Abstract
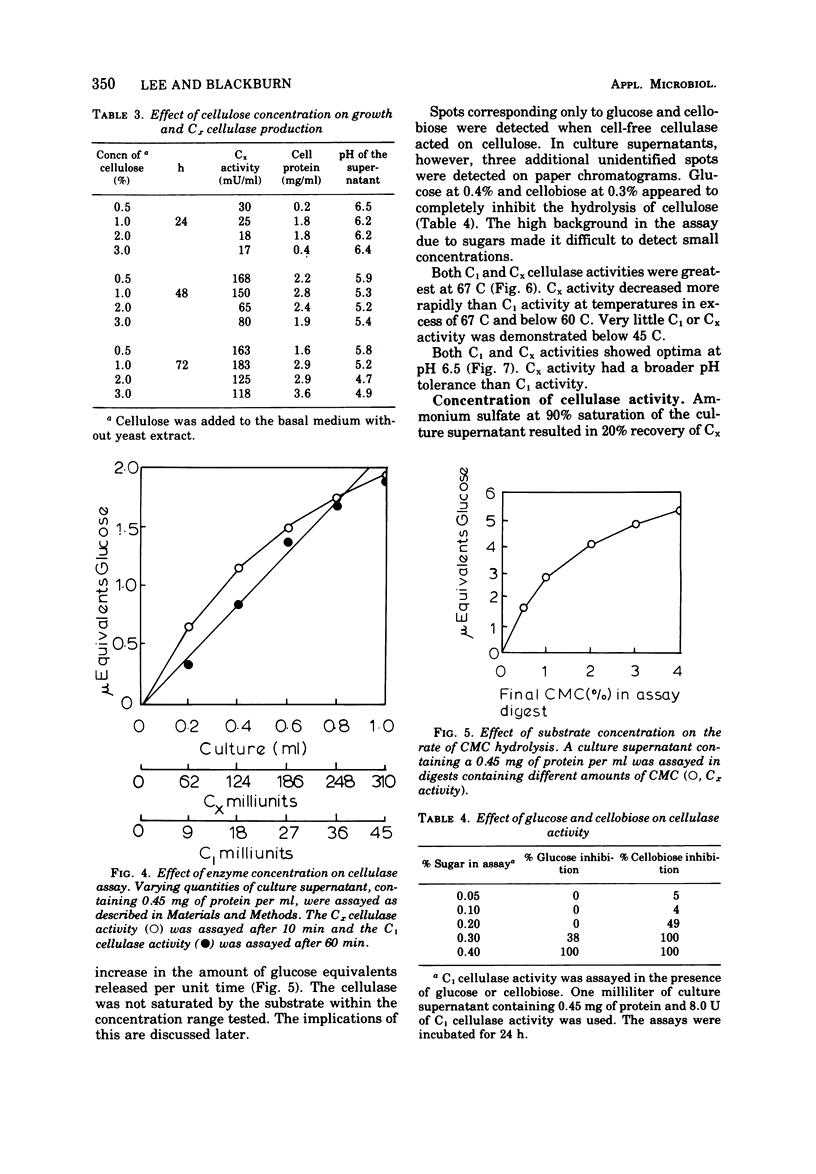
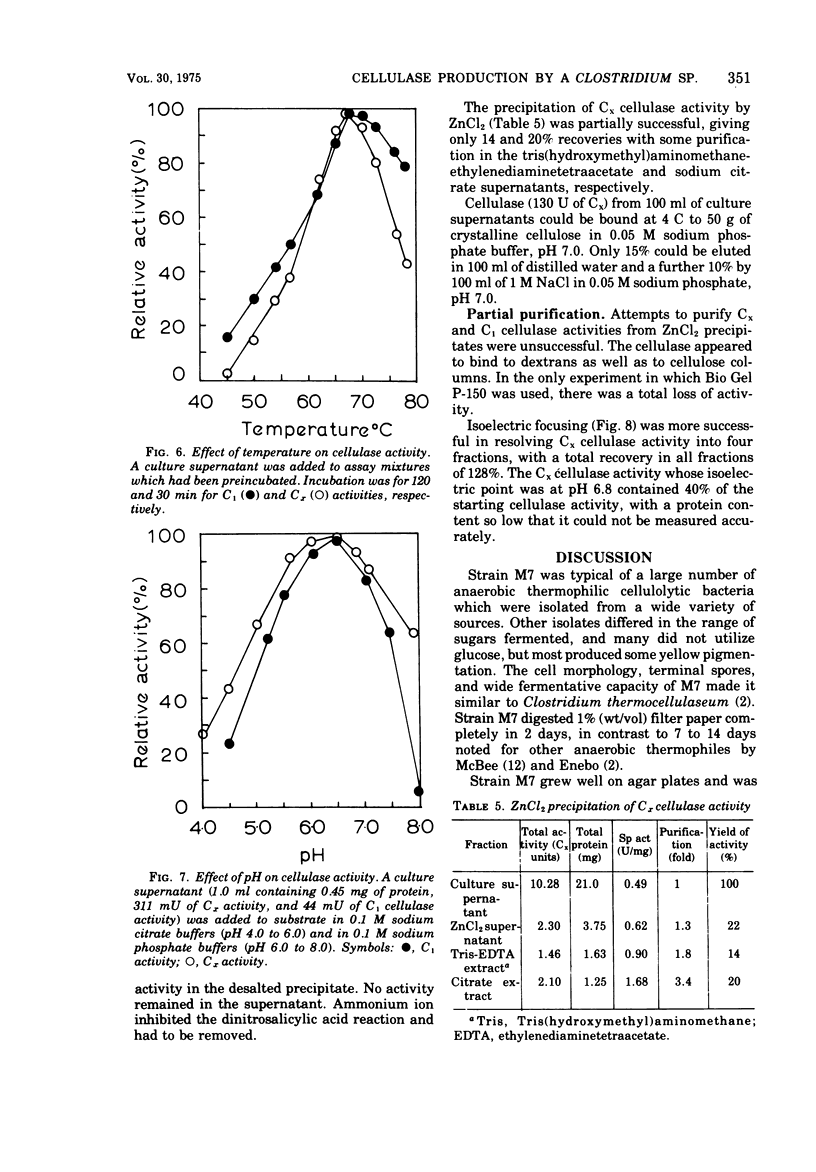
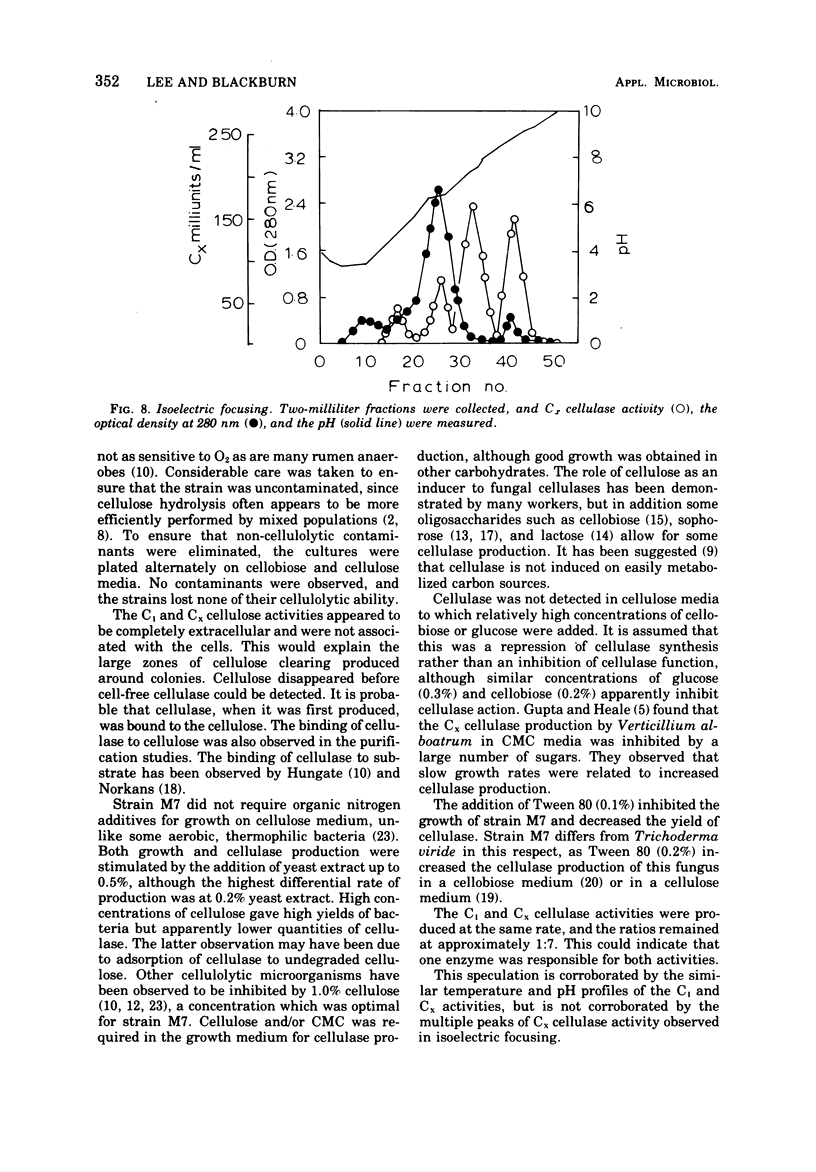
Strain M7, a thermophilic, anaerobic, terminally sporing bacterium (0.6 by 4.0 μm) was isolated from manure. It degraded filter paper in 1 to 2 days at 60 C in a minimal cellulose medium but was stimulated by yeast extract. It fermented a wide variety of sugars but produced cellulase only in cellulose or carboxymethyl-cellulose media. Cellulase synthesis not only was probably repressed by 0.4% glucose and 0.3% cellobiose, but also cellulase activity appeared to be inhibited by these sugars at these concentrations. Both C1 cellulase (degrades native cellulose) and Cx cellulase (β-1,4-glucanase) activities in strain M7 cultures were assayed by measuring the liberation of reducing sugars with dinitrosalicylic acid. Both activities had optima at pH 6.5 and 67 C. One milliliter of a 48-h culture of strain M7 hydrolyzed 0.044-meq of glucose per min from cotton fibers. The cellulase(s) from strain M7 was extracellular, produced during exponential growth, but was not free in the growth medium until approximately 30% of the cellulose was hydrolyzed. Glucose and cellobiose were the major soluble products liberated from cellulose by the cellulase. ZnCl2 precipitation appeared initially to be a good method for the concentration of cellulase activity, but subsequent purification was not successful. Isoelectric focusing indicated the presence of four Cx cellulases (pI 4.5, 6.3, 6.8, and 8.7). The rapid production and high activity of cellulases from this organism strongly support the basic premise that increased hydrolysis of native cellulose is possible at elevated temperature.