Abstract
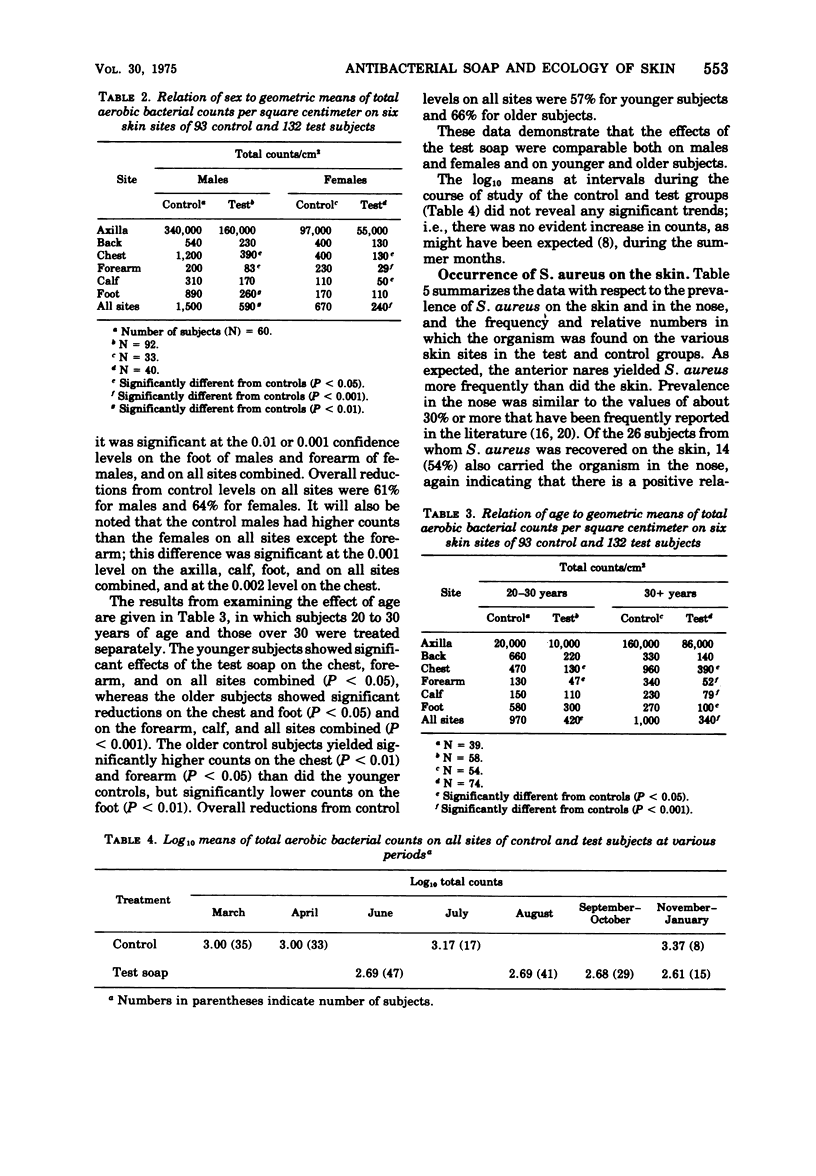
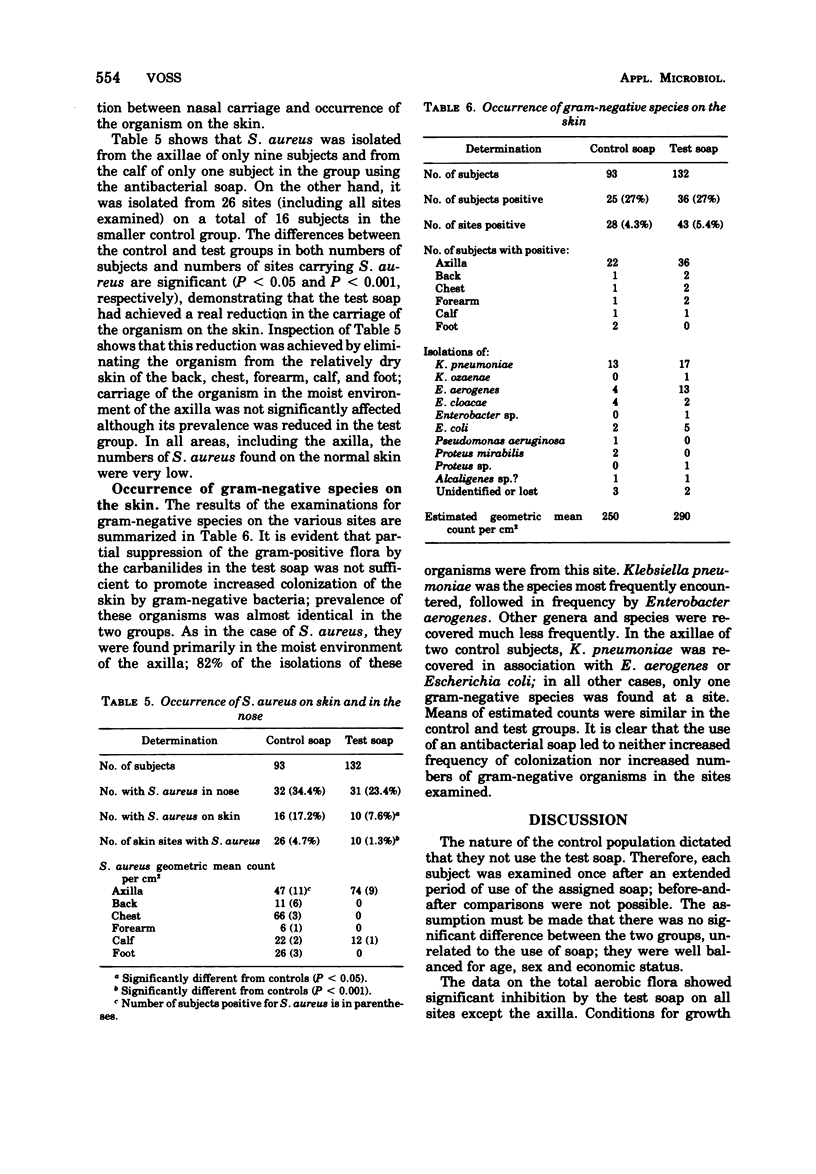
The effects of ad lib use of an antibacterial soap containing 1.0% trichlorocarbanilide and 0.5% trifluoromethyldichlorocarbanilide on the bacterial flora of six skin sites of 132 subjects were measured by comparison with the flora of 93 control subjects who avoided the use of topical antibacterials. Each subject was examined once. The test soap produced significant reductions in geometric mean counts of the total aerobic flora on the back, chest, forearm, calf, and foot; counts were also reduced in the axilla, but not to a significant extent. The overall reduction by the test soap on all sites was 62% (P < 0.001). Neither age nor sex influenced the effect of the soap on the flora. The antibacterial soap also reduced the prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus on the skin, mostly by virtually eliminating it from areas other than the axilla. Partial inhibition of the gram-positive flora was not accompanied by an increase in gram-negative species. The latter were found principally in the axilla; Klebsiella pneumoniae and Enterobacter aerogenes were the species most frequently found.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen A. M., Taplin D. Skin infections in eastern Panama. Survey of two representative communities. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1974 Sep;23(5):950–956. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1974.23.950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen A. M., Taplin D., Twigg L. Cutaneous streptococcal infections in Vietnam. Arch Dermatol. 1971 Sep;104(3):271–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewar N. E., Gravens D. L. Effectiveness of septisol antiseptic foam as a surgical scrub agent. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Oct;26(4):544–549. doi: 10.1128/am.26.4.544-549.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudding B. A., Burnett J. W., Chapman S. S., Wannamaker L. W. The role of normal skin in the spread of streptococcal pyoderma. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Mar;68(1):19–28. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400028461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan W. C., Dodge B. G., Knox J. M. Prevention of superficial pyogenic skin infections. Arch Dermatol. 1969 Apr;99(4):465–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan W. C., McBride M. E., Knox J. M. Bacterial flora. The role of environmental factors. J Invest Dermatol. 1969 May;52(5):479–484. doi: 10.1038/jid.1969.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans Z. A., Rendtorff R. C., Robinson H., Rosenberg E. W. Ecological influence of hexachlorophene on skin bacteria. J Invest Dermatol. 1973 Apr;60(4):207–214. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12724479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forfar J. O., Gould J. C., Maccabe A. F. Effect of hexachlorophane on incidence of staphylococcal and gram-negative infection in the newborn. Lancet. 