Abstract
The tumor suppressor p53 regulates cell cycle progression and apoptosis in response to various types of stress, whereas excess p53 activity creates unwanted effects. Tight regulation of p53 is essential for maintaining normal cell growth. p53-associated cellular protein-testes derived (PACT, also known as P2P-R, RBBP6) is a 250-kDa Ring finger-containing protein that can directly bind to p53. PACT is highly up-regulated in esophageal cancer and may be a promising target for immunotherapy. However, the physiological role of the PACT–p53 interaction remains largely unclear. Here, we demonstrate that the disruption of PACT in mice leads to early embryonic lethality before embryonic day 7.5 (E7.5), accompanied by an accumulation of p53 and widespread apoptosis. p53-null mutation partially rescues the lethality phenotype and prolonged survival to E11.5. Endogenous PACT can interact with Hdm2 and enhance Hdm2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of p53 as a result of the increase of the p53–Hdm2 affinity. Consequently, PACT represses p53-dependent gene transcription. Knockdown of PACT significantly attenuates the p53–Hdm2 interaction, reduces p53 polyubiquitination, and enhances p53 accumulation, leading to both apoptosis and cell growth retardation. Taken together, our data demonstrate that the PACT–p53 interaction plays a critical role in embryonic development and tumorigenesis and identify PACT as a member of negative regulators of p53.
Keywords: apoptosis, embryonic lethality, ubiquitination
The tumor suppressor p53 regulates cell cycle progression and apoptosis in response to various types of stress, including DNA damage and abnormal proliferative signals (1). Although p53 mutations have been documented in more than half of all human tumors, defects in other components of the p53 pathway are observed in most other cancer types that retain wild-type p53 (2, 3). Notably, excess p53 activity comes with unwanted effects (4). Thus, tight regulation of p53 is essential for maintaining normal cell growth and preventing tumorigenesis. P53 regulation occurs primarily through posttranslation modifications of p53 by involvement of multiple partners (5–7).
p53-associated cellular protein-testes derived (PACT, also known as P2P-R, RBBP6) is a 250-kDa nuclear protein containing a conserved N-terminal Ring-finger domain, which was first isolated from a mouse testes expression library using p53 as a probe (8). It has been shown that PACT interacts with both p53 and Rb in vitro and in vivo (9). PACT is highly up-regulated in esophageal cancer and may be a promising target for immunotherapy (10). Stable overexpression of specific segments of the PACT restricts mitotic progression at prometaphase and promotes mitotic apoptosis and camptothecin-induced apoptosis (11–13). However, little is known about the significance of the interaction between PACT and p53 until now.
To study the biological functions of Pact, we generated PACT knockout mice and found that disruption of PACT leads to early embryonic lethality before embryonic day 7.5 (E7.5) accompanied by widespread apoptosis. More importantly, the introduction of a p53-null mutation into Pact−/− embryos partially rescues the lethality phenotype and prolonged survival to E11.5. Meanwhile, we explored the role and mechanism of PACT in p53 regulation. It was demonstrated that endogenous PACT could interact with Hdm2 and enhance Hdm2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of p53 as the result of an increase of the p53–Hdm2 affinity. Consequently, PACT repressed p53-dependent transactivation. Nevetheless, knockdown of endogenous PACT resulted in p53 accumulation in vivo and then induced both apoptosis and cell growth retardation in a p53-dependent manner, which are consistent with the phenotype of the Pact−/− embryos. Taken together, our data identify that PACT is involved in the negative regulation of p53 function through ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis and implies a critical role for PACT in development.
Results
Targeted Disruption of PACT Leads to Early Embryonic Lethality That Can Be Partially Rescued by p53-Null Mutation.
