Abstract
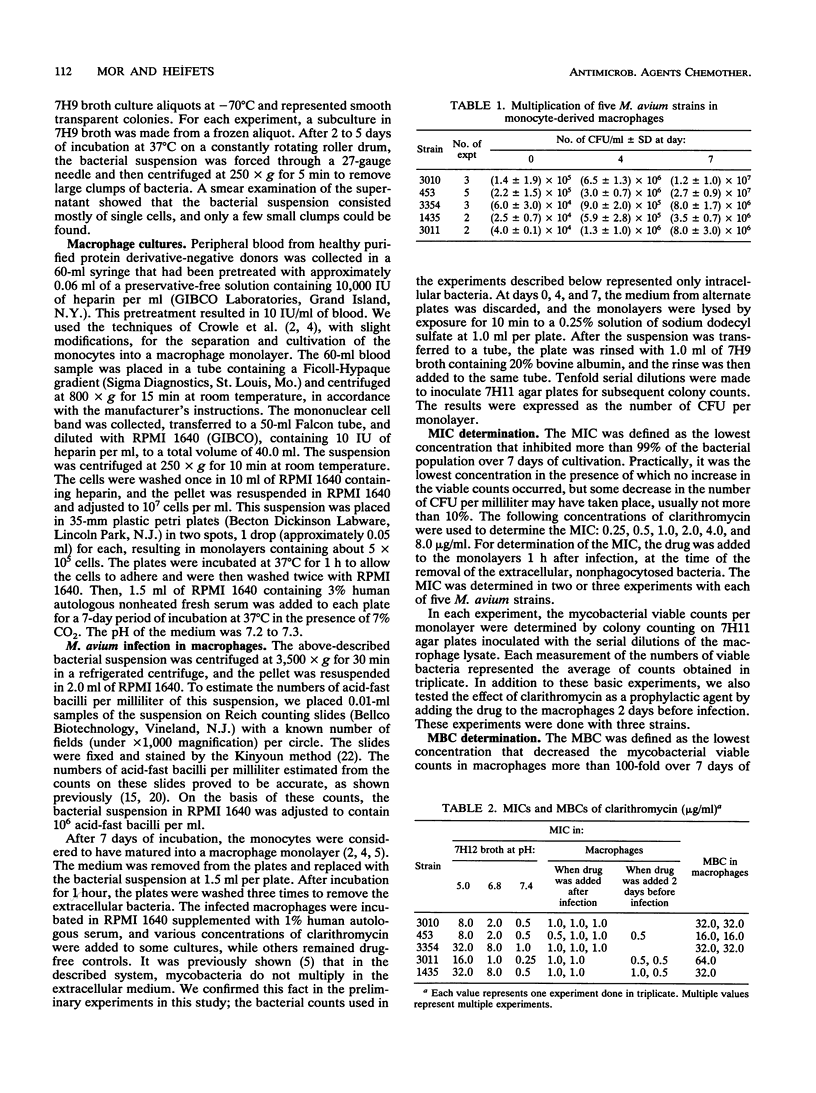
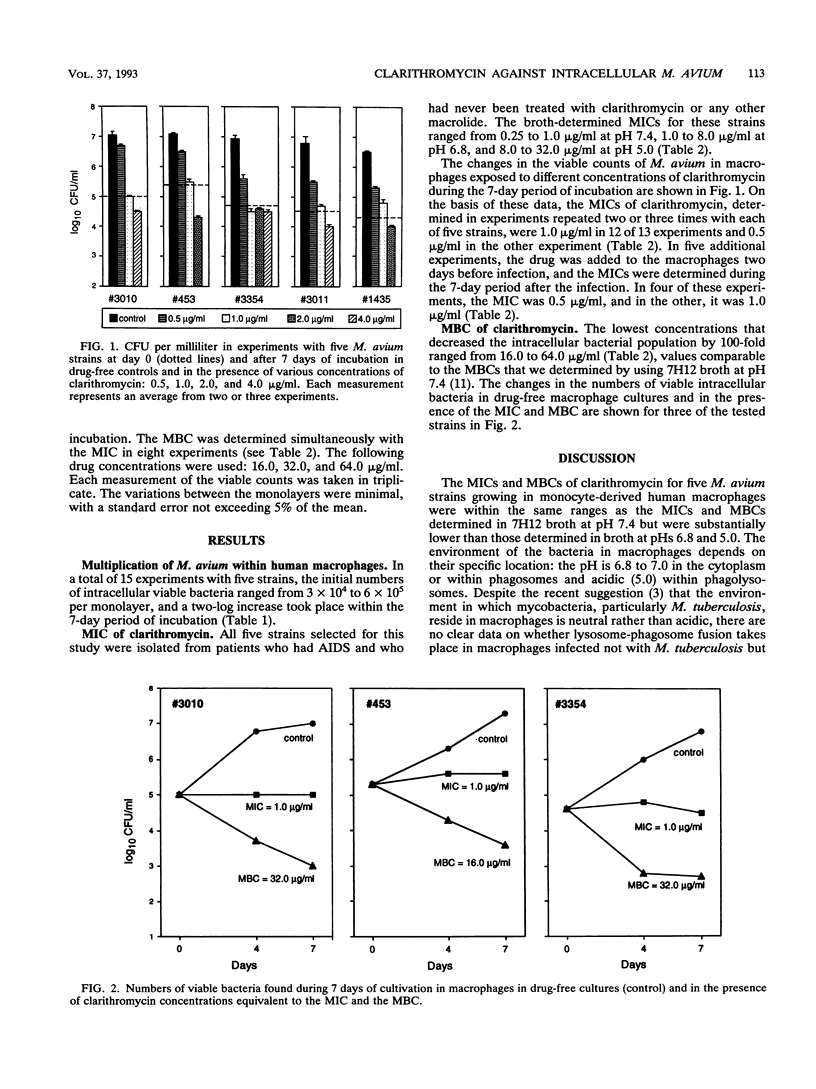
The inhibitory and bactericidal activities of clarithromycin were determined quantitatively against the intracellular populations of five Mycobacterium avium strains growing in monocyte-derived human macrophages. The MICs were 1.0 microgram/ml, and the MBCs ranged from 16.0 to 64.0 micrograms/ml; these values were similar to the MICs and MBCs found in broth cultures at pH 7.4 and were substantially lower than those found in broth cultures at pHs 6.8 and 5.0. Since the intracellular environment has a neutral or even an acidic pH, relatively low MICs and MBCs found in macrophage cultures can be associated with the fact that the drug concentrations in macrophages are substantially higher than those in the medium in which these cells are cultivated. Pretreatment of the macrophages 2 days prior to infection decreased the MICs twofold in comparison with results of experiments in which the drug was added to already infected macrophages.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahal N., Nahata M. C. The new macrolide antibiotics: azithromycin, clarithromycin, dirithromycin, and roxithromycin. Ann Pharmacother. 1992 Jan;26(1):46–55. doi: 10.1177/106002809202600112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Dahl R., Ross E., May M. H. Evidence that vesicles containing living, virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis or Mycobacterium avium in cultured human macrophages are not acidic. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1823–1831. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1823-1831.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Elkins N., May M. H. Effectiveness of ofloxacin against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium, and rifampin against M. tuberculosis in cultured human macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 May;137(5):1141–1146. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.5.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., May M. Preliminary demonstration of human tuberculoimmunity in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):453–464. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.453-464.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Tsang A. Y., Vatter A. E., May M. H. Comparison of 15 laboratory and patient-derived strains of Mycobacterium avium for ability to infect and multiply in cultured human macrophages. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):812–821. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.812-821.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dautzenberg B., Truffot C., Legris S., Meyohas M. C., Berlie H. C., Mercat A., Chevret S., Grosset J. Activity of clarithromycin against Mycobacterium avium infection in patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. A controlled clinical trial. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Sep;144(3 Pt 1):564–569. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.3_Pt_1.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes P. B., Hardy D. J., McDaniel D., Hanson C. W., Swanson R. N. In vitro and in vivo activities of clarithromycin against Mycobacterium avium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1531–1534. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George K. L., Falkinham J. O., 3rd Selective medium for the isolation and enumeration of Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare and M. scrofulaceum. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Jan;32(1):10–14. doi: 10.1139/m86-003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorzynski E. A., Gutman S. I., Allen W. Comparative antimycobacterial activities of difloxacin, temafloxacin, enoxacin, pefloxacin, reference fluoroquinolones, and a new macrolide, clarithromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):591–592. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heifets L. B., Lindholm-Levy P. J., Comstock R. D. Clarithromycin minimal inhibitory and bactericidal concentrations against Mycobacterium avium. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Apr;145(4 Pt 1):856–858. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.4_Pt_1.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro M., Koga H., Kohno S., Hayashi T., Yamaguchi K., Hirota M. Penetration of macrolides into human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Nov;24(5):719–729. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.5.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm-Levy P. J., Heifets L. B. Clofazimine and other rimino-compounds: minimal inhibitory and minimal bactericidal concentrations at different pHs for Mycobacterium avium complex. Tubercle. 1988 Sep;69(3):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(88)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mor N., Lutsky I., Levy L. Response in the hindfoot pad and popliteal lymph node of C57BL mice to infection with Mycobacterium marinum. Isr J Med Sci. 1981 Apr;17(4):236–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naik S., Ruck R. In vitro activities of several new macrolide antibiotics against Mycobacterium avium complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1614–1616. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perronne C., Gikas A., Truffot-Pernot C., Grosset J., Pocidalo J. J., Vilde J. L. Activities of clarithromycin, sulfisoxazole, and rifabutin against Mycobacterium avium complex multiplication within human macrophages. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Aug;34(8):1508–1511. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.8.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perronne C., Gikas A., Truffot-Pernot C., Grosset J., Vilde J. L., Pocidalo J. J. Activities of sparfloxacin, azithromycin, temafloxacin, and rifapentine compared with that of clarithromycin against multiplication of Mycobacterium avium complex within human macrophages. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jul;35(7):1356–1359. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.7.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi N., Labrousse V. Extracellular and intracellular activities of clarithromycin used alone and in association with ethambutol and rifampin against Mycobacterium avium complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Mar;35(3):462–470. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.3.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard C. C., McRae D. H. A method for counting acid-fast bacteria. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1968 Jan-Mar;36(1):78–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truffot-Pernot C., Ji B., Grosset J. Effect of pH on the in vitro potency of clarithromycin against Mycobacterium avium complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Aug;35(8):1677–1678. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.8.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajko D. M., Nassos P. S., Sanders C. A., Gonzalez P. C., Hadley W. K. Comparison of the intracellular activities of clarithromycin and erythromycin against Mycobacterium avium complex strains in J774 cells and in alveolar macrophages from human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected individuals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 May;36(5):1163–1165. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.5.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



