Abstract
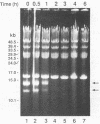
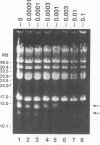
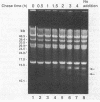
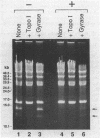
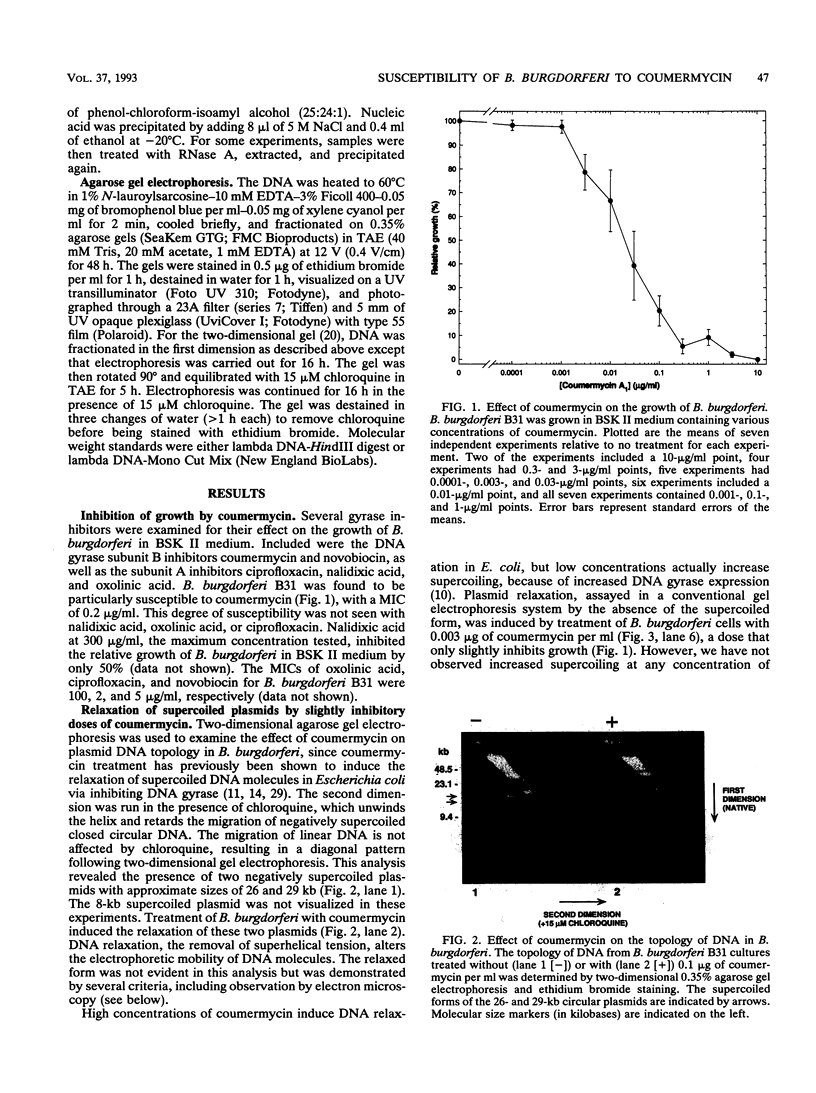
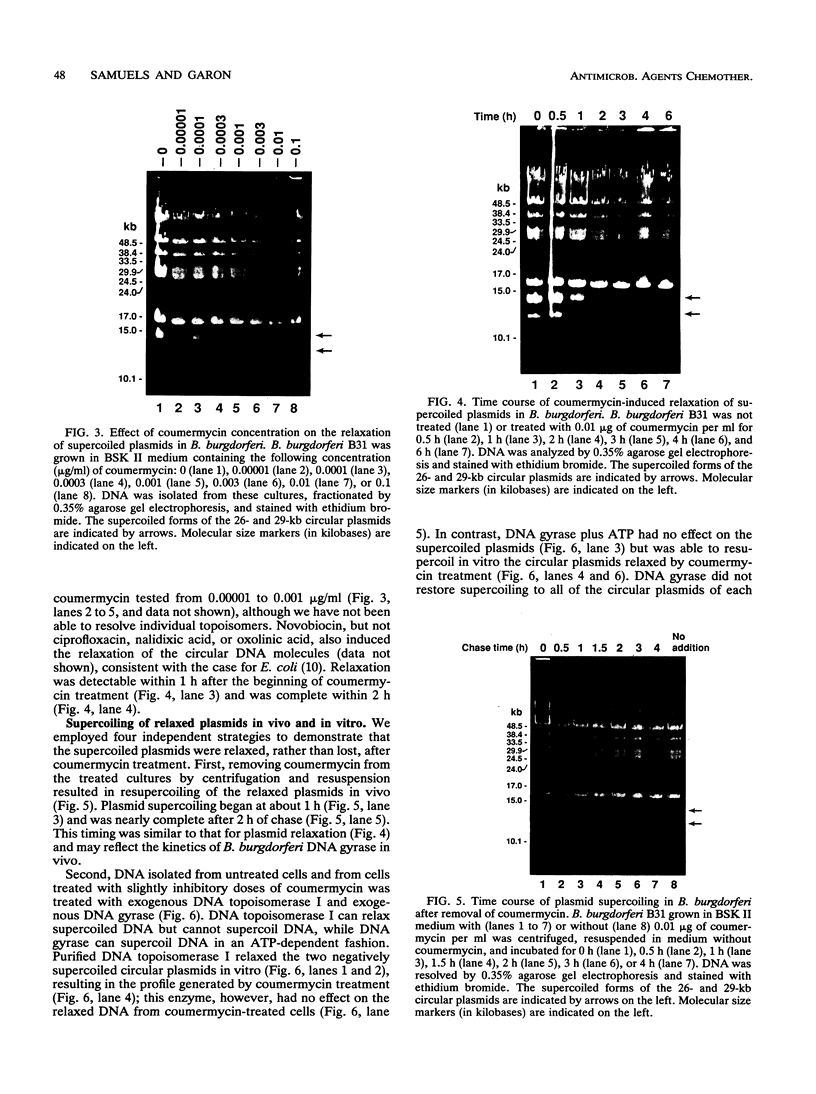
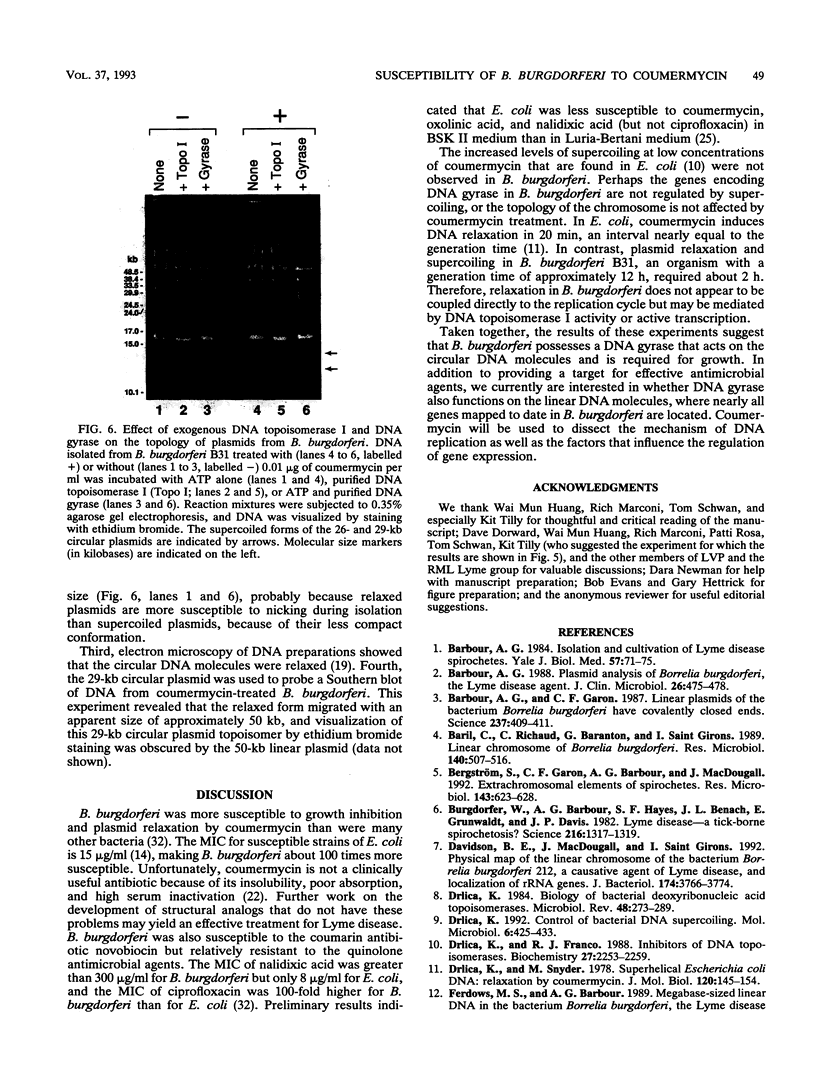
Coumermycin A1 is an inhibitor of DNA gyrase, an enzyme that catalyzes supercoiling of DNA and is required for bacterial DNA replication. We have investigated the activity of this coumarin antibiotic on Borrelia burgdorferi, a spirochete and the causative agent of Lyme disease. B. burgdorferi was more susceptible than many other eubacteria to coumermycin as well as novobiocin, another coumarin antibiotic; this contrasted with its relative resistance to the DNA gyrase inhibitors nalidixic acid, oxolinic acid, and ciprofloxacin. Coumermycin at 0.2 micrograms/ml inhibited the growth of B. burgdorferi B31 in BSK II medium. A 100-fold-lower concentration induced the relaxation of two negatively supercoiled circular plasmids within 2 h. Plasmid supercoiling was restored within 2 h of removal of coumermycin. These results suggest that B. burgdorferi has a DNA gyrase and that this enzyme's activity is required for growth. Furthermore, structural analogs of coumermycin may be considered as treatments for Lyme disease.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G., Garon C. F. Linear plasmids of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi have covalently closed ends. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):409–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3603026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Plasmid analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):475–478. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.475-478.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baril C., Richaud C., Baranton G., Saint Girons I. S. Linear chromosome of Borrelia burgdorferi. Res Microbiol. 1989 Oct;140(8):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Garon C. F., Barbour A. G., MacDougall J. Extrachromosomal elements of spirochetes. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jul-Aug;143(6):623–628. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90120-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B. E., MacDougall J., Saint Girons I. Physical map of the linear chromosome of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi 212, a causative agent of Lyme disease, and localization of rRNA genes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3766–3774. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3766-3774.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K. Biology of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid topoisomerases. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):273–289. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.273-289.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K. Control of bacterial DNA supercoiling. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):425–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Franco R. J. Inhibitors of DNA topoisomerases. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2253–2259. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Snyder M. Superhelical Escherichia coli DNA: relaxation by coumermycin. J Mol Biol. 1978 Apr 5;120(2):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. Novobiocin and coumermycin inhibit DNA supercoiling catalyzed by DNA gyrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch J., Barbour A. G. Linear plasmids of Borrelia burgdorferi have a telomeric structure and sequence similar to those of a eukaryotic virus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7233–7239. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7233-7239.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde F. W., Johnson R. C. Genetic relationship of lyme disease spirochetes to Borrelia, Treponema, and Leptospira spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):151–154. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.151-154.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:351–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss G. J. DNA topoisomerase I mutants. Increased heterogeneity in linking number and other replicon-dependent changes in DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 5;185(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss G. J., Drlica K. DNA supercoiling and prokaryotic transcription. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):521–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90574-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reece R. J., Maxwell A. DNA gyrase: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;26(3-4):335–375. doi: 10.3109/10409239109114072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P. A., Schwan T. G. A specific and sensitive assay for the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi using the polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):1018–1029. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rádl S. Structure-activity relationships in DNA gyrase inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;48(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90014-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Garon C. F., Schwan T. G. Analysis of supercoiled circular plasmids in infectious and non-infectious Borrelia burgdorferi. Microb Pathog. 1990 Feb;8(2):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Higgins N. P., Brown P. O., Peebles C. L., Cozzarelli N. R. Energy coupling in DNA gyrase and the mechanism of action of novobiocin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4838–4842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. A., Gootz T. D., Barrett J. F. Biochemical characteristics and physiological significance of major DNA topoisomerases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Dec;33(12):2027–2033. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.12.2027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Recent studies of DNA topoisomerases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 6;909(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer C., Störl K., Störl J. Microbial DNA topoisomerases and their inhibition by antibiotics. J Basic Microbiol. 1990;30(3):209–224. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3620300312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]