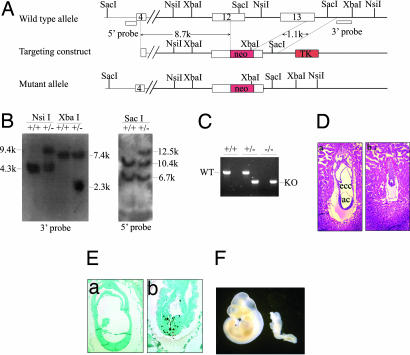
To elucidate the role of PACT in vivo, we generated PACT-deficient mice by gene targeting in ES cells. We replaced exons 11–12, comprising the p53 binding domain, with a neomycin resistance (neor) gene (Fig. 1A) and identified the targeted ES cell clones with Southern blot analysis using probes external to the targeting construct (Fig. 1B). Targeted ES cell clones contributed to the germ line of chimeric mice and yielded progeny heterozygous for the PACT mutant allele (Pact+/−). Heterozygous male and female mice displayed no overt phenotype and were fertile. In contrast, we identified no viable PACT homozygous mice (Pact−/−) among 108 offspring born from crosses between PACT heterozygous mice, which suggests an embryonic lethal phenotype for homozygous mutant mice (Table 1). To determine the timing of this lethality, embryos from heterozygous mating were dissected and genotyped at different gestational days (Fig. 1C and Table 1). We found that Pact−/− embryos died before E7.5 and were smaller and developmentally retarded compared with their littermate controls (Fig. 1D). TUNEL assay showed that the apoptotic cells in Pact−/− embryos were much more than in normal embryos (Fig. 1E). It is well known that the p53 tumor suppressor mediates apoptosis in response to many genotoxic stresses (14) and that PACT has proven to be a p53-binding protein. A question that is raised by these observations is whether p53 is responsible for the lethal apoptosis occurring in Pact−/− embryos.
Fig. 1.
Targeted disruption of PACT leads to early embryonic lethality, which can be partially rescued by a p53-null mutation. (A) A targeting strategy used for inactivation of the murine PACT gene is shown. The targeting construct contained a 9.8-kb genomic sequence of PACT with a pLoxP neo cassette. A homologous recombination within the PACT locus introduces the neo gene and deletes exons 12 and 13 of PACT. (B) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA isolated from targeted ES cell clones. The band of 6.7 kb corresponds to the Pact pseudogene. (C) Genotyping of PACT embryos with PCR. The wild-type PACT allele was detected using primers that amplified a fragment of 600 bp (WT) from the DNA of wild-type and heterozygous mice (lanes 2, 4, and 6). A fragment of 400 bp (KO) was amplified from the targeted allele of heterozygous and homozygous mice (lanes 1, 3, and 5). (D) Histological analysis of embryos derived from heterozygous intercrosses. (a) E7.5 wild-type embryos clearly display the distinct germ layers as well as three cavities. (b) E7.5 Pact−/− embryos are developmentally delayed. The extraembryonic ectoderm and extraembryonic endoderm of the mutant embryos grew slowly, although no normal structures were visible. (Magnification: ×200.) ac, amnion cavity; ecc, exocoelomic cavity. (E) TUNEL assay of E7.5 embryos. In the Pact−/− embryos (b), the apoptotic cell ratio remarkably increased, but the wild-type embryos (a) exhibited hardly any apoptosis. (Magnification: a, ×200; b, ×400.) (F) Partial rescue of Pact−/− embryos by a null mutation of p53. Whole-mount preparations of embryos from Pact+/−p53−/− intercrosses at E10.5. Although less advanced than their Pact+/+p53−/− littermates (Left), Pact−/−p53−/− embryos developed an anterior−posterior pattern with a head, trunk, and tail region (Right).
Table 1.
Genotypes of offspring and embryos from PACT heterozygous matings
| Age, day | No. of progeny with indicated genotype |
No. of resorptions | Total no. of progeny | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +/+ | +/− | −/− | |||
| E6.5 | 5 | 10 | 3 | 0 | 18 |
| E7.5 | 10 | 16 | 9 | 0 | 35 |
| E8.5 | 4 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 19 |
| E9.5 | 6 | 10 | 0 | 2 | 18 |
| E10.5 | 10 | 16 | 0 | 8 | 34 |
| E11.5 | 7 | 12 | 0 | 4 | 23 |
| E12.5 | 8 | 15 | 0 | 7 | 30 |
| E13.5 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 12 |
| E16.5 | 4 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 12 |
| Live birth | 33 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 108 |
To test this prediction, we introduced the PACT mutation into a p53-null background. Thirty-eight embryos from Pact+/−p53−/− intercrosses were retrieved at E11.5 and genotyped with PCR. Seven Pact−/− embryos in a p53-null background were obtained (Table 2). Although smaller than their wild-type littermates, double-mutant embryos developed past the gastrulation stage with a distinct anterior–posterior pattern (Fig. 1F). The double mutants died later, indicating that the p53−/− mutation failed to completely rescue embryos from the effects of a PACT deficiency on development. This result is perhaps not surprising, because PACT is a very large protein and may play multiple roles in development. However, the double mutants lived much longer and developed further than Pact−/− embryos did in a wild-type p53 background, supporting the hypothesis that developmental arrest in early (i.e., E7.5) Pact−/− embryos is a consequence of p53 accumulation. These results suggest that PACT plays a pivotal role in early embryonic development and that the PACT–p53 interaction might be involved in this process.
