Abstract
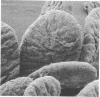
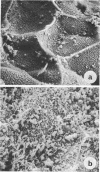
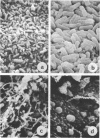
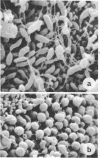
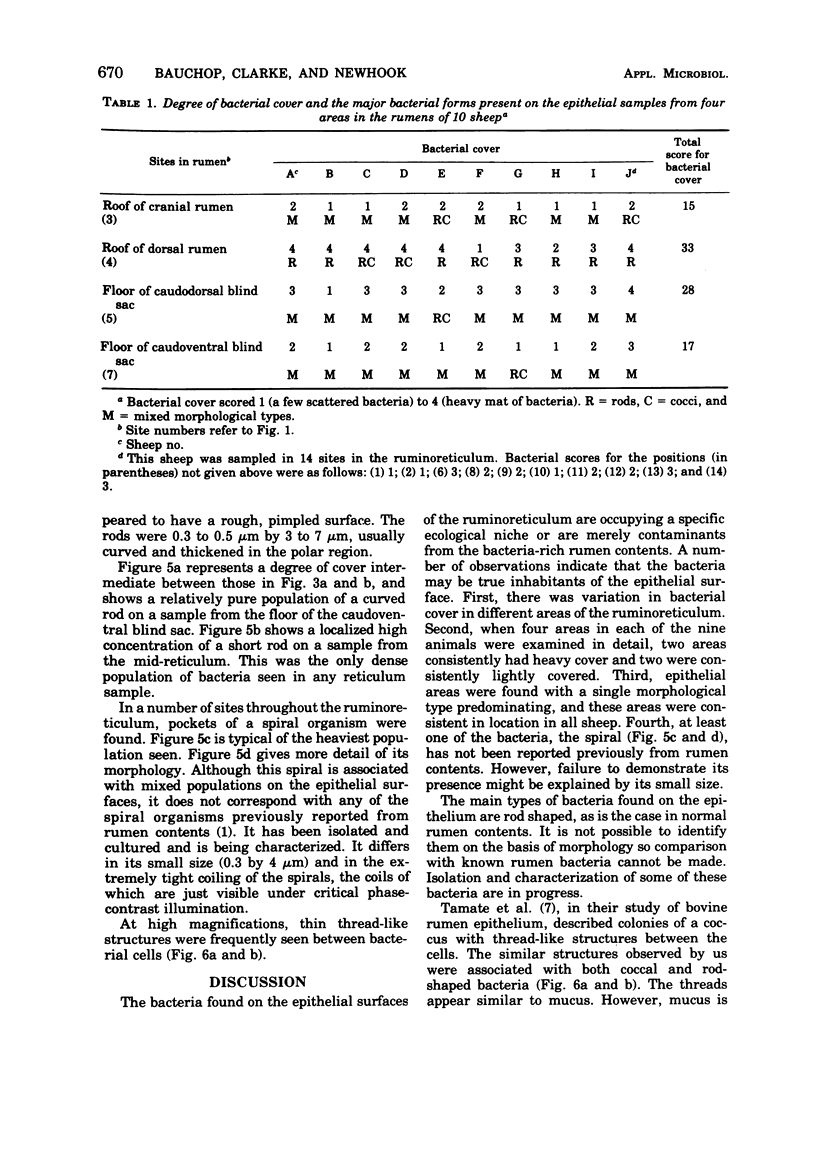
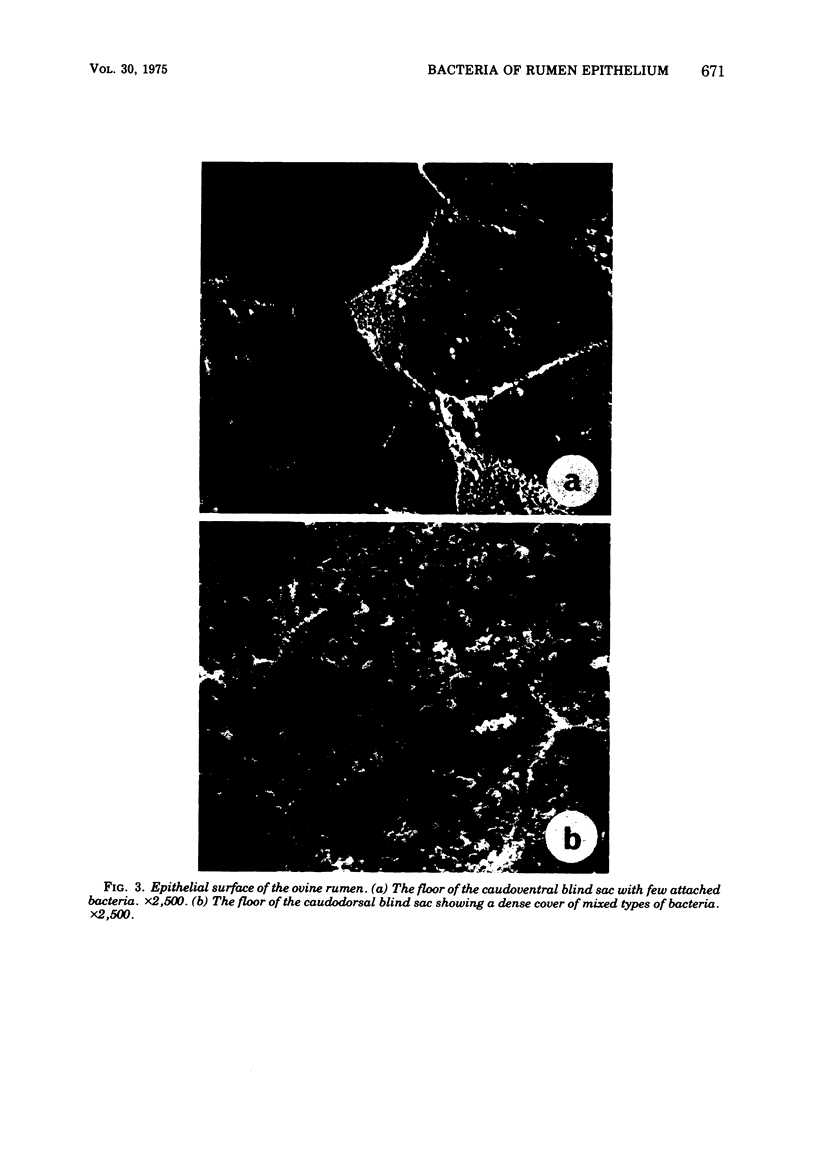
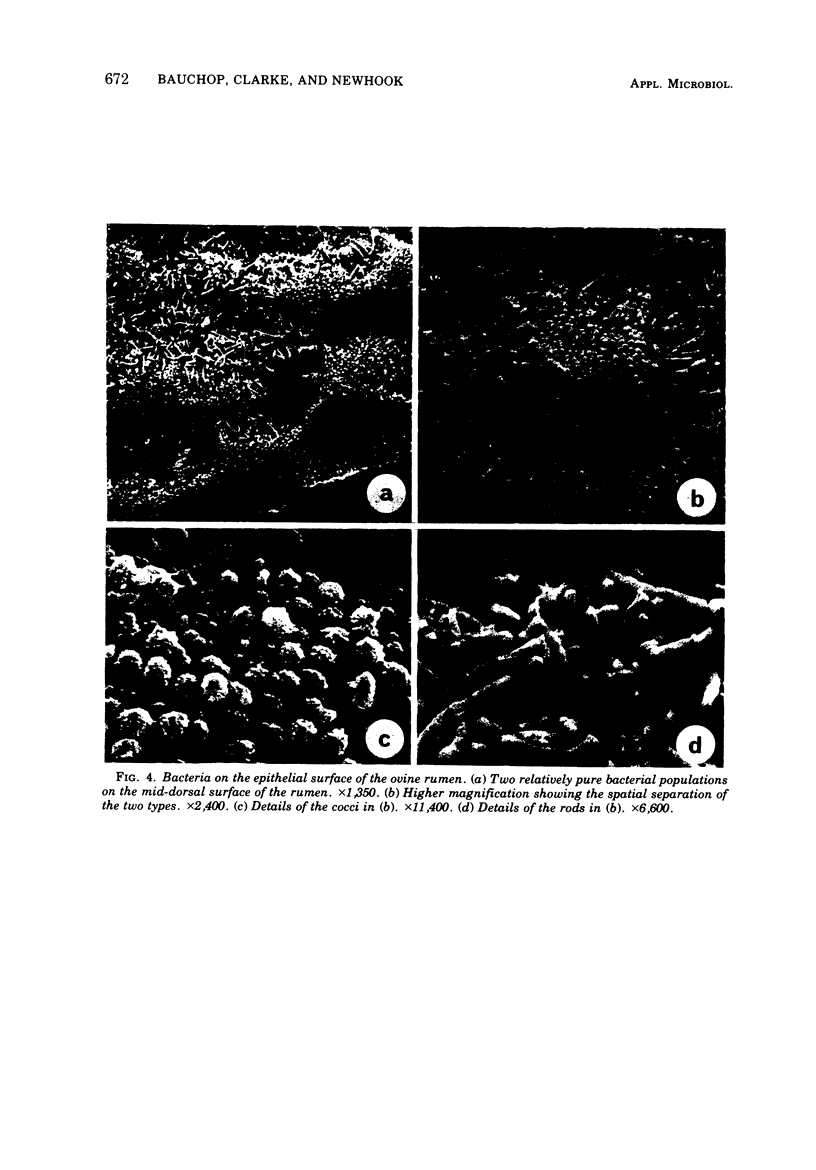
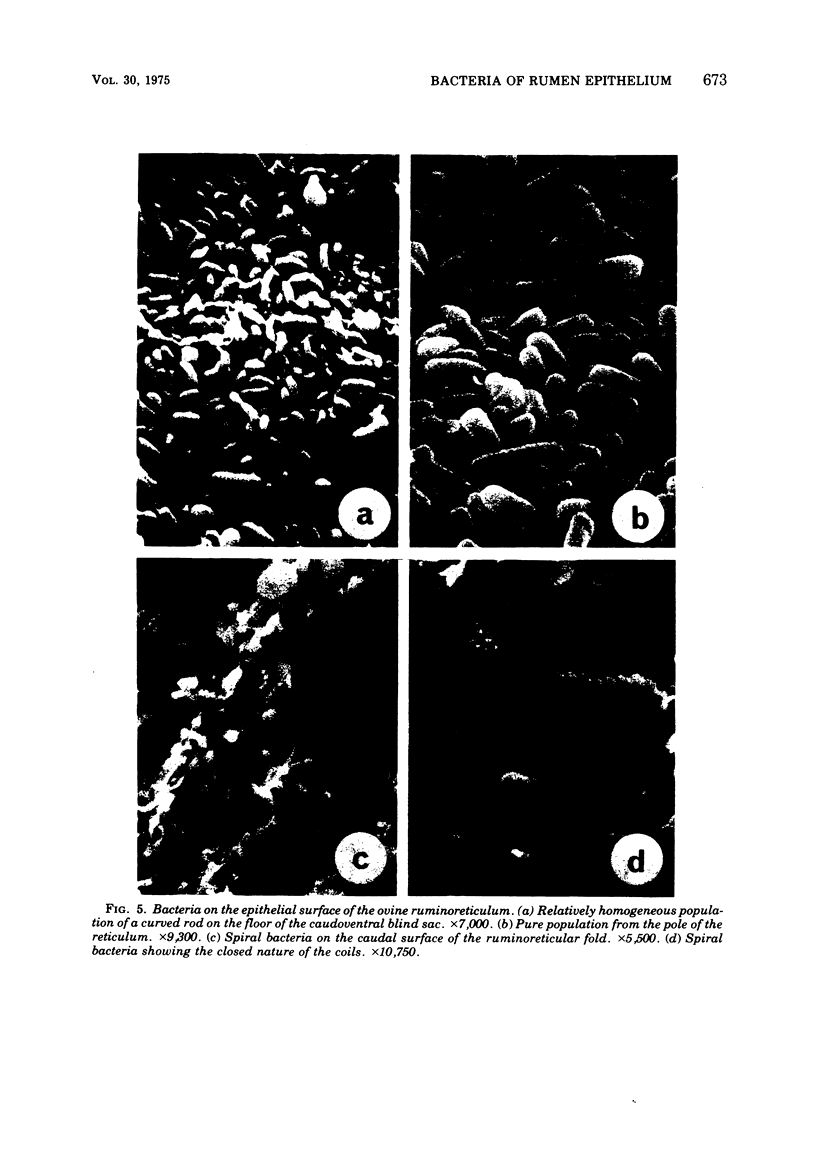
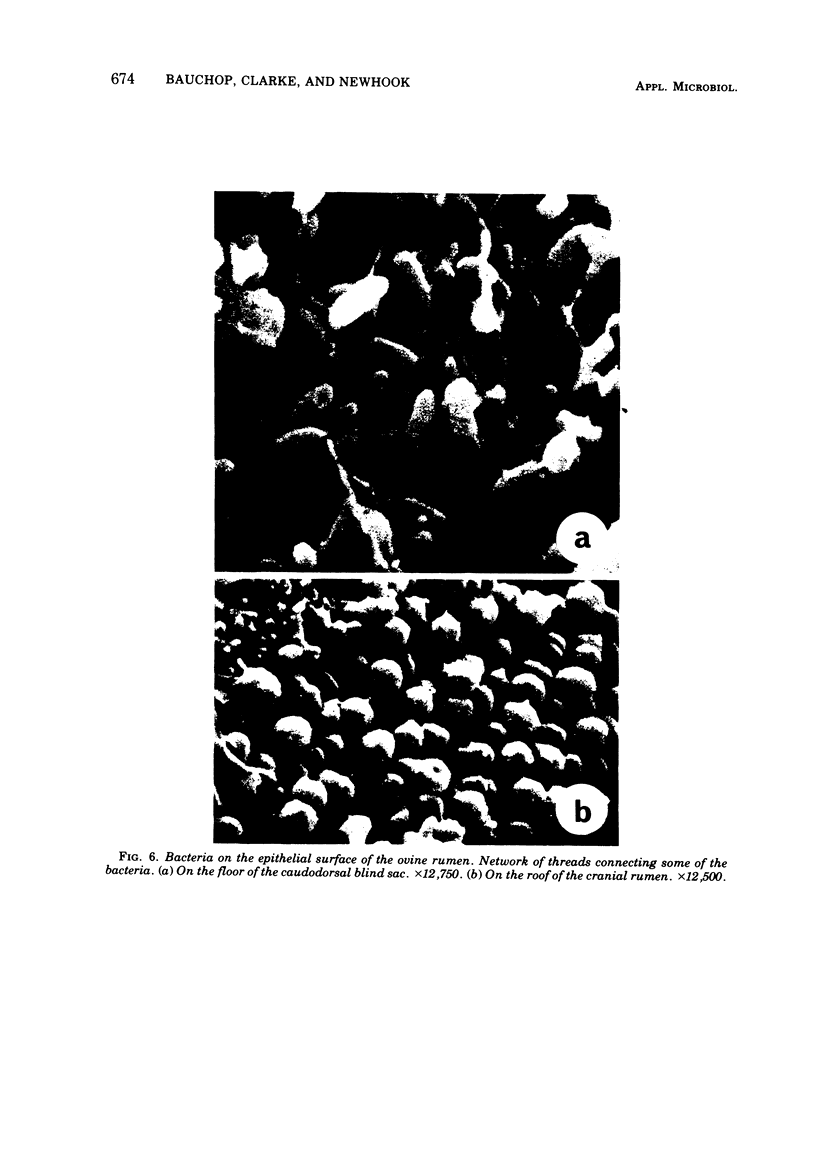
Examination of the rumen epithelium of sheep by scanning electron microscopy revealed bacteria associated with the epithelial surface. Comparison of epithelial surfaces from 10 sheep revealed areas that were consistently densely covered with bacteria and other areas where the cover was consistently light. The bacterial populations were frequently of mixed morphological types, but areas populated with a single type were also observed. This finding, together with the discovery of bacterial forms not previously described in rumen contents, suggests that a specific flora may exist on the rumen epithelial surface. The functional significance of such a population is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYANT M. P. The isolation and characteristics of a spirochete from the bovine rumen. J Bacteriol. 1952 Sep;64(3):325–335. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.3.325-335.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R., Turvey A. [Bacteria associated with the intestinal wall of the fowl (Gallus domesticus)]. J Appl Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;34(3):617–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1971.tb02325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner I. C., Scott A. Lysosomal structures in the stratum corneum of the ruminal epithelium of the sheep. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch. 1972;86(2):297–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Associations and physiological interactions of indigenous microorganisms and gastrointestinal epithelia. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1372–1379. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamate H., Kikuchi T., Onodera A., Nagatani T. Scanning electron microscopic observation on the surface structure of the bovine rumen mucosa. Arch Histol Jpn. 1971 Oct;33(4):273–282. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.33.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolton D. P., Stanley C., Savage D. C. Influence of the indigenous gastrointestinal microbial flora on duodenal alkaline phosphatase activity in mice. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):768–773. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.768-773.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]