1968 Jul 27;2(7561):177–179. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92618-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. R. Prevention of superficial cutaneous infections. Arch Dermatol. 1967 May;95(5):520–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light I. J., Sutherland J. M., Cochran M. L., Sutorius J. Ecologic relation between Staphylococcus aureus and pseudomonas in a nursery population. Another example of bacterial interference. N Engl J Med. 1968 Jun 6;278(23):1243–1247. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196806062782301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie A. R. Effectiveness of antibacterial soaps in a healthy population. JAMA. 1970 Feb 9;211(6):973–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marples R. R., Williamson P. Effects of systemic demethylchlortetracycline on human cutaneous microflora. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Aug;18(2):228–234. doi: 10.1128/am.18.2.228-234.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaud R. N., McGrath M. B., Goss W. A. Improved experimental model for measuring skin degerming activity on the human hand. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jul;2(1):8–15. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phair J. P., Watanakunakorn C., Goldberg L., Carleton J. Ecology of staphylococci in a general medical service. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Dec;24(6):967–971. doi: 10.1128/am.24.6.967-971.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUINN H., VOSS J. G., WHITEHOUSE H. S. A method for the in vivo evaluation of skin sanitizing soaps. Appl Microbiol. 1954 Jul;2(4):202–204. doi: 10.1128/am.2.4.202-204.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEHADEH N. H., KLIGMAN A. M. The effect of topical antibacterial agents on the bacterial flora of the axilla. J Invest Dermatol. 1963 Jan;40:61–71. doi: 10.1038/jid.1963.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrett A. R., Finklea J. F., Potter E. V., Poon-King T., Earle D. P. The control of streptococcal skin infections in South Trinidad. Am J Epidemiol. 1974 Jun;99(6):408–413. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taplin D., Lansdell L., Allen A. M., Rodriguez R., Cortes A. Prevalence of streptococcal pyoderma in relation to climate and hygiene. Lancet. 1973 Mar 10;1(7802):501–503. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90324-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson P., Kligman A. M. A new method for the quantitative investigation of cutaneous bacteria. J Invest Dermatol. 1965 Dec;45(6):498–503. doi: 10.1038/jid.1965.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. E. A comparison of methods for assessing the value of antibacterial soaps. J Appl Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;33(3):574–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1970.tb02236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