Table 2.
Embryonic lethality of PACT disruption can be partially rescued by p53-null mutation
| Cross | Total embryos | Genotypes | Predicted number | Actual number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p53+/+PACT+/− × p53+/+PACT+/− | 23 | p53+/+PACT+/+ | 6 | 7 |
| p53+/+PACT+/− | 12 | 12 | ||
| p53+/+PACT−/− | 6 | 0* | ||
| p53−/−PACT+/− × p53−/−PACT+/− | 38 | p53−/−PACT+/+ | 10 | 10 |
| p53−/−PACT+/− | 20 | 16 | ||
| p53−/−PACT−/− | 10 | 7† |
*The genotypes of all embryos were determined with PCR, except for four resorbed embryos at E11.5.
†The genotypes of all embryos were determined with PCR, except for five resorbed embryos at E11.5.
PACT Promotes p53 Ubiquitination and Degradation Mediated by Hdm2.
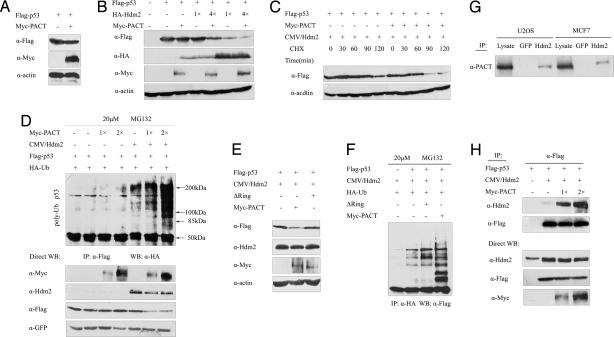
The Ring-finger is a hallmark of E3 ligase, and some Ring-finger proteins, such as Hdm2, Pirh2, and COP1 (15–17), are interacting proteins and negative regulators of p53. To assess the possibility for PACT to negatively regulate p53, we used HEK293 cells to detect whether PACT can modulate the levels of p53 protein. We found that the protein level of ectopically expressed p53 was unaffected by overexpression of PACT (Fig. 2A). Moreover, HDM2 decreased the level of p53, which was further decreased by coexpression of PACT (Fig. 2B). The amount of p53 protein in cells is determined mainly by the rate at which it is degraded, rather than the rate at which it is made (2). Our results showed that the decrease in the p53 level by PACT also was caused by an increase in the degradation rate (Fig. 2C). Meanwhile, PACT overexpression alone had very little effect on p53 ubiquitination, whereas PACT significantly enhanced p53 ubiquitination in the presence of transfected Hdm2 (Fig. 2D). In contrast, the ΔRing mutant of PACT that lacks the Ring-finger domain hardly had any effect on p53 degradation (Fig. 2E) and ubiquitination (Fig. 2F) in the presence of overexpressed Hdm2. These results argue strongly that PACT stimulates p53 ubiquitination and decreases the protein level of p53 dependent of Hdm2.
Fig. 2.
