Abstract
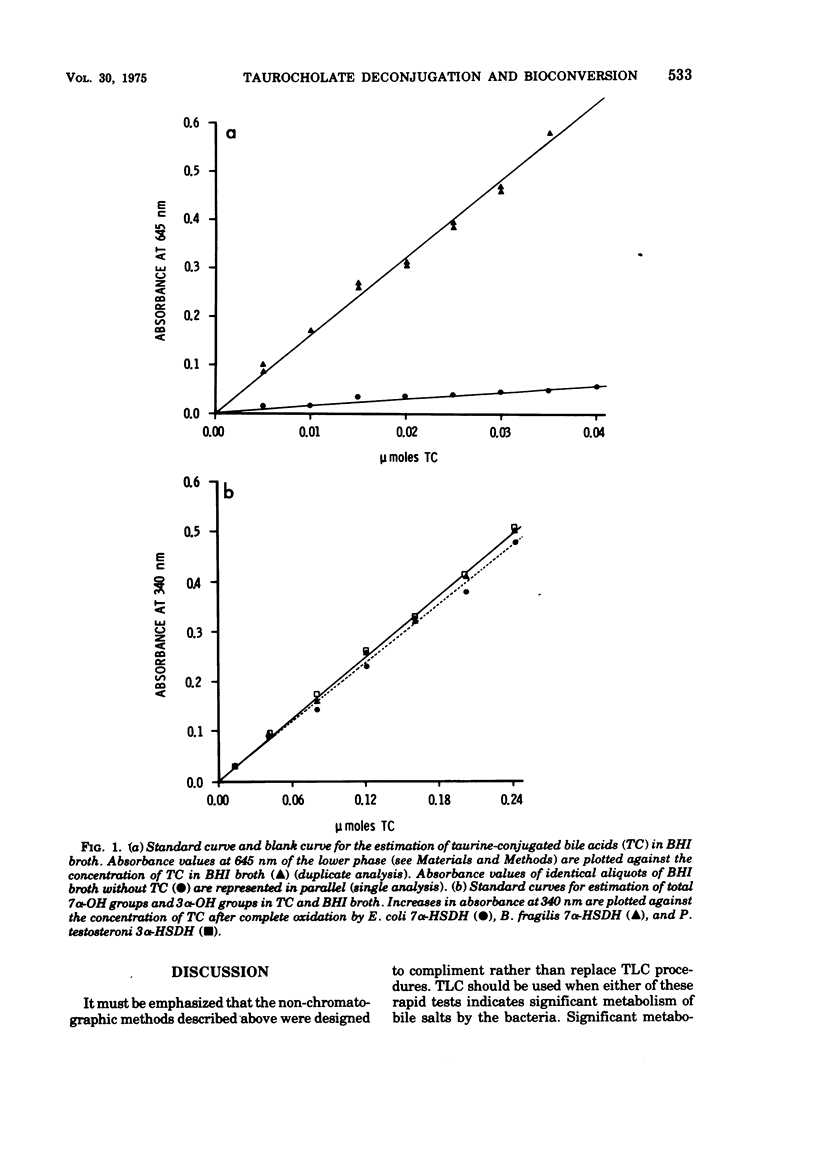
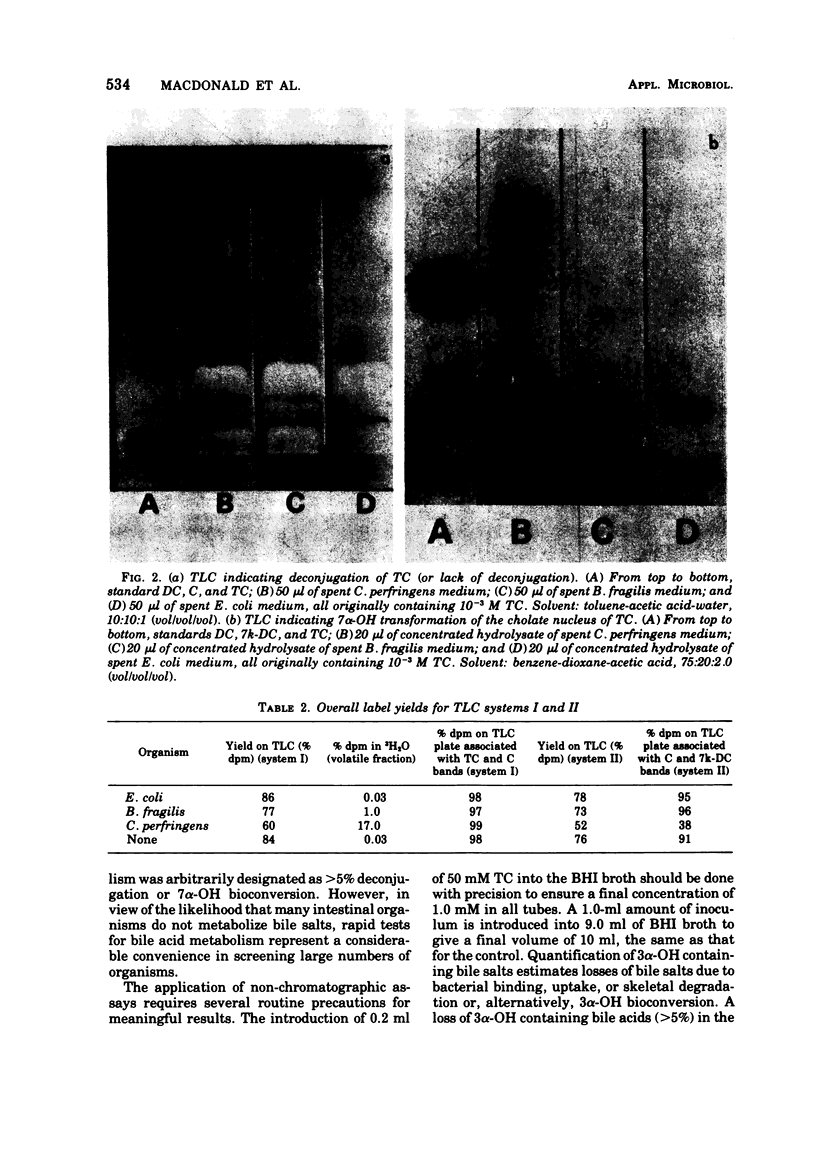
We described two convenient assay methods to estimate bile acid deconjugation and bile acid bioconversion at the 7α-OH position by individual microorganisms grown in media containing taurocholic acid. The methods are based on (i) a selective chemical assay for taurine conjugates previously described and (ii) the use of a cell-free preparation of 7α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli to directly quantify 7α-OH groups. These non-chromatographic approaches have been applied to the study of three model strains of intestinal organisms, E. coli, Bacteriodes fragilis, and Clostridium perfringens, grown in standard media in the presence of purified tritiated taurocholate. Assay results were confirmed by thin-layer chromatography solvent systems designed to separate conjugated from unconjugated bile acid and unmodified cholic acid nucleus from 7α-OH bioconversion product(s) (primarily 3α,12α dihydroxy, 7-keto-cholanoic acid). In addition, 7α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity was demonstrated in cell-free extracts of all three organisms. Of the three organisms, only C. perfringens was demonstrated to (i) deconjugate taurocholic acid, (ii) contain 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity, (iii) convert cholic acid into at least five labeled metabolites visible on thin-layer chromatography, and (iv) catalyze significant tritium exchange with water in the medium.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aries V., Hill M. J. Degradation of steroids by intestinal bacteria. I. Deconjugation of bile salts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 5;202(3):526–534. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aries V., Hill M. J. Degradation of steroids by intestinal bacteria. II. Enzymes catalysing the oxidoreduction of the 3 alpha-, 7 alpha- and 12 alpha-hydroxyl groups in cholic acid, and the dehydroxylation of the 7-hydroxyl group. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 5;202(3):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Filburn B., Floch M. Bile acid inhibition of intestinal anaerobic organisms. Am J Clin Nutr. 1975 Feb;28(2):119–125. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/28.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie W. H., Macdonald I. A., Williams C. N. Non chromatographic colorimetric assay for total taurine-conjugated bile acids: application of measurements of glycine: taurine ratio in bile. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Mar;85(3):505–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson A. B., Gustafsson B. E., Norman A. Determination of bile acid conversion potencies of intestinal bacteria by screening in vitro and subsequent establishment in germfree rats. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(5):691–698. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENEROTH P. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF BILE ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1963 Jan;4:11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., Attebery H. R., Sutter V. L. Effect of diet on human fecal flora: comparison of Japanese and American diets. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Dec;27(12):1456–1469. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.12.1456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslewood G. A., Murphy G. M., Richardson J. M. A direct enzymic assay for 7 -hydroxy bile acids and their conjugates. Clin Sci. 1973 Jan;44(1):95–98. doi: 10.1042/cs0440095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa S. Microbiological transformation of bile acids. Adv Lipid Res. 1973;11:143–192. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024911-4.50011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. J., Drasar B. S. Degradation of bile salts by human intestinal bacteria. Gut. 1968 Feb;9(1):22–27. doi: 10.1136/gut.9.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IWATA T., YAMASAKI K. ENZYMATIC DETERMINATION AND THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF BILE ACIDS IN BLOOD. J Biochem. 1964 Nov;56:424–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRusso N. F., Hoffman N. E., Hofmann A. F. Validity of using 2,4-3H-labeled bile acids to study bile acid kinetics in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Nov;84(5):759–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R., Gorbach S. Modification of bile acids by intestinal bacteria. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Oct;130(4):545–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald I. A., Williams C. N., Mahony D. E. 7Alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli B: preliminary studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 6;309(2):243–253. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald I. A., Williams C. N., Mahony D. E. A 3 alpha- and 7 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase assay for conjugated dihydroxy-bile acid mixtures. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jan;57(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald I. A., Williams C. N., Mahony D. E., Christie W. M. NAD- and NADP-dependent 7alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases from bacteroides fragilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 28;384(1):12–24. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midtvedt T., Norman A. Anaerobic, bile acid transforming microorganisms in rat intestinal content. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;72(2):337–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb01347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair P. P., Gordon M., Gordon S., Reback J., Mendeloff A. I. The cleavage of bile acid conjugates by cell-free extracts from Clostridium perfringens. Life Sci. 1965 Oct;4(19):1887–1892. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair P. P., Gordon M., Reback J. The enzymatic cleavage of the carbon-nitrogen bond in 3-alpha, 7-alpha, 12-alpha-trihydroxy-5-beta-cholan-24-oylglycine. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 10;242(1):7–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panveliwalla D. K., Pertsemlidis D., Ahrens E. H., Jr Tritiated bile acids: problems and recommendations. J Lipid Res. 1974 Sep;15(5):530–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]