Abstract
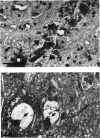
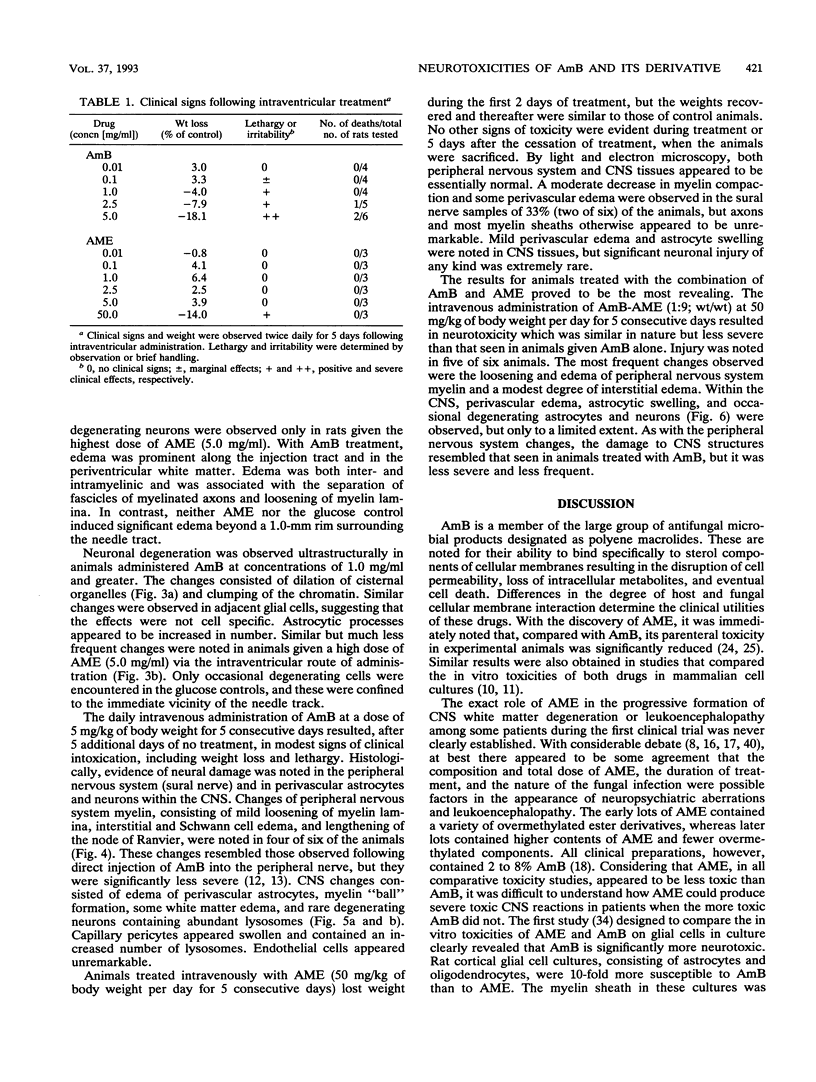
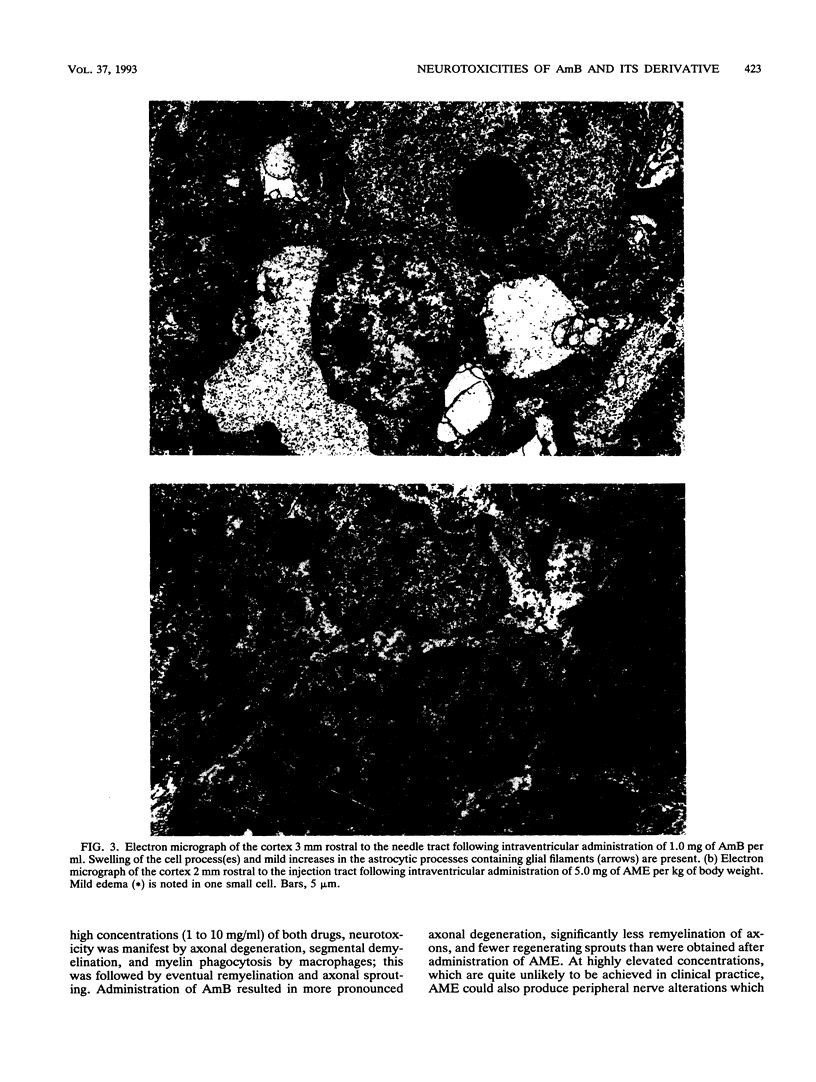
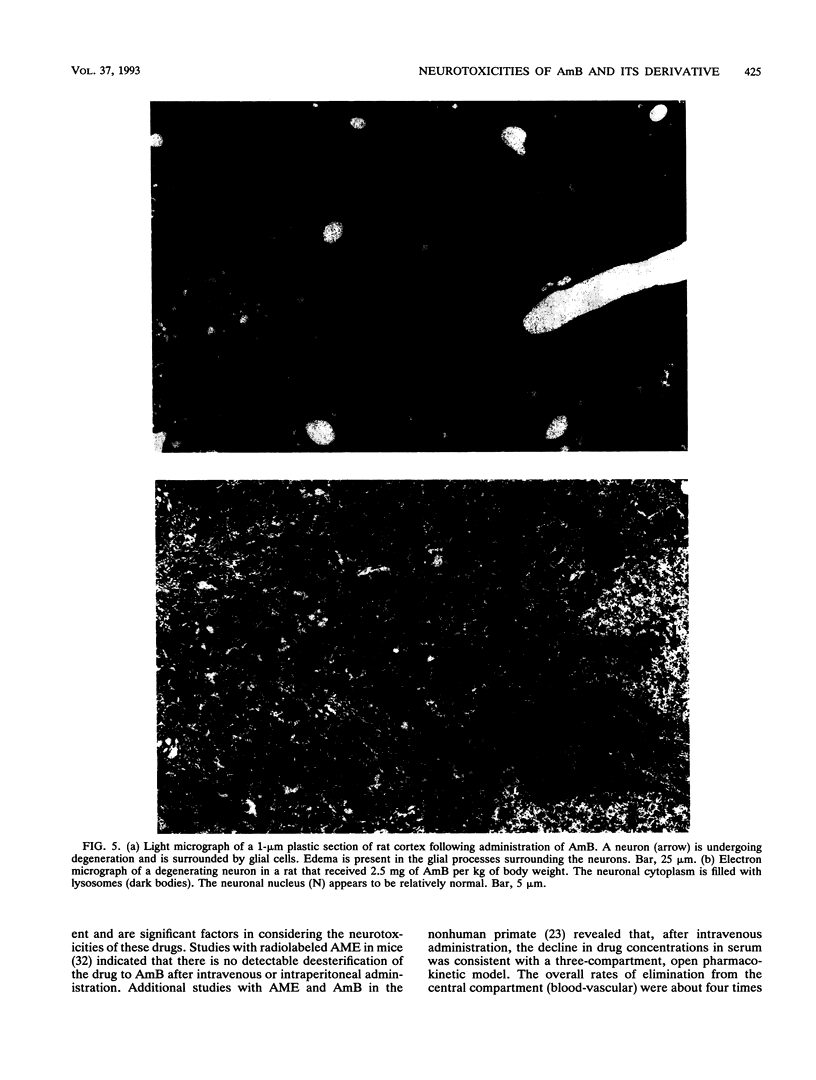
The intracisternal administration of amphotericin B (AmB) and its mono-methyl ester derivative (AME), via direct intraventricular injection (0.01 to 5 mg/ml, 6 microliters) in adult female Wistar rats, revealed that AmB was significantly more toxic than AME, as measured by weight loss, lethargy, death, and central nervous system histopathology. Light and electron microscopy confirmed a greater neurotoxicity for AmB, manifested as edema and modest gliosis extending along and beyond the injection tract. Neuronal degeneration and myelin damage were present in AmB-treated (1 mg/ml) animals but were present only modestly in animals treated with AME at a fivefold greater concentration. Intravenous administration of AmB to adult female Wistar rats as five daily doses of 5 mg/kg of body weight resulted in significant weight loss and some deaths. Histopathologic examination of the brains, spinal cords, and sural nerves of surviving animals revealed neurotoxicity manifested by neuronal degeneration, gliosis, and myelin edema. In sharp contrast, similar treatment with AME at a 10-fold greater dose resulted in neither death nor significant neurotoxicity. The administration of five daily doses of a mixture of AME-AmB (9:1; wt/wt) at 50 mg/kg of body weight resulted in neurotoxicity. These results indicate that AmB exhibits significantly greater in vivo neurotoxicity than AME.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner D. P., Mechlinski W., Schaffner C. P. Polyene macrolide derivatives. 3. Biological properties of polyene macrolide ester salts. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Apr;25(4):261–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner D. P., Tewari R. P., Solotorovsky M., Mechlinski W., Schaffner C. P. Comparative chemotherapeutic activity of amphotericin B and amphotericine B methy ester. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jun;7(6):724–729. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.6.724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnevale N. T., Galgiani J. N., Stevens D. A., Herrick M. K., Langston J. W. Amphotericin B-induced myelopathy. Arch Intern Med. 1980 Sep;140(9):1189–1192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemons K. V., Stevens D. A. Comparative efficacies of amphotericin B lipid complex and amphotericin B deoxycholate suspension against murine blastomycosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Oct;35(10):2144–2146. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.10.2144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemons K. V., Stevens D. A. Comparative efficacy of amphotericin B colloidal dispersion and amphotericin B deoxycholate suspension in treatment of murine coccidioidomycosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Sep;35(9):1829–1833. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.9.