PACT promotes p53 ubiquitination and degradation mediated by Hdm2. (A) PACT alone did not affect the protein level of p53. HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with plasmids expressing Flag-p53 and Myc-PACT (lane 2) or vector alone (lane 1). Cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting (WB). (B) PACT led to a decreased steady level of exogenous p53 in an Hdm2-dependent manner. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Flag-p53, HA-Hdm2, and Myc-PACT, as indicated. Levels of p53 were analyzed by WB. p53/Hdm2 molar ratios were 4:1 in lanes 4 and 5 and 1:1 in lanes 6 and 7. (C) PACT increases p53 turnover. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing p53 and Hdm2 (1:1 molar ratio) together with or without PACT, treated with cycloheximide, and harvested at the indicated times. Lysates were analyzed with WB by using the indicated antibodies. (D) PACT overexpression stimulates Hdm2-mediated p53 ubiquitination. Increasing amounts (indicated on the top) of Myc-PACT were cotransfected into cells with plasmids encoding Hdm2, Flag-p53, and poly-HA-tagged ubiquitin. Cells were grown in medium containing MG132 (20 μM) for 6 h (lanes 2 to 7). Then, p53 was isolated with immunoprecipitation (IP) and analyzed with WB using an HA antibody. (E) The Ring-finger domain of PACT is required for p53 degradation in vivo. A PACT mutant lacking the Ring-finger domain (PACT-ΔRing-myc) was included in this study. HEK293 cells were transfected with the plasmids as indicated. p53 was detected with WB with anti-flag. (F) The Ring-finger domain of PACT is required for p53 ubiquitination in vivo. HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated combinations of expression plasmids and treated with MG132 (20 μM). Ubiquitinated p53 was detected with IP with anti-HA and WB with anti-flag. (G) PACT interacts with Hdm2 in vivo. Total U2OS and MCF7 cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with Hdm2 or GFP antibody. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed with Western blotting using a PACT monoclonal antibody. (H) Overexpression of PACT enhanced the Hdm2–p53 interaction. HEK293 cells were transfected with Hdm2 in the absence or presence of Flag-p53 and increasing amounts of PACT. Whole-cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibodies, and coimmunoprecipitated Hdm2 was detected with Western blot analysis. The levels of Hdm2, p53, and PACT in the whole-cell lysates were determined with WB.
P53 is controlled primarily by Hdm2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome. Recent studies suggest that additional proteins may regulate Hdm2-mediated p53 ubiquitination (18–21). To seek evidence that PACT regulates Hdm2-mediated p53 ubiquitination via its physical interaction with Hdm2, we investigated whether PACT associated with Hdm2. Importantly, endogenous PACT also interacted with Hdm2 in U2OS and MCF7 cell lysates (Fig. 2G), indicating that the PACT can bind Hdm2 in vivo. To determine the consequence of the PACT–Hdm2 interaction, we analyzed the effect of PACT on the Hdm2–p53 interaction. Interestingly, overexpression of PACT enhanced the interaction between p53 and Hdm2 (Fig. 2H), indicating that PACT may function as a scaffold protein to promote the assembly of the p53–Hdm2 complex.
PACT Inhibits the Transcriptional Activity of p53.
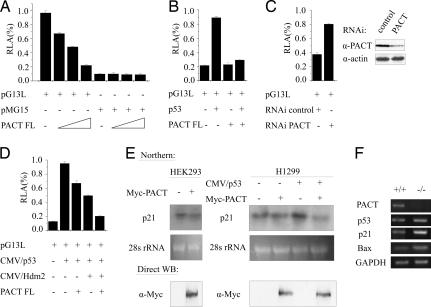
To determine the effect of PACT on p53-dependent transactivation, we transfected HEK293 cells with a luciferase promoter reporter plasmid pG13L and increasing amounts of PACT. The results showed that the p53 transcriptional activity was strongly inhibited by PACT in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 3A). In another assay, p53 was transfected to activate pG13L in the H1299 cells (p53 null). PACT also can inhibit the exogenous p53 transcriptional activity (Fig. 3B). Knockdown of PACT in U2OS cells resulted in increased p53 transcriptional activity, indicating that endogenous PACT negatively regulates p53 (Fig. 3C). Moreover, expression of Hdm2 inhibited p53 transcriptional activity, and coexpression of PACT further inhibited p53 in cooperation with Hdm2 (Fig. 3D). Northern blotting results showed that the mRNA level of p21, a downstream effector of p53, was dramatically reduced with the overexpression of PACT (Fig. 3E). Furthermore, we detected the expression of p53, p21, and Bax in Pact−/− embryos with RT-PCR analysis. Interestingly, the level of p53 mRNA was hardly affected by PACT knockout, which is consistent with the fact that PACT affects the rate and/or the stability of p53 protein. However, transcription of p21 and Bax was increased (Fig. 3F). These results demonstrated that PACT can inhibit the transcriptional activity of p53 and the expression of p53 target genes.
Fig. 3.
