Abstract
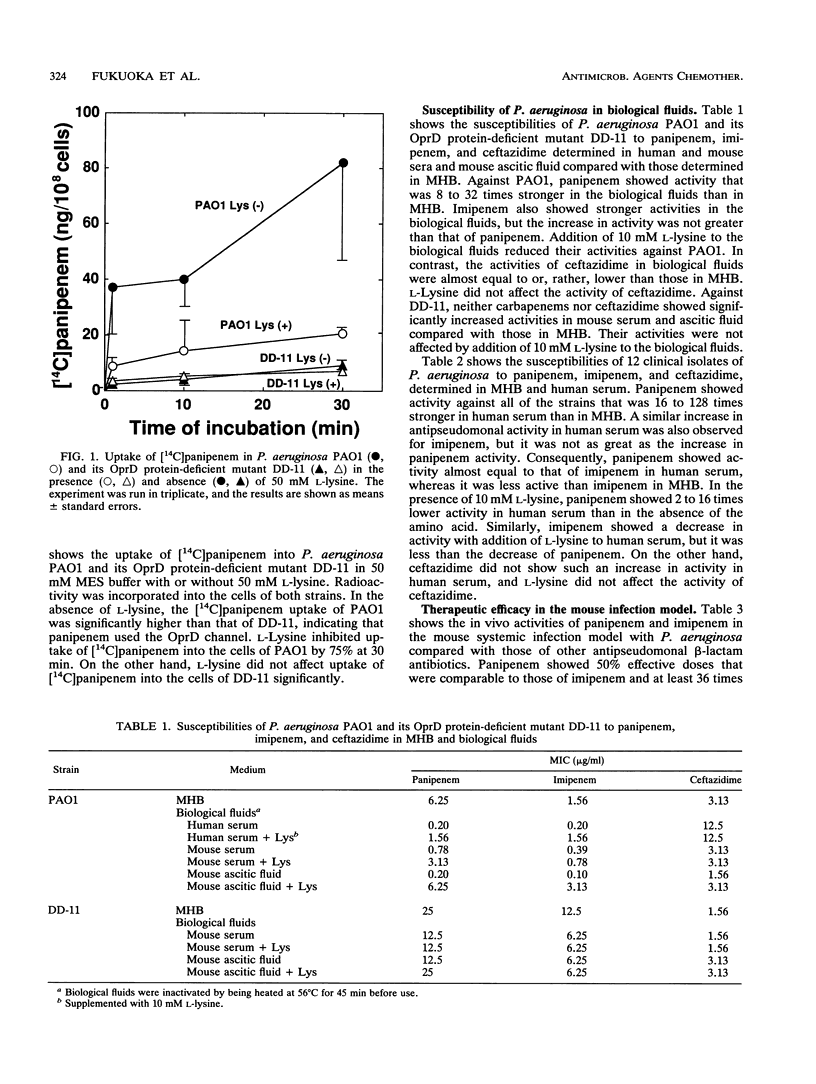
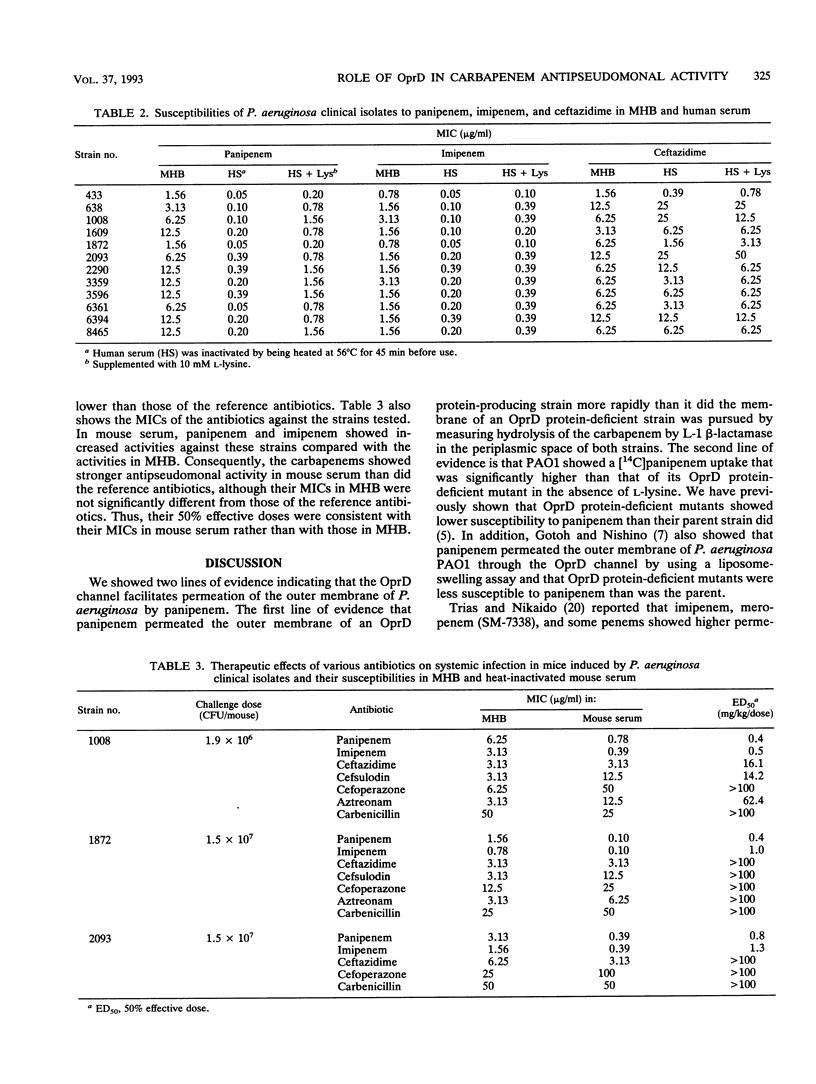
Evidence of permeation of panipenem through the OprD (D2) channel of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane was shown by using OprD protein-producing and -nonproducing strains which contained plasmid pHN4, which codes for L-1 beta-lactamase of Xanthomonas maltophilia. Permeation by panipenem was determined by measuring hydrolysis of the carbapenem by beta-lactamase in the periplasmic space. Permeation by panipenem was also determined by counting uptake of [14C]panipenem into P. aeruginosa PAO1 and its OprD protein-deficient mutant, and this permeation of PAO1 was inhibited by L-lysine. These results indicate that panipenem, as well as imipenem, uses the OprD channel, which functions as a specific channel for diffusion of basic amino acids. Panipenem and imipenem showed stronger activities against PAO1 and clinical isolates in human serum than in Mueller-Hinton broth, which contains more amino acids than human serum does. The activities of the carbapenems were reduced by addition of L-lysine to human serum. Similar results were obtained with mouse serum and ascitic fluid. In contrast, such a change in the activities of carbapenems was not observed with an OprD protein-deficient mutant, suggesting that the main reason for the strong activities of carbapenems in biological fluids is a decrease in competition between the antibiotics and basic amino acids for permeation through the OprD channel. Panipenem and imipenem showed much stronger therapeutic efficacies against experimental infections with P. aeruginosa in mice than did the reference antibiotics. Their in vivo activities were more consistent with their MICs in biological fluids than with those in Mueller-Hinton broth.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bustamante C. I., Drusano G. L., Tatem B. A., Standiford H. C. Postantibiotic effect of imipenem on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Nov;26(5):678–682. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.5.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cristiano P., Iovene M. R., Simioli F., Pezza M., Raucci G., Lobello R. Clinical evaluation of the imipenem/cilastatin combination in the therapy of severe infections in patients with malignant diseases. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1990;16(6):293–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day S. E., Vasli K. K., Russell R. J., Arbuthnott J. P. A simple method for the study in vivo of bacterial growth and accompanying host response. J Infect. 1980 Mar;2(1):39–51. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(80)91773-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichtenbaum C. J., Smith M. J. Treatment of endocarditis due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa with imipenem. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):353–354. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuoka T., Masuda N., Takenouchi T., Sekine N., Iijima M., Ohya S. Increase in susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to carbapenem antibiotics in low-amino-acid media. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Mar;35(3):529–532. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.3.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlitz P. H., Sunderman F. W., Jr, Hohnadel D. C. Ion-exchange chromatography of amino acids in sweat collected from healthy subjects during sauna bathing. Clin Chem. 1974 Oct;20(10):1305–1312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh N., Nishino T. Decreases of the susceptibility to low molecular weight beta-lactam antibiotics in imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants: role of outer membrane protein D2 in their diffusion. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Feb;25(2):191–198. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.2.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan F. M., Kropp H., Sundelof J. G., Birnbaum J. Thienamycin: development of imipenen-cilastatin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Dec;12 (Suppl 500):1–35. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_d.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropp H., Sundelof J. G., Kahan J. S., Kahan F. M., Birnbaum J. MK0787 (N-formimidoyl thienamycin): evaluation of in vitro and in vivo activities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):993–1000. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi S. In-vitro and in-vivo antibacterial activity of imipenem against clinical isolates of bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Dec;12 (Suppl 500):53–64. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_d.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Chin N. X., Saha G., Labthavikul P. In vitro activity against aerobic and anaerobic gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and beta-lactamase stability of RS-533, a novel carbapenem. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):828–834. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. Comparative in vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic species and its beta-lactamase stability. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):180–187. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Rosenberg E. Y., Foulds J. Porin channels in Escherichia coli: studies with beta-lactams in intact cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):232–240. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.232-240.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., Dudek E. J., DiVincenzo C. A., Lucks D. A., Lerner S. A. Emergence of resistance to imipenem during therapy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):289–294. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trias J., Dufresne J., Levesque R. C., Nikaido H. Decreased outer membrane permeability in imipenem-resistant mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1202–1206. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trias J., Nikaido H. Outer membrane protein D2 catalyzes facilitated diffusion of carbapenems and penems through the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):52–57. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trias J., Nikaido H. Protein D2 channel of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane has a binding site for basic amino acids and peptides. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15680–15684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., McGrattan M. A., Busuttil R. W. Imipenem therapy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other serious bacterial infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Nov;26(5):673–677. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.5.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Nikaido H. Permeability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane to hydrophilic solutes. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):636–642. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.636-642.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


