pallesen G., Franzmann M. B., Karkov J., Black F., Skinhøj P., Pedersen C. AIDS-related lymphoma. Histopathology, immunophenotype, and association with Epstein-Barr virus as demonstrated by in situ nucleic acid hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):149–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Rea D., Raphael M., Sandvej K., Delecluse H. J., Gisselbrecht C., Marelle L., van Krieken H. J., Pallesen G. Epstein-Barr virus-latent gene expression and tumor cell phenotype in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Correlation of lymphoma phenotype with three distinct patterns of viral latency. Am J Pathol. 1993 Oct;143(4):1072–1085. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Huen D., Rowe M., Dawson C., Johnson G., Rickinson A. Epstein-Barr virus-coded BHRF1 protein, a viral homologue of Bcl-2, protects human B cells from programmed cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8479–8483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. G., Steitz J. A. Localization of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9006–9010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiwa N. M., Kanavaros P., De Bruin P. C., van der Valk P., Horstman A., Vos W., Mullink H., Walboomers J. M., Meijer C. J. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus harbouring small and intermediate-sized cells in Hodgkin's disease. Is there a relationship with Reed-Sternberg cells? J Pathol. 1993 Jun;170(2):129–136. doi: 10.1002/path.1711700206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiwa N. M., Oudejans J. J., Dukers D. F., Vos W., Horstman A., van der Valk P., Middledorp J. M., Walboomers J. M., Meijer C. J. Immunohistochemical demonstration of different latent membrane protein-1 epitopes of Epstein-Barr virus in lymphoproliferative diseases. J Clin Pathol. 1995 May;48(5):438–442. doi: 10.1136/jcp.48.5.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joske D. J., Emery-Goodman A., Bachmann E., Bachmann F., Odermatt B., Knecht H. Epstein-Barr virus burden in Hodgkin's disease is related to latent membrane protein gene expression but not to active viral replication. Blood. 1992 Nov 15;80(10):2610–2613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. A., Ferry J. A., Harris N. L., Jacobson J. O. Clonal analysis of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders, using both episomal Epstein-Barr virus and immunoglobulin genes as markers. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994 May;101(5):590–596. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/101.5.590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye K. M., Izumi K. M., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 is essential for B-lymphocyte growth transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9150–9154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles D. M., Cesarman E., Chadburn A., Frizzera G., Chen J., Rose E. A., Michler R. E. Correlative morphologic and molecular genetic analysis demonstrates three distinct categories of posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood. 1995 Jan 15;85(2):552–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lear A. L., Rowe M., Kurilla M. G., Lee S., Henderson S., Kieff E., Rickinson A. B. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 1 BamHI F promoter is activated on entry of EBV-transformed B cells into the lytic cycle. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7461–7468. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7461-7468.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton T., Gahn T. A., Martin J. M., Sugden B. Immortalizing genes of Epstein-Barr virus. Adv Virus Res. 1991;40:19–55. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60276-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki I., Cheung R. K., Dosch H. M. Viral interleukin 10 is critical for the induction of B cell growth transformation by Epstein-Barr virus. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):439–447. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudejans J. J., van den Brule A. J., Jiwa N. M., de Bruin P. C., Ossenkoppele G. J., van der Valk P., Walboomers J. M., Meijer C. J. BHRF1, the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) homologue of the BCL-2 protooncogene, is transcribed in EBV-associated B-cell lymphomas and in reactive lymphocytes. Blood. 1995 Sep 1;86(5):1893–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen G., Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Rowe M., Lisse I., Ralfkiaer E., Sandvej K., Young L. S. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus replicative proteins in AIDS-related non-Hodgkin's lymphoma cells. J Pathol. 1991 Dec;165(4):289–299. doi: 10.1002/path.1711650404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisa P., Cannon M. J., Pisa E. K., Cooper N. R., Fox R. I. Epstein-Barr virus induced lymphoproliferative tumors in severe combined immunodeficient mice are oligoclonal. Blood. 1992 Jan 1;79(1):173–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu L., Rowe D. T. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in uncultured peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3715–3724. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3715-3724.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea D., Fourcade C., Leblond V., Rowe M., Joab I., Edelman L., Bitker M. O., Gandjbakhch I., Suberbielle C., Farcet J. P. Patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent and replicative gene expression in Epstein-Barr virus B cell lymphoproliferative disorders after organ transplantation. Transplantation. 1994 Aug 15;58(3):317–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochford R., Hobbs M. V., Garnier J. L., Cooper N. R., Cannon M. J. Plasmacytoid differentiation of Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B cells in vivo is associated with reduced expression of viral latent genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):352–356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C. M., Rowe D. T., Ragot T., Farrell P. J. The spliced BZLF1 gene of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) transactivates an early EBV promoter and induces the virus productive cycle. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3109–3116. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3109-3116.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Lear A. L., Croom-Carter D., Davies A. H., Rickinson A. B. Three pathways of Epstein-Barr virus gene activation from EBNA1-positive latency in B lymphocytes. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):122–131. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.122-131.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Rowe D. T., Gregory C. D., Young L. S., Farrell P. J., Rupani H., Rickinson A. B. Differences in B cell growth phenotype reflect novel patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2743–2751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Brooks L., Sample C., Young L., Rowe M., Gregory C., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Restricted Epstein-Barr virus protein expression in Burkitt lymphoma is due to a different Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6343–6347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer B. C., Woisetschlaeger M., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Exclusive expression of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 in Burkitt lymphoma arises from a third promoter, distinct from the promoters used in latently infected lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6550–6554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Allday M. J., Crawford D. H. Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disorders in immunocompromised individuals. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;57:329–380. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)61003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Hotchin N. A., Allday M. J., Amlot P., Rose M., Yacoub M., Crawford D. H. Immunohistology of Epstein-Barr virus-associated antigens in B cell disorders from immunocompromised individuals. Transplantation. 1990 May;49(5):944–953. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199005000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L., Alfieri C., Hennessy K., Evans H., O'Hara C., Anderson K. C., Ritz J., Shapiro R. S., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus transformation-associated genes in tissues of patients with EBV lymphoproliferative disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 19;321(16):1080–1085. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910193211604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]