PACT inhibits the transcriptional activity of p53. (A) Activity of the pG13L reporter gene in HEK293 cells transfected with PACT or mock vector. Reporter activity was assayed as described in Materials and Methods and represented as the mean ± SD of three separate experiments. (B) Activity of the pG13L reporter gene in H1299 cells transfected with p53 in the absence or presence of PACT or mock vector. (C) Expression of Hdm2 inhibited p53 transcriptional activity, and coexpression of PACT further inhibited p53 in cooperation with Hdm2. HEK293 cells were transfected as indicated. (D) shRNA ablation of PACT elevates the transcriptional activity of p53. U2OS cells were transfected as indicated. (E) PACT down-regulates the p21 mRNA level. Northern blot analysis was performed on RNA from HEK293 and H1299 cells transfected as indicated. (F) Investigation of p53 expression by RT-PCR at E7.5 embryos. The expression levels of PACT, p53, p21, and Bax were analyzed using RT-PCR on RNA from E7.5 Pact+/+ and Pact−/− embryos. GAPDH was used as a control for RNA sample quantity.
Inactivation of PACT Stabilizes p53 and Induces p53-Dependent Apoptosis or Growth Retardation.
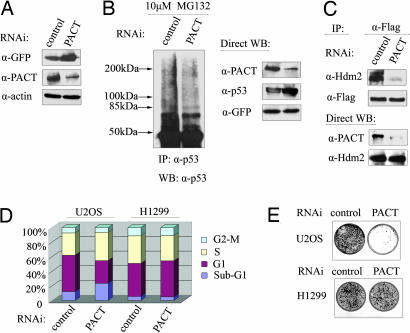
To uncover the role of PACT in a more physiological setting, endogenous PACT was subject to ablation by RNAi, and any effect on endogenous p53 steady-levels was assessed. Down-regulation of PACT in U2OS cells caused a pronounced accumulation of p53 protein (Fig. 4A); meanwhile, endogenous p53 polyubiquitination was reduced (Fig. 4B) as the result of a decrease in the interaction between p53 and Hdm2 (Fig. 4C), suggesting that PACT is required for efficient p53 degradation and ubiquitination in vivo. Furthermore, knockdown of PACT in U2OS cells caused a prominent increase of apoptosis but had no effect in the H1299 cells (Fig. 4D), indicating that the observed apoptosis occurred in a p53-dependent manner. In line with the aforementioned results, the use of a colony-formation assay showed the number of G418-resistant colonies was significantly reduced as a result of PACT depletion in U2OS cells, whereas the number of colonies remains unchanged in H1299 cells (Fig. 4E), suggesting that PACT is essential for cell growth and that its deficiency can result in either apoptosis or growth suppression dependent of p53.
Fig. 4.
Inactivation of PACT stabilizes p53 and induces p53-dependent apoptosis or growth retardation. (A) Knockdown of PACT increases the p53 protein level. U2OS cells were transfected with shRNA. Lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (B) Endogenous p53 ubiquitination is regulated with PACT. U2OS cells were transfected with shRNA. The cells were treated with MG132 (20 μM) for 8 h before harvesting. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with a p53 antibody and Western blotted with a p53 antibody. (C) PACT RNAi decreases the interaction between Hdm2 and p53. U2OS cells were transfected with shRNA, pCMV/Hdm2, and pCMV/p53. Cell lysates were normalized using p53 as the reference, immunoprecipitated with a p53 antibody, and analyzed with Western blot (Upper). Direct Western blot of the samples used are shown (Lower). (D) Inactivation of PACT induces apoptosis. U2OS or H1299 cells were transfected with either PACT-RNAi or control-RNAi, and then the cell cycle profile was analyzed for apoptotic cells (subG1) according to DNA content with propidium iodide staining and FACS. (E) PACT depletion causes cell growth retardation. U2OS and H1299 cells were transfected with shRNA plasmid containing the neoexpression cassette and selected with 400 mg/ml of G418 for ≈10 days. The foci were detected with crystal violet.
