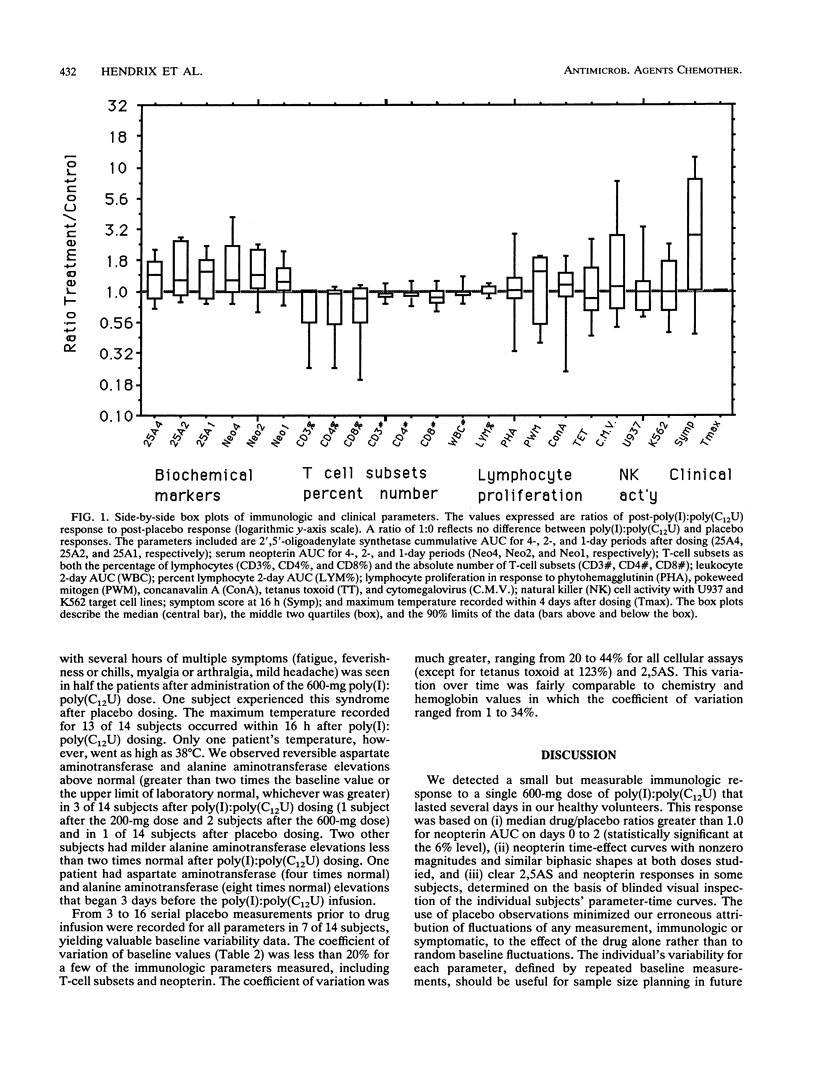
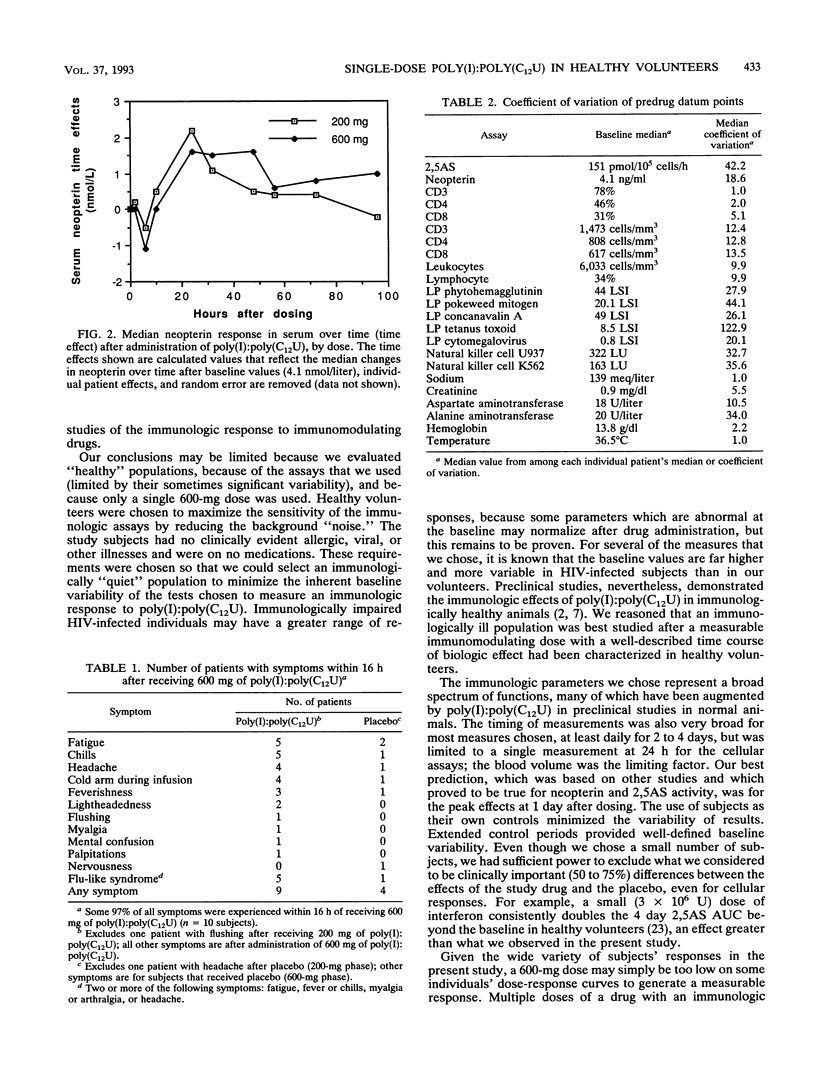
Abstract
Poly(I):poly(C12U) (mismatched double-stranded RNA; atvogen), an interferon inducer, is active against human immunodeficiency virus in vitro. To determine the extent and duration of the biologic effects of poly(I):poly(C12U), we administered a single dose of the drug to healthy volunteers in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 2-week crossover study. We analyzed blood for alpha and gamma interferons, neopterin, 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase, lymphocyte surface markers, lymphocyte proliferation after exposure to soluble antigens and mitogens, and natural killer cell activity. Minimal biologic effects were observed after administration of a single 200-mg dose to four volunteers; therefore, the dose was increased to 600 mg in 10 subjects. Only neopterin levels and symptoms were greater after administration of 600 mg of poly(I):poly(C12U) than after administration of placebo (Wilcoxon signed rank sum test, P = 0.06). A definite response in 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase activity, however, was seen in a few subjects. Neither alpha nor gamma interferon was detectable in serum after poly(I):poly(C12U) dosing. The neopterin changes after administration of poly(I):poly(C12U) were similar at both poly(I):poly(C12U) dose levels, with an early decrease at 6 h, a peak at 1 day, and a gradual decrease toward the baseline over the following 3 days. A mild flu-like syndrome occurred in one-half of the subjects following administration of poly(I):poly(C12U) and in only one subject following administration of placebo. This syndrome resolved within 16 h after poly(I):poly(C12U) dosing. We conclude that poly(I):poly(C12U) does not induce measurable levels of interferon and causes only minimal biologic or toxic effects among those parameters measured after administration of a single dose in the 200- to 600-mg dose range in health volunteers.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A., McMahon D., Huang X. L., Pazin G. J., Gupta P., Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Schoenfeld D. A., Gaccione P., Tripoli C. A., Bensasi S. A phase I study of ampligen in human immunodeficiency virus-infected subjects. J Infect Dis. 1992 Oct;166(4):717–722. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.4.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aurelian L., Rinehart C. L., Wachsman M., Kulka M., Ts'o P. O. Augmentation of natural immune defence mechanisms and therapeutic potential of a mismatched double-stranded polynucleotide in cutaneous herpes simplex virus type 2 infection. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2831–2838. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky I., Strayer D. R., Krueger L. J., Carter W. A. Clinical studies with ampligen (mismatched double-stranded RNA). J Biol Response Mod. 1985 Dec;4(6):669–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. A., Pitha P. M., Marshall L. W., Tazawa I., Tazawa S., Ts'o P. O. Structural requirements of the rI n -rC n complex for induction of human interferon. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):567–587. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90560-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. A., Strayer D. R., Brodsky I., Lewin M., Pellegrino M. G., Einck L., Henriques H. F., Simon G. L., Parenti D. M., Scheib R. G. Clinical, immunological, and virological effects of ampligen, a mismatched double-stranded RNA, in patients with AIDS or AIDS-related complex. Lancet. 1987 Jun 6;1(8545):1286–1292. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90543-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. A., Strayer D. R., Hubbell H. R., Brodsky I. Preclinical studies with Ampligen (mismatched double-stranded RNA). J Biol Response Mod. 1985 Oct;4(5):495–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Baca L., Turpin J. A., Kalter D. C., Hansen B. D., Orenstein J. M., Friedman R. M., Meltzer M. S. Restriction of HIV replication in infected T cells and monocytes by interferon-alpha. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Aug;6(8):1045–1049. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Davey V., Kovacs J. A., Feinberg J., Metcalf J. A., Herpin B., Walker R., Deyton L., Davey R. T., Jr, Falloon J. Interferon-alpha in patients with asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Jun 1;112(11):805–811. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-11-805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurence J., Kulkosky J., Friedman S. M., Posnett D. N., Ts'o P. O. PolyI.polyC12U-mediated inhibition of loss of alloantigen responsiveness viral replication in human CD4+ T cell clones exposed to human immunodeficiency virus in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1631–1639. doi: 10.1172/JCI113251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Double-stranded RNA and interferon action. J Interferon Res. 1987 Oct;7(5):511–519. doi: 10.1089/jir.1987.7.