Abstract
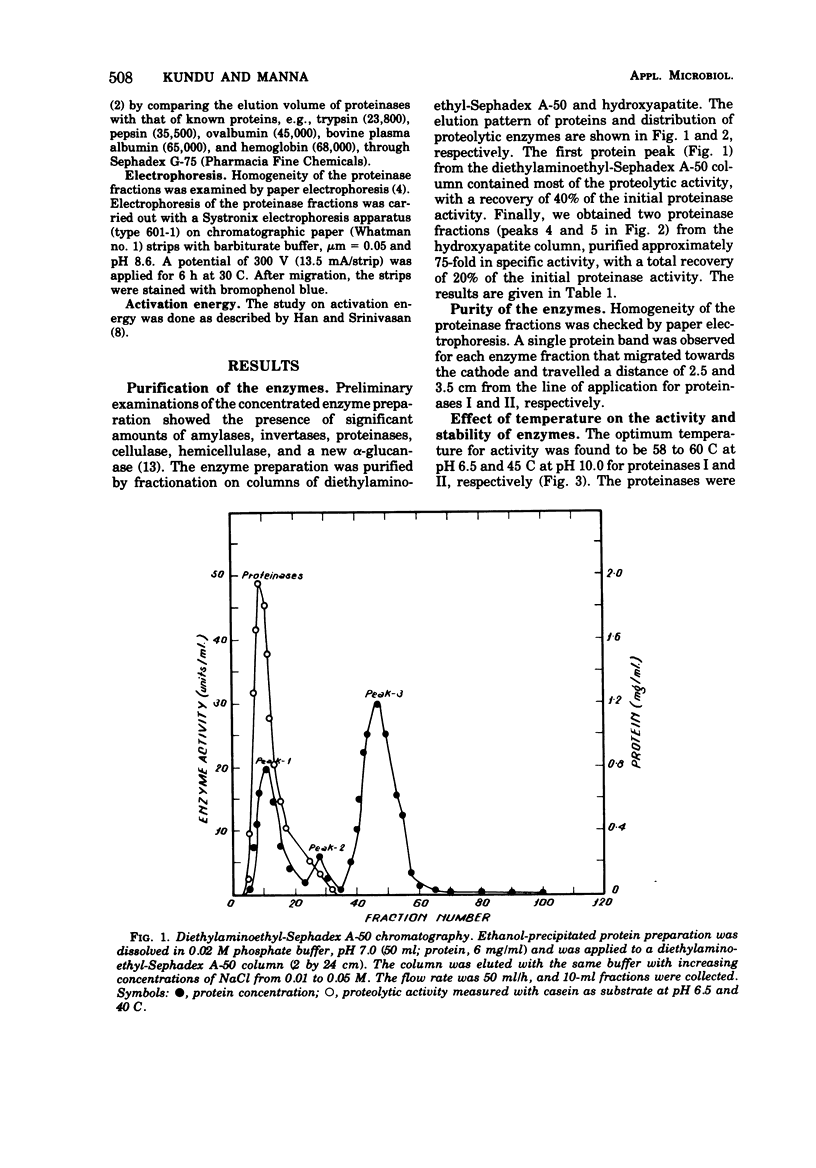
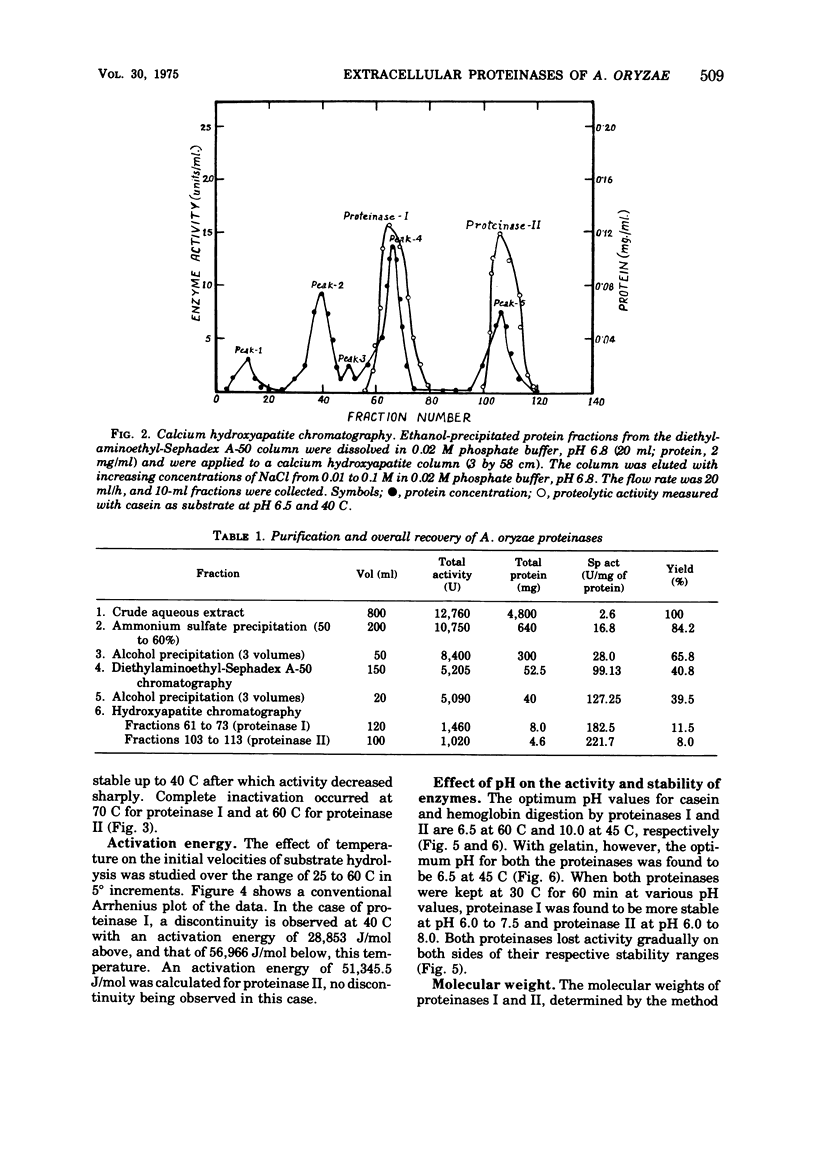
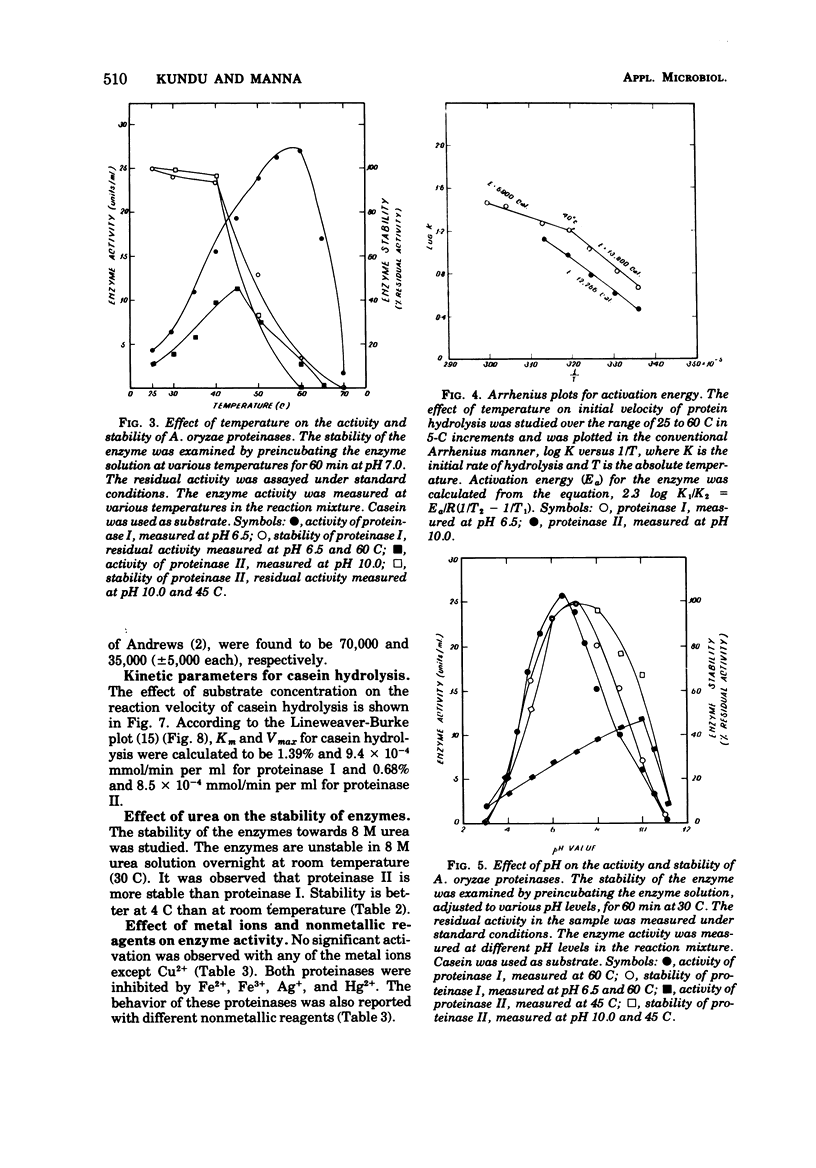
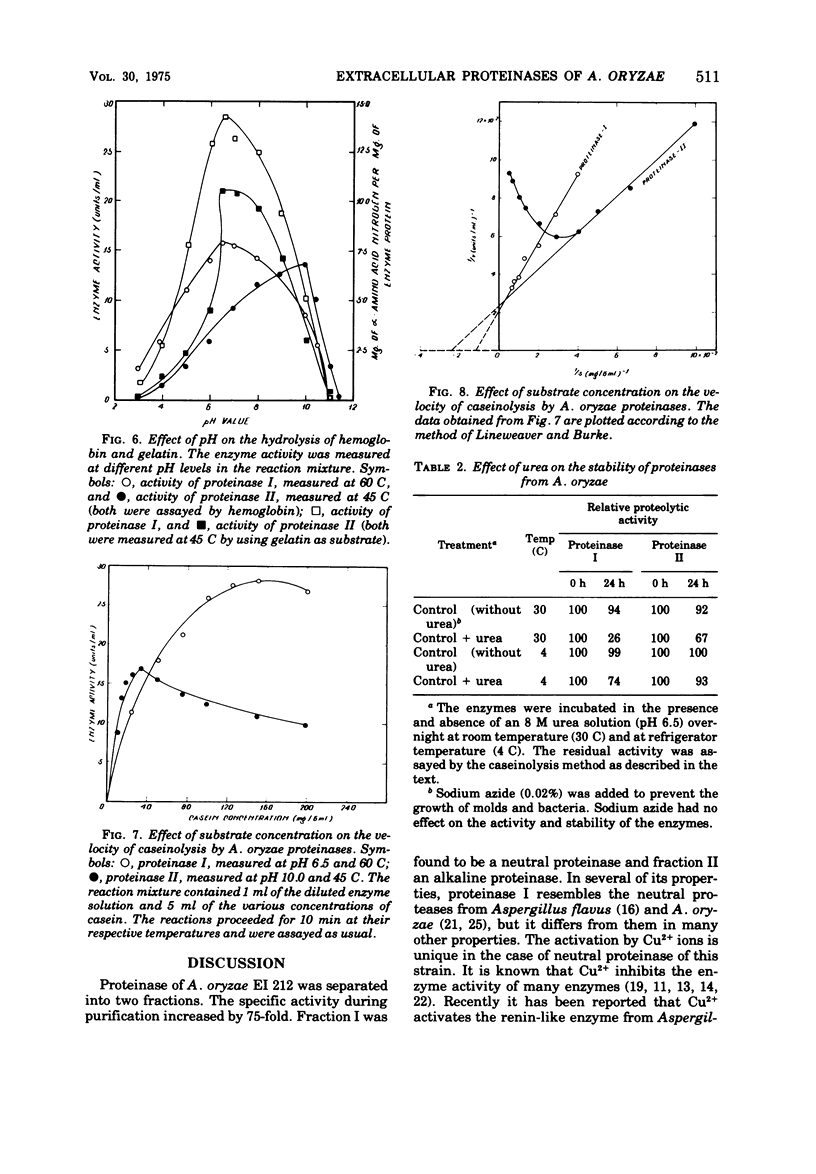
The extracellular proteinases of Aspergillus oryzae EI 212 were separated into two active fractions by (NH4)2SO4 and ethanol fractionation followed by diethyl-aminoethyl-Sephadex A-50 and hydroxyapatite chromatography. The molecular weight was estimated by gel filtration to be about 70,000 and 35,000 for proteinases I and II, respectively. Optimum pH for casein and hemoglobin hydrolysis was 6.5 at 60 C for proteinase I and 10.0 at 45 C for proteinase II, and for gelatin hydrolysis it was 6.5 at 45 C for both enzymes. The enzymes were stable over the pH range 6 to 8 at 30 C for 60 min. The enzyme activity for both the proteinases was accelerated by Cu2+ and inhibited by Fe2+, Fe3+, Hg2+, and Ag+. Halogenators (e.g., N-chlorosuccinimide) and diisopropyl fluorophosphate inhibited proteinase II. Sulfhydryl reagents such as p-chloromercuribenzoate and iodoacetate inhibited proteinase