Discussion
Tight regulation of p53 activity in an appropriate range is imperative for maintaining normal cell growth and preventing tumorigenesis. There is no question that Hdm2, a p53-interacting partner, plays a pivotal role in down-regulating p53 activities in numerous cellular settings such as a ubiquitin E3 ligase. To date, seven negative and three positive feedback loops were documented, six through the Hdm2 protein to regulate p53 activity (5). Recently, increasing amounts of data suggest that p53 ubiquitination and degradation are more complex than once thought. More E3 ligases were found with specificity for p53 dependent or independent of Hdm2 (22–24). In this paper, we demonstrate that PACT is another negative regulator of p53 by the involvement of Hdm2, acting as an E3 ligase.
In the previous study, stable overexpression of specific segments of PACT was shown to contribute to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis (11–13). However, little is known about the function of full-length and endogenous PACT. Here, we systematically analyzed PACT's function and identified PACT as a pivotal negative regulator of p53. Our results lead to three major conclusions or implications: First, PACT is a negative regulator of p53 mediated by Hdm2, possibly acting as an E4 ligase. There is no question that Hdm2 plays a pivotal role in down-regulating p53 activities in numerous cellular settings. Nevertheless, growing evidence suggests that additional proteins may regulate Hdm2-mediated p53 ubiquitination. Here, we demonstrated that PACT could inhibit the accumulation of p53 by promoting its degradation mediated by Hdm2, repressing p53-dependent transactivation. Knockdown of endogenous PACT resulted in p53 accumulation in vivo and then induced both apoptosis and cell growth retardation in a p53-dependent manner. Our data identified that PACT is involved in the negative regulation of p53 function through physical interaction with Hdm2 and ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. It is possible that PACT may provide a platform to promote the assembly of the p53–Hdm2 complex and fine-tune the p53 network. Second, PACT is essential for development, and its deficiency leads to early embryonic lethality, which is consistent with the fact that mutation of its homologue, SNAMA, results in apoptosis in embryos in Drosophila (25). During normal early mouse development, p53 activation is controlled by its negative regulators, and p53 is not activated before E11 (26). Otherwise, an excess of p53 activity in early embryos comes with unwanted effects. PACT may play an important role for monitoring p53 activity at this stage. This hypothesis is illustrated by studies conducted in mice, in whom inactivation of p53 was shown to partially rescue the embryonic lethality caused by loss of PACT function. Third, alteration of PACT expression and/or activity may be an important event during tumorigenesis. Consistent with this hypothesis, PACT is widely expressed in many tumor cell lines, and its expression is found to be increased in tumors, such as esophageal (10) and breast cancer (L.L., unpublished data). However, the correlation of PACT overexpression and tumorigenesis remains unclear. Because inactivation of p53 is one of the hallmarks of cancer cells, our results demonstrated that PACT could inhibit tumor suppressor p53 function, providing a new possible functional mechanism by which PACT could promote tumorigenesis.
Notably, there are few proteins that could also bind Rb among the p53-negative regulators, except for Hdm2 and gankyrin, which play important roles in both of the two tumor suppressor pathways (27). PACT may be a member of the small family and function as a scaffold protein to promote the assembly of tumor suppressor complexes. Taken together, our findings highlight the complexity of the Hdm2–p53 ubiquitination process and prove that p53 ubiquitination and degradation are subjected to regulation at multiple partnerships. Further research into the role of PACT as a modulator of p53 function may lead to new strategies for controlling development and growth of tumors.
Materials and Methods
Targeting Construct.
A 16-kb mouse PACT genomic DNA was isolated from a 129/Sv mouse genomic library (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA). A 1.1-kb XhoI-EcoRI genomic fragment containing part of exon 13 was inserted into SalI/EcoRI sites of pLoxPI to create pLoxPshort. An 8.7-kb SalI fragment containing sequences 5′ to exon 12 was subcloned into a pBluescript SK(+) vector. This subclone was digested with NotI/XhoI, and the 8.7-kb fragment was released. This fragment was subcloned into NotI/XhoI-digested pLoxPshort to create pPACTneo (Fig. 1A), which was linearized with NotI.
Targeting/Genotyping.
Electroporation of the construct into TC1 ES cells (28) and selection for homologous recombinants were performed according to standard procedures. We screened targeted ES colonies with Southern blot hybridization and generated chimaeric mice. They were mated with C57BL/6J wild-type mice, and offsprings were genotyped with PCR. Primers A (5′-AAAACTCACGGTACATTATGCACTCCACTCTG-3′) and B (5′-CTTTCCCATTCCCGGTAGCGTTCTTTCTCAA-3′) were used to detect the wild-type allele. The targeted allele was detected using primers C (5′-GCCGCTCACATTCTCGCTCCTATTCAC-3′) and D (5′-CCAGACTGCCTTGGGAAAAGCGCCTCCCCTACC-3′). P53−/− mutant mice were genotyped as previously described (29).
