Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (311.6 KB).
Figure 1.
M mode echocardiogram showing paradoxical left ventricular septal wall contraction and late systolic/early diastolic thickening of the posterior wall.
Figure 2.

Reduction in regional ejection fraction (septal regions 2 and 3) on MUGA scan in the patient in fig 1.
Figure 3.
Optimisation of atrioventricular delay. Left ventricular (LV) inflow pulsed wave Doppler at the level of mitral valve leaflets. (A) Atrioventricular (AV) delay 160 ms: uniphasic transmitral flow (fused E and A wave) with reduced left ventricular filling time (t) < 40% R-R interval. The onset of filling is delayed commencing after the end of the T wave on the ECG (white arrow). (B) AV delay 90 ms: mitral valve closure line coincides with the end of the A wave maximising LV filling time and restoring biphasic transmitral flow with E and A wave separation. (C) AV delay 70 ms: the end of the A wave is now truncated by mitral valve closure (seen arrowed and aliasing), with the commencement of mitral regurgitation and reduced LV filling time. AV optimisation can now be improved by increasing the AV delay in 10 ms increments until mitral valve closure line coincides with the end of the A wave without truncation.
Figure 4.
Presystolic mitral regurgitation in the patient from fig 1. The arrow indicates the frame is acquired before onset of the QRS complex.
Figure 5.
Aortic pre-ejection time (Ao) is measured as the time from QRS onset to blood flow. The time from the aortic valve opening to closure represents the ejection period (EP).
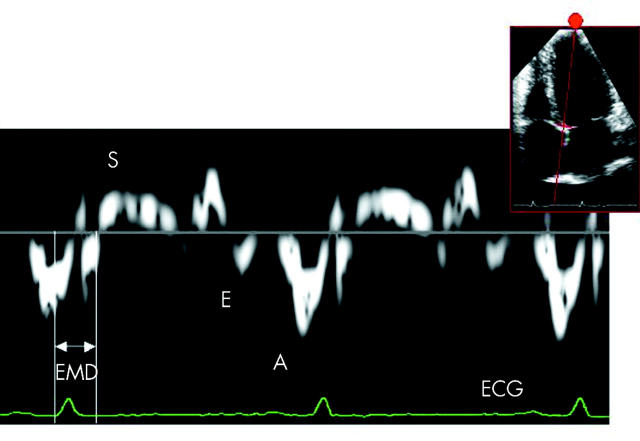
Figure 6.
Pulsed wave tissue Doppler imaging of the basal interventricular septum acquired from an apical four chamber view. A broad complex QRS is seen. The upward deflection following QRS complex represents longitudinal shortening toward the transducer during ventricular systole (S wave). The two main deflections below the baseline represent E and A waves occurring during ventricular filling as the sampled region moves away from the transducer at the cardiac apex. The heights of S, E, and A waves (cm/s) measure the velocities of motion of the sampled region during systole and diastole respectively. Regional electromechanical delay (EMD) may be calculated from the start of QRS to the onset or peak of the S wave.
Figure 7.
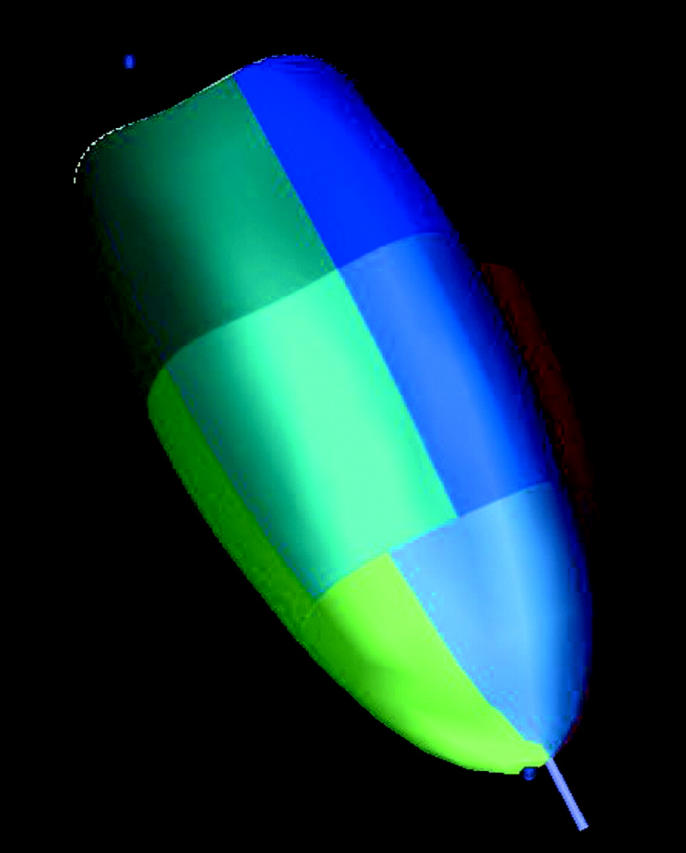
Three dimensional reconstruction of the left ventricle, which is divided into different regions. The timing of contraction and relaxation is assessed for each of these regions.