I. Sulfhydryl compounds accelerated the action of both enzymes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christison J., Martin S. M. Isolation and preliminary characterization of an extracellular protease of Cytophaga sp. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Sep;17(9):1207–1216. doi: 10.1139/m71-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS N. C., SMITH E. L. Assay of proteolytic enzymes. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:215–257. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJERTEN S., LEVIN O., TISELIUS A. Protein chromatography on calcium phosphate columns. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Nov;65(1):132–155. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han Y. W., Srinivasan V. R. Purification and characterization of beta-glucosidase of Alcaligenes faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1355–1363. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1355-1363.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundu A. K., Das S., Manna S., Pal N. Extracellular proteinases of Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Nov;16(11):1799–1801. doi: 10.1128/am.16.11.1799-1801.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundu A. K., Das S. Production of amylase in liquid culture by a strain of Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Apr;19(4):598–603. doi: 10.1128/am.19.4.598-603.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundu A. K., Manna S., Pal N. Purification and properties of a new extracellular collagenase from Aspergillus sclerotiorum. Indian J Exp Biol. 1974 Sep;12(5):441–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundu A. K., Manna S. Purification and properties of a new alpha-glucanase from Aspergillus oryzae. Indian J Exp Biol. 1971 Jan;9(1):75–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysenkov N. V., Tsyperovich A. S. Vlastyvosti proteazy Aspergillus flavus. Ukr Biokhim Zh. 1969;41(2):157–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASSEY V. Studies on fumarase. III. The effect of temperature. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):72–79. doi: 10.1042/bj0530072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordwig A., Jahn W. F. A collagenolytic enzyme from Aspergillus oryzae. Purification and properties. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Feb;3(4):519–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb19562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordwig A., Jahn W. F. Spezifitätseigenschaften einer Protease aus Aspergillus oryzae. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1966;345(4):284–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleniacz W. S., Pisano M. A. Proteinase production by a species of Cephalosporium. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jan;16(1):90–96. doi: 10.1128/am.16.1.90-96.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heyningen S., Secher D. S. A new alkaline protease from Acremonium kiliense. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(4):1159–1160. doi: 10.1042/bj1251159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