In Situ Embryo Analysis.
Decidua with embryos from pregnant mice were isolated, embedded in paraffin, and serially sectioned. Sections were then used for H&E staining with standard procedures. The TUNEL reaction was performed with the FITC-labeled Apotag kit (Chemicon, Temecula, CA) in accordance with the manufacturer's protocol.
RNA Extraction, RT-PCR.
Total RNA was extracted from E7.5 embryos using TRIzol (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). RT-PCR amplification was performed using the GAPDH-specific primer set (5′-CAGACACCCAACTTTCGCAT-3′, 5′-TGTTCCGGGTGGTTCTGCAG-3′). RNA from wide-type and PACT mutant embryos, which showed GAPDH bands of equal intensity, were chosen for PCR amplification experiments. Specific primers used in the PCRs were PACT (5′-ATGGAAGGTGATGTTGAAAAGCTGG-3′, 5′-GCCGTAGCCGATGGCTTAGTAGTGAC-3′), p53 (5′-GGATAGGAAAGAGCACAGAGC-3′, 5′-CCAGTCTTCGGAGAAGCGTG AC-3′), p21 (5′-GACGACCTGGGAGGGGACAAG-3′, 5′-TAAGGTTTGGAGACTGGGAGAG-3′), and Bax (5′-TGCAGAGGATGATTGCTGAC-3′, 5′-GAGGACTCCAGCCACAAAGA-3′).
Cell Culture, Antibodies, and Plasmids.
HEK293, 293T, and U2OS were cultured in DMEM (HyClone, Logan, UT) supplemented with 10% FBS, and H1299 cells were maintained in RPMI medium 1640 with 10% FBS. Mouse monoclonal antibody of PACT was raised against the 766–921 aa. Anti-Myc and anti-GFP antibodies were purchased from Clontech (Mountain View, CA). Anti-Flag M2 antibody, CHX, and MG132 were from Sigma. G418 was from Invitrogen. The following antibodies were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA): p53 (DO-1 and FL-393), Hdm2 (SMP14), p21 (F5), and β-actin. Anti-HA (12CA5) was purchased from Roche (Indianapolis, IN). pCMV/p53, pCMV/Hdm2, and pcDNA3/poly-HA-tagged ubiquitin were gifts from Y. Xiong (University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC), and pG13-Luc and pMG15 were gifts from B. Vogelstein (Johns Hopkins Oncology Center, Baltimore, MD).
Gene Reporter Assays.
Luciferase reporter plasmids pG13-Luc and pRL-CMV (Promega, Madison, WI) were cotransfected with increasing amounts of Myc-PACT. After 48 h, cells were lysed in 100 μl of a passive lysis buffer (Promega). Luciferase activity was measured with the Luciferase Assay System (Promega) according to the manufacturer's protocol. In some experiments, plasmids expressing p53 and/or Mdm2 also were cotransfected.
In Vivo Ubiquitination Assays.
For in vivo ubiquitination assay, HEK293 cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing Flag-p53, Hdm2, myc-PACT, and HA-tagged ubiquitin in various combinations. Before collection after 48 h, cells were treated with MG132 (20 μM) for 6 h. Then, cells were lysed in modified RIPA buffer (10 mM Tris·HCl, pH 7.5/5 mM EDTA/150 mM NaCl/1% Nonidet P-40/1% sodium deoxycholate/0.025% SDS/protease inhibitors), and lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody and analyzed with immunoblotting.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Moshe Oren and Bert Vogelstein for p53 reporter gene plasmids; Dr. Yue Xiong for p53, Hdm2, and ubiquitin expression constructs; Drs. Lawrence A. Donehower and Chu-xia Deng for p53−/− mice and mouse ES cells; Mr. Bo Dong for the flow-cytometry analysis; and Drs. Yue Xiong, Wei Gu, Yang Shi, and Kun-liang Guan for the critical reading of the manuscript. This work was partially supported by Chinese National Natural Science Foundation Projects 30400236 and 30621063, the Chinese National High-Tech Programs 2004AA221100 and 2005AA220060, and the Chinese National Basic Research Programs 2001CB510205, 2005CB522506, and 2006CB910802.