Figure 8.
Echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular dyssynchrony. Each line represents movement of one of the left ventricular segments shown in fig 7. This ventricle contracts synchronously.
Figure 9.
Echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular dyssynchrony. This shows an abnormal, dyssynchronous ventricle.
Figure 10.
(A) LV velocity time integral (VTI) of 10.3 cm with an optimised AV delay at an interventricular pacing interval (IVPI) of 0 ms. (B) The same patient with an LV VTI of 12.9 cm at an IVPI delay of 20 ms (LV ahead of RV).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham William T., Fisher Westby G., Smith Andrew L., Delurgio David B., Leon Angel R., Loh Evan, Kocovic Dusan Z., Packer Milton, Clavell Alfredo L., Hayes David L. Cardiac resynchronization in chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2002 Jun 13;346(24):1845–1853. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa013168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansalone Gerardo, Giannantoni Paride, Ricci Renato, Trambaiolo Paolo, Fedele Francesco, Santini Massimo. Doppler myocardial imaging to evaluate the effectiveness of pacing sites in patients receiving biventricular pacing. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002 Feb 6;39(3):489–499. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(01)01772-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auricchio A., Salo R. W., Klein H., Hartung W. Problems and pitfalls in evaluating studies for pacing in heart failure. G Ital Cardiol. 1997 Jun;27(6):593–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auricchio A., Sommariva L., Salo R. W., Scafuri A., Chiariello L. Improvement of cardiac function in patients with severe congestive heart failure and coronary artery disease by dual chamber pacing with shortened AV delay. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1993 Oct;16(10):2034–2043. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1993.tb00997.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breithardt Ole A., Sinha Anil M., Schwammenthal Ehud, Bidaoui Nadim, Markus Kai U., Franke Andreas, Stellbrink Christoph. Acute effects of cardiac resynchronization therapy on functional mitral regurgitation in advanced systolic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003 Mar 5;41(5):765–770. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(02)02937-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breithardt Ole-A, Stellbrink Christoph, Franke Andreas, Balta Osman, Diem Björn H., Bakker Patricia, Sack Stefan, Auricchio Angelo, Pochet Thierry, Salo Rodney. Acute effects of cardiac resynchronization therapy on left ventricular Doppler indices in patients with congestive heart failure. Am Heart J. 2002 Jan;143(1):34–44. doi: 10.1067/mhj.2002.119616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristow Michael R., Saxon Leslie A., Boehmer John, Krueger Steven, Kass David A., De Marco Teresa, Carson Peter, DiCarlo Lorenzo, DeMets David, White Bill G. Cardiac-resynchronization therapy with or without an implantable defibrillator in advanced chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2004 May 20;350(21):2140–2150. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa032423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazeau S., Bordachar P., Jauvert G., Lazarus A., Alonso C., Vandrell M. C., Mugica J., Ritter P. Echocardiographic modeling of cardiac dyssynchrony before and during multisite stimulation: a prospective study. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2003 Jan;26(1 Pt 2):137–143. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9592.2003.00003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazeau S., Leclercq C., Lavergne T., Walker S., Varma C., Linde C., Garrigue S., Kappenberger L., Haywood G. A., Santini M. Effects of multisite biventricular pacing in patients with heart failure and intraventricular conduction delay. N Engl J Med. 2001 Mar 22;344(12):873–880. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200103223441202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell R., Morris-Thurgood J., Ilsley C., Paul V. Septal short atrioventricular delay pacing: additional hemodynamic improvements in heart failure. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1994 Nov;17(11 Pt 2):1980–1983. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1994.tb03784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etienne Y., Mansourati J., Touiza A., Gilard M., Bertault-Valls V., Guillo P., Boschat J., Blanc J. J. Evaluation of left ventricular function and mitral regurgitation during left ventricular-based pacing in patients with heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2001 Aug;3(4):441–447. doi: 10.1016/s1388-9842(01)00145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. J., Thomas J. D., Klein A. L. New Doppler echocardiographic applications for the study of diastolic function. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998 Oct;32(4):865–875. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(98)00345-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrigue S., Jaïs P., Espil G., Labeque J. N., Hocini M., Shah D. C., Haïssaguerre M., Clementy J. Comparison of chronic biventricular pacing between epicardial and endocardial left ventricular stimulation using Doppler tissue imaging in patients with heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 2001 Oct 15;88(8):858–862. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(01)01892-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasparini Maurizio, Mantica Massimo, Galimberti Paola, Marconi Manuel, Genovese Luca, Faletra Francesco, Simonini Stefano, Klersy Catherine, Coates Robert, Gronda Edoardo. Beneficial effects of biventricular pacing in patients with a "narrow" QRS. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2003 Jan;26(1 Pt 2):169–174. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9592.2003.00010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grines C. L., Bashore T. M., Boudoulas H., Olson S., Shafer P., Wooley C. F. Functional abnormalities in isolated left bundle branch block. The effect of interventricular asynchrony. Circulation. 1989 Apr;79(4):845–853. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.79.4.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huth C., Friedl A., Klein H., Auricchio A. Schrittmachertherapie der Herzinsuffizienz unter Berücksichtigung der Ergebnisse der PATH-CHF-Studie. Z Kardiol. 2001;90 (Suppl 1):10–15. doi: 10.1007/s003920170053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Sumita S., Kimura K., Kikuchi M., Kosuge M., Nakagawa T., Matsushita K., Usui T., Umemura S. Efficacy of atrioventricular sequential pacing and diastolic mitral regurgitation in patients with intrinsic atrioventricular conduction. Jpn Circ J. 2000 Aug;64(8):579–582. doi: 10.1253/jcj.64.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim W. Y., Søgaard P., Mortensen P. T., Jensen H. K., Pedersen A. K., Kristensen B. O., Egeblad H. Three dimensional echocardiography documents haemodynamic improvement by biventricular pacing in patients with severe heart failure. Heart. 2001 May;85(5):514–520. doi: 10.1136/heart.85.5.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq Christophe, Faris Owen, Tunin Richard, Johnson Jennifer, Kato Ritsuchi, Evans Frank, Spinelli Julio, Halperin Henry, McVeigh Elliot, Kass David A. Systolic improvement and mechanical resynchronization does not require electrical synchrony in the dilated failing heart with left bundle-branch block. Circulation. 2002 Oct 1;106(14):1760–1763. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000035037.11968.5c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson G. S., Berger R. D., Fetics B. J., Talbot M., Spinelli J. C., Hare J. M., Kass D. A. Left ventricular or biventricular pacing improves cardiac function at diminished energy cost in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy and left bundle-branch block. Circulation. 2000 Dec 19;102(25):3053–3059. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.102.25.3053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura R. A., Hayes D. L., Ilstrup D. M., Holmes D. R., Jr, Tajik A. J. Effect of dual-chamber pacing on systolic and diastolic function in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Acute Doppler echocardiographic and catheterization hemodynamic study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996 Feb;27(2):421–430. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(95)00445-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oguz Enis, Dagdeviren Bahadir, Bilsel Tuba, Akdemir Osman, Erdinler Izzet, Akyol Ahmet, Ulufer Tanju, Tezel Tuna, Gurkan Kadir. Echocardiographic prediction of long-term response to biventricular pacemaker in severe heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2002 Jan;4(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/s1388-9842(01)00188-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penicka Martin, Bartunek Jozef, De Bruyne Bernard, Vanderheyden Marc, Goethals Marc, De Zutter Marc, Brugada Pedro, Geelen Peter. Improvement of left ventricular function after cardiac resynchronization therapy is predicted by tissue Doppler imaging echocardiography. Circulation. 