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell W. M., Montefiori D. C., Robinson W. E., Jr, Strayer D. R., Carter W. A. Mismatched double-stranded RNA (ampligen) reduces concentration of zidovudine (azidothymidine) required for in-vitro inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus. Lancet. 1987 Apr 18;1(8538):890–892. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92862-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montefiori D. C., Mitchell W. M. Antiviral activity of mismatched double-stranded RNA against human immunodeficiency virus in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2985–2989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolibe D., Aumaitre E., Thang M. N. In vivo augmentation of rat lung natural killer cell activity and inhibition of experimental metastases by double-stranded polynucleotides. Cancer Res. 1985 Oct;45(10):4774–4778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schattner A., Wallach D., Merlin G., Hahn T., Levin S., Revel M. Assay of an interferon-induced enzyme in white blood cells as a diagnostic aid in viral diseases. Lancet. 1981 Sep 5;2(8245):497–500. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90883-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strayer D. R., Carter W. A., Brodsky I., Gillespie D. H., Greene J. J., Ts'o P. O. Clinical studies with mismatched double-stranded RNA. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1981;41:663–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ts'o P. O., Alderfer J. L., Levy J., Marshall L. W., O'Malley J., Horoszewicz J. S., Carter W. A. An integrated and comparative study of the antiviral effects and other biological properties of the polyinosinic acid-polycytidylic acid and its mismatched analogues. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;12(2):299–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witter F., Barouki F., Griffin D., Nadler P., Woods A., Wood D., Lietman P. Biologic response (antiviral) to recombinant human interferon alpha 2a as a function of dose and route of administration in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1987 Nov;42(5):567–575. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1987.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Schlais J., Eskra L., Greene J. J., Ts'o P. O., Carter W. A. Augmentation of human natural killer cell activity by polyinosinic acid-polycytidylic acid and its nontoxic mismatched analogues. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1852–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