Abbreviations
- PACT
P53-associated cellular protein-testes derived
- En
embryonic day n.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Vousden KH. Cell. 2000;103:691–694. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00171-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ. Nature. 2000;408:307–310. doi: 10.1038/35042675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hollstein M, Hergenhahn M, Yang Q, Bartsch H, Wang ZQ, Hainaut P. Mutat Res. 1999;431:199–209. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(99)00162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sharpless NE, DePinho RA. Cell. 2002;110:9–12. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00818-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yang Y, Li CC, Weissman AM. Oncogene. 2004;23:2096–2106. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Michael D, Oren M. Semin Cancer Biol. 2003;13:49–58. doi: 10.1016/s1044-579x(02)00099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bode AM, Dong Z. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:793–805. doi: 10.1038/nrc1455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Simons A, Melamed-Bessudo C, Wolkowicz R, Sperling J, Sperling R, Eisenbach L, Rotter V. Oncogene. 1997;14:145–155. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1200825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Witte MM, Scott RE. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:1212–1217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.4.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yoshitake Y, Nakatsura T, Monji M, Senju S, Matsuyoshi H, Tsukamoto H, Hosaka S, Komori H, Fukuma D, Ikuta Y, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:6437–6448. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gao S, Scott RE. J Cell Physiol. 2002;193:199–207. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gao S, Scott RE. J Cell Physiol. 2003;197:445–452. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Scott RE, Giannakouros T, Gao S, Peidis P. J Cell Biochem. 2003;90:6–12. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Appella E, Anderson CW. Eur J Biochem. 2001;268:2764–2772. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2001.02225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fang S, Jensen JP, Ludwig RL, Vousden KH, Weissman AM. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:8945–8951. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.12.8945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Leng RP, Lin Y, Ma W, Wu H, Lemmers B, Chung S, Parant JM, Lozano G, Hakem R, Benchimol S. Cell. 2003;112:779–791. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dornan D, Wertz I, Shimizu H, Arnott D, Frantz GD, Dowd P, O'Rourke K, Koeppen H, Dixit VM. Nature. 2004;429:86–92. doi: 10.1038/nature02514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brooks CL, Gu W. Mol Cell. 2006;21:307–315. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.01.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cummings JM, Rago C, Kohli M, Kinzler KW, Lengauer C, Vogelstein B. Nature. 2004;416:648–653. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Grossman SR, Deato ME, Brignone C, Chan HM, Kung AL, Tagami H, Nakatani Y, Livingston DM. Science. 2003;300:342–344. doi: 10.1126/science.1080386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Li M, Brooks CL, Kon N, Gu W. Mol Cell. 2004;13:879–886. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(04)00157-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sui G, Affar el B, Shi Y, Brignone C, Wall NR, Yin P, Donohoe M, Luke MP, Calvo D, Grossman SR, et al. Cell. 2004;117:859–872. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Higashitsuji H, Higashitsuji H, Itoh K, Sakurai T, Nagao T, Sumitomo Y, Masuda T, Dawson S, Shimada Y, Mayer RJ, et al. Cancer Cell. 2005;8:75–87. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2005.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Chen D, Kon N, Li M, Zhang W, Qin J, Gu W. Cell. 2005;121:1071–1083. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.03.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mather A, Rakgotho M, Ntwasa M. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1727:169–176. doi: 10.1016/j.bbaexp.2005.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Komarova EA, Chernov MV, Franks R, Wang K, Armin G, Zelnick CR, Chin DM, Bacus SS, Stark GR, Gudkov AV. EMBO J. 1997;16:1391–1400. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sdek P, Ying H, Chang DL, Qiu W, Zheng H, Touitou R, Allday MJ, Xiao ZX. Mol Cell. 2005;20:699–708. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.10.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Deng C, Wynshaw-Boris A, Zhou F, Kuo A, Leder P. Cell. 1996;84:911–921. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Donehower LA, Harvey M, Slagle BL, McArthur MJ, Montgomery CA, Jr, Butel JS, Bradley A. Nature. 1992;356:215–221. doi: 10.1038/356215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]