2004 Feb 9;109(8):978–983. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000116765.43251.D7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perego Giovanni B., Chianca Roberto, Facchini Mario, Frattola Alessandra, Balla Eva, Zucchi Stefania, Cavaglià Sergio, Vicini Ilaria, Negretto Marco, Osculati Giuseppe. Simultaneous vs. sequential biventricular pacing in dilated cardiomyopathy: an acute hemodynamic study. Eur J Heart Fail. 2003 Jun;5(3):305–313. doi: 10.1016/s1388-9842(02)00204-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitzalis Maria Vittoria, Iacoviello Massimo, Romito Roberta, Massari Francesco, Rizzon Brian, Luzzi Giovanni, Guida Pietro, Andriani Andrea, Mastropasqua Filippo, Rizzon Paolo. Cardiac resynchronization therapy tailored by echocardiographic evaluation of ventricular asynchrony. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002 Nov 6;40(9):1615–1622. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(02)02337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter Sylvain, Garrigue Stephane, Barold S. Serge, Jais Pierre, Hocini Meleze, Haissaguerre Michel, Clementy Jacques. Comparison of characteristics in responders versus nonresponders with biventricular pacing for drug-resistant congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 2002 Feb 1;89(3):346–350. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(01)02240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogaard Peter, Egeblad Henrik, Pedersen Anders K., Kim Won Yong, Kristensen Bent O., Hansen Peter S., Mortensen Peter T. Sequential versus simultaneous biventricular resynchronization for severe heart failure: evaluation by tissue Doppler imaging. Circulation. 2002 Oct 15;106(16):2078–2084. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000034512.90874.8e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Søgaard P., Kim W. Y., Jensen H. K., Mortensen P., Pedersen A. K., Kristensen B. Ø, Egeblad H. Impact of acute biventricular pacing on left ventricular performance and volumes in patients with severe heart failure. A tissue doppler and three-dimensional echocardiographic study. Cardiology. 2001;95(4):173–182. doi: 10.1159/000047369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Søgaard Peter, Egeblad Henrik, Kim W. Yong, Jensen Henrik K., Pedersen Anders K., Kristensen Bent Ø, Mortensen Peter T. Tissue Doppler imaging predicts improved systolic performance and reversed left ventricular remodeling during long-term cardiac resynchronization therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002 Aug 21;40(4):723–730. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(02)02010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H. B., Lee C. H., Gibson D. G. Effect of left bundle branch block on diastolic function in dilated cardiomyopathy. Br Heart J. 1991 Dec;66(6):443–447. doi: 10.1136/hrt.66.6.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C-M, Lin H., Zhang Q., Sanderson J. E. High prevalence of left ventricular systolic and diastolic asynchrony in patients with congestive heart failure and normal QRS duration. Heart. 2003 Jan;89(1):54–60. doi: 10.1136/heart.89.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Cheuk-Man, Chau Elaine, Sanderson John E., Fan Katherine, Tang Man-Oi, Fung Wing-Hong, Lin Hong, Kong Shun-Ling, Lam Yui-Ming, Hill Michael R. S. Tissue Doppler echocardiographic evidence of reverse remodeling and improved synchronicity by simultaneously delaying regional contraction after biventricular pacing therapy in heart failure. Circulation. 2002 Jan 29;105(4):438–445. doi: 10.1161/hc0402.102623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Cheuk-Man, Yang Hua, Lau Chu-Pak, Wang Qiong, Wang Shelley, Lam Linda, Sanderson John E. Regional left ventricle mechanical asynchrony in patients with heart disease and normal QRS duration: implication for biventricular pacing therapy. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2003 Feb;26(2 Pt 1):562–570. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9592.2003.00095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q., Henein M., Coats A., Gibson D. Different effects of abnormal activation and myocardial disease on left ventricular ejection and filling times. Heart. 2000 Sep;84(3):272–276. doi: 10.1136/heart.84.3.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoneraich S., Zoneraich O., Rhee J. J. Echocardiographic evaluation of septal motion in patients with artificial pacemakers: vectorcardiographic correlations. Am Heart J. 1977 May;93(5):596–602. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8703(77)80010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]