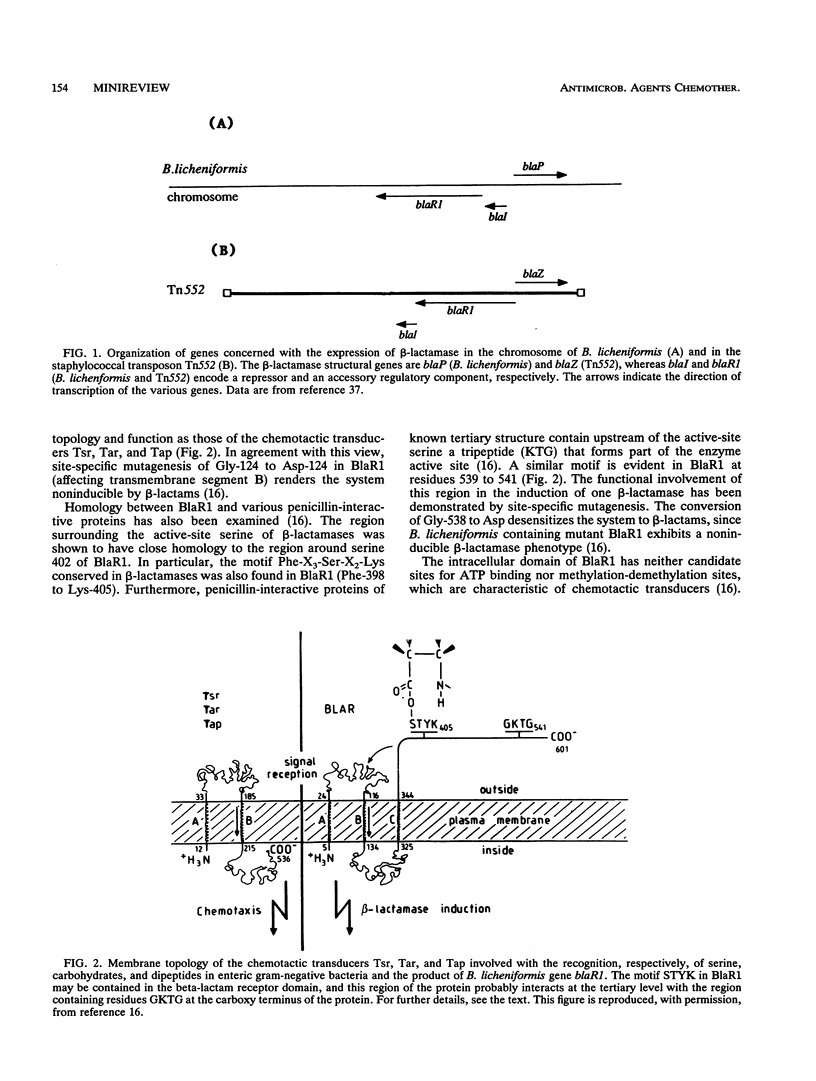
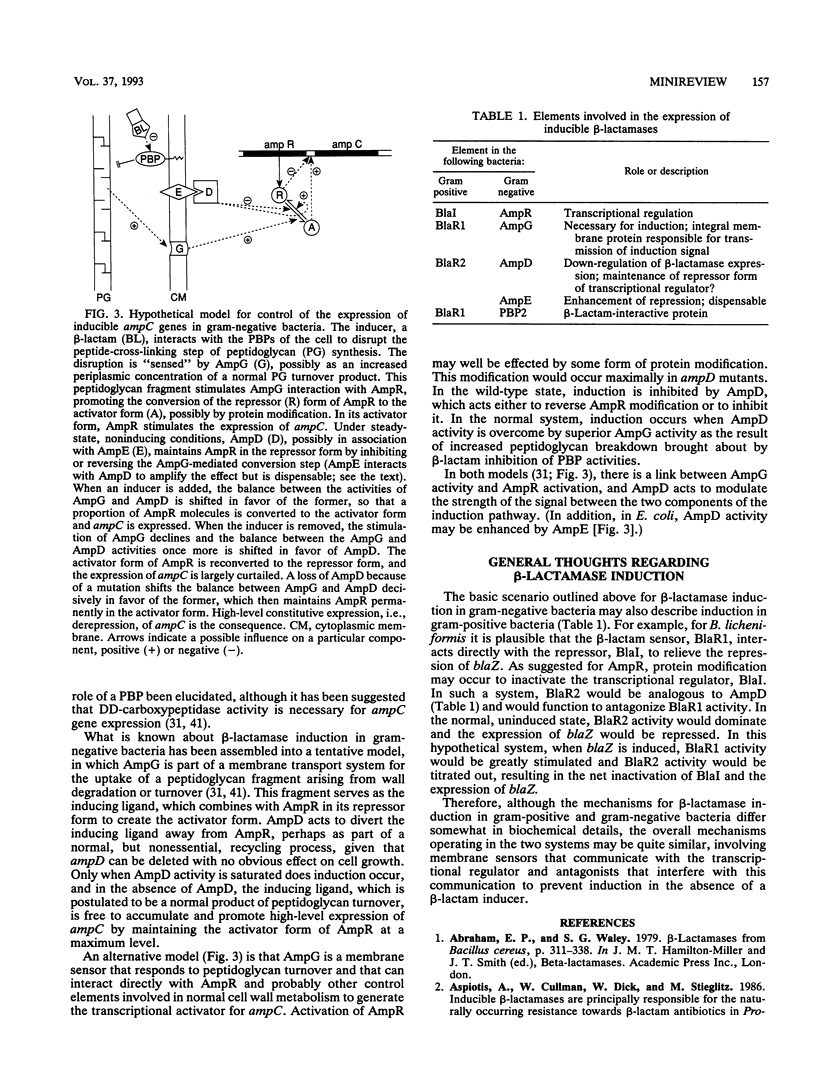
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartowsky E., Normark S. Purification and mutant analysis of Citrobacter freundii AmpR, the regulator for chromosomal AmpC beta-lactamase. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jul;5(7):1715–1725. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begg K. J., Donachie W. D. Cell shape and division in Escherichia coli: experiments with shape and division mutants. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):615–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.615-622.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Olsson O., Normark S. Common evolutionary origin of chromosomal beta-lactamase genes in enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):528–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.528-534.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett M. J., Chopra I., Bennett P. M. Induction of the Citrobacter freundii group I beta-lactamase in Escherichia coli is not dependent on entry of beta-lactam into the cytoplasm. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Dec;34(12):2429–2430. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.12.2429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J. Plasmid-determined resistance to antimicrobial drugs and toxic metal ions in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):361–409. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.361-409.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Haughn G. W., Calvo J. M., Wallace J. C. A large family of bacterial activator proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6602–6606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessey T. D. Inducible beta-lactamase in Enterobacter. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Nov;49(2):277–285. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himeno T., Imanaka T., Aiba S. Nucleotide sequence of the penicillinase repressor gene penI of Bacillus licheniformis and regulation of penP and penI by the repressor. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1128–1132. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1128-1132.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré N., Nicolas M. H., Cole S. T. Inducible cephalosporinase production in clinical isolates of Enterobacter cloacae is controlled by a regulatory gene that has been deleted from Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3709–3714. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04704.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré N., Nicolas M. H., Cole S. T. Regulation of enterobacterial cephalosporinase production: the role of a membrane-bound sensory transducer. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1121–1130. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iaconis J. P., Sanders C. C. Purification and characterization of inducible beta-lactamases in Aeromonas spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):44–51. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris B., Ledent P., Kobayashi T., Lampen J. O., Ghuysen J. M. Expression in Escherichia coli of the carboxy terminal domain of the BLAR sensory-transducer protein of Bacillus licheniformis as a water-soluble Mr 26,000 penicillin-binding protein. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jun 15;58(1):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Zhu Y. F., Nicholls N. J., Lampen J. O. A second regulatory gene, blaR1, encoding a potential penicillin-binding protein required for induction of beta-lactamase in Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):3873–3878. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.3873-3878.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Takahashi I., Nakae T. Diffusion of beta-lactam antibiotics through liposome membranes containing purified porins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Nov;22(5):775–780. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.5.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korfmann G., Sanders C. C., Moland E. S. Altered phenotypes associated with ampD mutations in Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):358–364. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korfmann G., Sanders C. C. ampG is essential for high-level expression of AmpC beta-lactamase in Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1946–1951. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroyer J., Chang S. The promoter-proximal region of the Bacillus licheniformis penicillinase gene: Nucleotide sequence and predicted leader peptide sequence. Gene. 1981 Dec;15(4):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Lindquist S., Normark S. Genetic basis of induction and overproduction of chromosomal class I beta-lactamase in nonfastidious gram-negative bacilli. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):782–785. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Lindquist S., Normark S. Inactivation of the ampD gene causes semiconstitutive overproduction of the inducible Citrobacter freundii beta-lactamase. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1923–1928. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1923-1928.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Normark S. Common mechanism of ampC beta-lactamase induction in enterobacteria: regulation of the cloned Enterobacter cloacae P99 beta-lactamase gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):758–763. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.758-763.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Westman L., Normark S. Regulatory components in Citrobacter freundii ampC beta-lactamase induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4620–4624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Galleni M., Lindberg F., Normark S. Signalling proteins in enterobacterial AmpC beta-lactamase regulation. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1091–1102. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00259.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Lindberg F., Normark S. Binding of the Citrobacter freundii AmpR regulator to a single DNA site provides both autoregulation and activation of the inducible ampC beta-lactamase gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3746–3753. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3746-3753.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon B. R., Skurray R. Antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus: genetic basis. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):88–134. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.88-134.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliva B., Bennett P. M., Chopra I. Penicillin-binding protein 2 is required for induction of the Citrobacter freundii class I chromosomal beta-lactamase in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jul;33(7):1116–1117. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.7.1116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottolenghi A. C., Ayala J. A. Induction of a class I beta-lactamase from Citrobacter freundii in Escherichia coli requires active ftsZ but not ftsA or ftsQ products. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Nov;35(11):2359–2365. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.11.2359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. DOMINANCE OF THE INDUCIBLE STATE IN STRAINS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS CONTAINING TWO DISTINCT PENICILLINASE PLASMIDS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:370–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.370-374.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland S. J., Dyke K. G. Tn552, a novel transposable element from Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jun;4(6):961–975. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherratt D. J., Collins J. F. Analysis by transformation of the penicillinase system in Bacillus licheniformis. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 May;76(1):217–230. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-1-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Penicillin-binding proteins and the future of beta-lactam antibiotics. The Seventh Fleming Lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1247–1260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Matthew M. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their role in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):115–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Lindquist S., Sande S., Galleni M., Light K., Gage D., Normark S. Coordinate regulation of beta-lactamase induction and peptidoglycan composition by the amp operon. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):201–204. doi: 10.1126/science.1987637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P. Z., Projan S. J., Novick R. P. Nucleotide sequence of beta-lactamase regulatory genes from staphylococcal plasmid pI258. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):4000–4000. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.4000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittman V., Wong H. C. Regulation of the penicillinase genes of Bacillus licheniformis: interaction of the pen repressor with its operators. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3206–3212. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3206-3212.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