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ensign J. C., Wolfe R. S. Characterization of a small proteolytic enzyme which lyses bacterial cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):524–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.524-534.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta D. P., Heale J. B. Induction of cellulase (Cx) in Verticillium albo-atrum. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Oct;63(2):163–173. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-2-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G. A microdetermination of cellulose in studies with cellulase. Biochem J. 1958 Apr;68(4):605–610. doi: 10.1042/bj0680605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G. The action of cellulolytic enzymes from Myrothecium verrucaria. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;79:185–192. doi: 10.1042/bj0790185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulme M. A., Stranks D. W. Induction and the regulation of production of cellulase by fungi. Nature. 1970 May 2;226(5244):469–470. doi: 10.1038/226469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungate R. E. Studies on Cellulose Fermentation: I. The Culture and Physiology of an Anaerobic Cellulose-digesting Bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1944 Nov;48(5):499–513. doi: 10.1128/jb.48.5.499-513.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELS M., PARRISH F. W., REESE E. T. Sophorose as an inducer of cellulase in Trichoderma viride. J Bacteriol. 1962 Feb;83:400–408. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.2.400-408.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELS M., REESE E. T. Induction of cellulase in Trichoderma viride as influenced by carbon sources and metals. J Bacteriol. 1957 Feb;73(2):269–278. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.2.269-278.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELS M., REESE E. T. Induction of cellulase in fungi by cellobiose. J Bacteriol. 1960 Jun;79:816–826. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.6.816-826.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBee R. H. The Culture and Physiology of a Thermophilic Cellulose-fermenting Bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1948 Nov;56(5):653–663. doi: 10.1128/jb.56.5.653-663.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisizawa T., Suzuki H., Nakayama M., Nisizawa K. Inductive formation of cellulase by sophorose in Trichoderma viride. J Biochem. 1971 Sep;70(3):375–385. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norkrans B. Cellulose and cellulolysis. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1967;9:91–130. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70526-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese E. T., Maguire A. Surfactants as stimulants of enzyme production by microorganisms. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Feb;17(2):242–245. doi: 10.1128/am.17.2.242-245.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEIN H. [Cholecystography in young infants]. Arch Kinderheilkd. 1961 Nov;165:27–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P. E., Williams S. G. Use of the liquid scintillation spectrometer for determining adenosine triphosphate by the luciferase enzyme. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jun;29(3):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90323-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutzenberger F. J. Cellulase production by Thermomonospora curvata isolated from municipal solid waste compost. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Aug;22(2):147–152. doi: 10.1128/am.22.2.147-152.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]