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devinsky O., Lemann W., Evans A. C., Moeller J. R., Rottenberg D. A. Akinetic mutism in a bone marrow transplant recipient following total-body irradiation and amphotericin B chemoprophylaxis. A positron emission tomographic and neuropathologic study. Arch Neurol. 1987 Apr;44(4):414–417. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520160048013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis W. G., Bencken E., LeCouteur R. A., Barbano J. R., Wolfe B. M., Jennings M. B. Neurotoxicity of amphotericin B methyl ester in dogs. Toxicol Pathol. 1988;16(1):1–9. doi: 10.1177/019262338801600101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis W. G., Sobel R. A., Nielsen S. L. Leukoencephalopathy in patients treated with amphotericin B methyl ester. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):125–137. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding R. M., Smith P. C., Wang L. H., Porter J., Guo L. S. Comparative pharmacokinetics of amphotericin B after administration of a novel colloidal delivery system, ABCD, and a conventional formulation to rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jun;35(6):1208–1213. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.6.1208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. B., Goldstein N. I., Bonner D. P., Mechlinski W., Bryson V., Schaffner C. P. Toxicity of amphotericin B and its methyl ester toward normal and tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1975 Aug;35(8):1996–1999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. B., Goldstein N. I., Bryson V., Schaffner C. P. Reduced toxicity of amphotericin B methyl ester (AME) vs. amphotericin B and fungizone in tissue culture. In Vitro. 1976 Feb;12(2):133–140. doi: 10.1007/BF02796361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABER R. W., JOSEPH M. Neurological manifestations after amphotericin B therapy. Br Med J. 1962 Jan 27;1(5273):230–231. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5273.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeprich P. D., Flynn N. M., Kawachi M. M., Lee K. K., Lawrence R. M., Heath L. K., Schaffner C. P. Treatment of fungal infections with semisynthetic derivatives of amphotericin B alpha. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;544:517–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb40449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeprich P. D., Huston A. C., Wolfe B. M. Toxicity of amphotericins on chronic administration to mongrel dogs. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;3(1):47–58. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(85)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeprich P. D. New antifungal drugs in the therapy of systemic mycoses. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(16):74–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeprich P. Amphotericin B methyl ester and leukoencephalopathy: the other side of the coin. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):173–176. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howarth W. R., Tewari R. P., Solotorovsky M. Comparative in vitro antifungal activity of amphotericin B and amphotericin B methyl ester. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jan;7(1):58–63. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huston A. C., Hoeprich P. D. Comparative susceptibility of four kinds of pathogenic fungi to amphotericin B and amphotericin B methyl ester. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jun;13(6):905–909. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.6.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagdis F. A., Hoeprich P. D., Lawrence R. M., Schaffner C. P. Comparative pharmacology of amphotericin B and amphotericin B methyl ester in the non-human primate, Macacca mulatta. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Nov;12(5):582–590. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.5.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keim G. R., Jr, Poutsiaka J. W., Kirpan J., Keysser C. H. Amphotericin B methyl ester hydrochloride and amphotericin B: comparative acute toxicity. Science. 1973 Feb 9;179(4073):584–585. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4073.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keim G. R., Sibley P. L., Yoon Y. H., Kulesza J. S., Zaidi I. H., Miller M. M., Poutsiaka J. W. Comparative toxicological studies of amphotericin B methyl ester and amphotericin B in mice, rats, and dogs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):687–690. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R. M., Hoeprich P. D. Comparison of amphotericin B and amphotericin B methyl ester: efficacy in murine coccidioidomycosis and toxicity. J Infect Dis. 1976 Feb;133(2):168–174. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.2.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R. M., Hoeprich P. D., Jagdis F. A., Monji N., Huston A. C., Schaffner C. P. Distribution of doubly radiolabelled amphotericin B methyl ester and amphotericin B in the non-human primate, Macaca mulatta. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Mar;6(2):241–249. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longuet P., Joly V., Amirault P., Seta N., Carbon C., Yeni P. Limited protection by small unilamellar liposomes against the renal tubular toxicity induced by repeated amphotericin B infusions in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jul;35(7):1303–1308. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.7.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Mehta R., Hopfer R. L., Mills K., Kasi L., Mehta K., Fainstein V., Luna M., Hersh E. M., Juliano R. Treatment and prophylaxis of disseminated infection due to Candida albicans in mice with liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):939–945. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massa T., Sinha D. P., Frantz J. D., Filipek M. E., Weglein R. C., Steinberg S. A., McGrath J. T., Murphy B. F., Szot R. J., Black H. E. Subchronic toxicity studies of N-D-ornithyl amphotericin B methyl ester in dogs and rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1985 Aug;5(4):737–753. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(85)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechlinski W., Schaffner C. P. Polyene macrolide derivatives. I. N-acylation and esterification reactions with amphotericin B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Apr;25(4):256–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monji N., Bonner D. P., Hashimoto Y., Schaffner C. P. Studies on the absorption, distribution and excretion of radioactivity after intravenous and intraperitoneal administration of 14C-methyl ester of amphotericin B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1975 Apr;28(4):317–324. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.28.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson T. F., Miniter P., Dijkstra J., Szoka F. C., Jr, Ryan J. L., Andriole V. T. Treatment of experimental invasive aspergillosis with novel amphotericin B/cholesterol-sulfate complexes. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):717–724. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racis S. P., Plescia O. J., Geller H. M., Schaffner C. P. Comparative toxicities of amphotericin B and its monomethyl ester derivative on glial cells in culture. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jul;34(7):1360–1365. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.7.1360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph E. D., Khazindar A. M., Barber K. R., Grant C. W. Comparative in vitro effects of liposomal amphotericin B, amphotericin B-deoxycholate, and free amphotericin B against fungal strains determined by using MIC and minimal lethal concentration susceptibility studies and time-kill curves. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):188–191. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinehart K. L., Jr Fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry. Science. 1982 Oct 15;218(4569):254–260. doi: 10.1126/science.218.4569.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner C. P., Mechlinski W. Polyene macrolide derivatives. II. Physical-chemical properties of polyene macrolide esters and their water soluble salts. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Apr;25(4):259–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. L., Williams D. M., Craven P. C., Graybill J. R., Drutz D. J., Magee W. E. Amphotericin B in liposomes: a novel therapy for histoplasmosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 May;125(5):610–611. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.5.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weddington W. W., Jr Delirium and depression associated with amphotericin B. Psychosomatics. 1982 Oct;23(10):1076–1078. doi: 10.1016/S0033-3182(82)73304-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn R. E., Bower J. H., Richards J. F. Acute toxic delirium. Neurotoxicity of intrathecal administration of amphotericin B. Arch Intern Med. 1979 Jun;139(6):706–707. doi: 10.1001/archinte.139.6.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]