Abstract
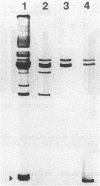
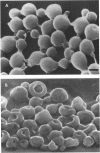
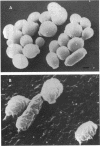
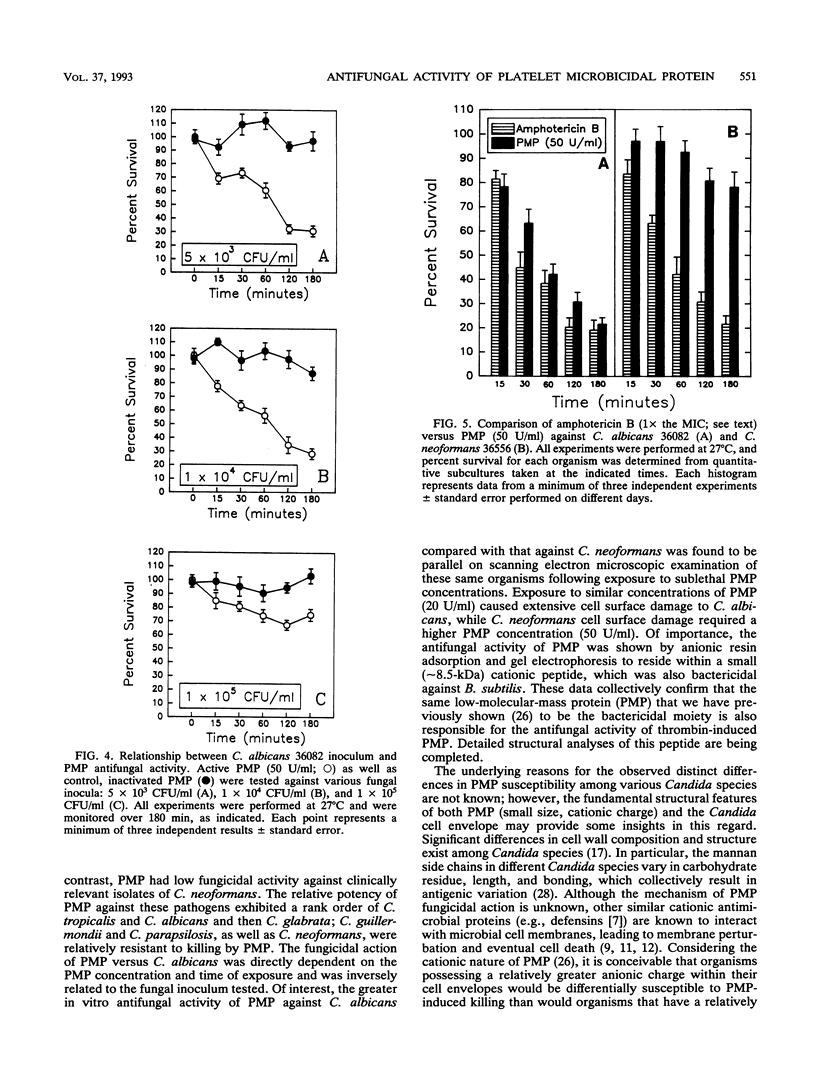
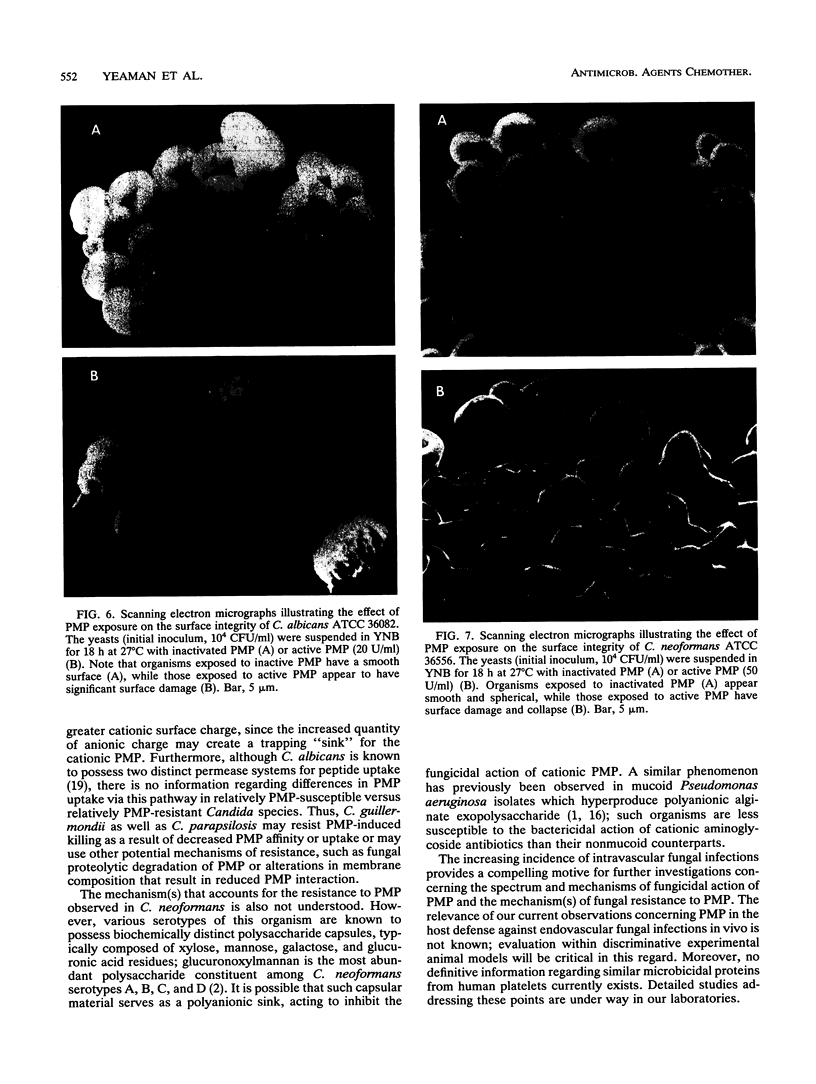
Platelet microbicidal protein (PMP) is released from platelets in response to thrombin stimulation. PMP is known to possess in vitro bactericidal activity against Staphylococcus aureus and viridans group streptococci. To determine whether PMP is active against other intravascular pathogens, we evaluated its potential fungicidal activity against strains of Candida species and Cryptococcus neoformans. Anionic resin adsorption and gel electrophoresis confirmed that the fungicidal activity of PMP resided in a small (approximately 8.5-kDa), cationic protein, identical to previous studies of PMP-induced bacterial killing (M.R. Yeaman, S.M. Puentes, D.C. Norman, and A.S. Bayer, Infect. Immun. 60:1202-1209, 1992). When assayed over a 180-min period in vitro, the susceptibilities of these fungi to PMP varied considerably. Generally, Candida albicans strains (mean survival, 33.5% +/- 6.9% [n = 6]) as well as isolates of Candida glabrata (mean survival, 50.8% +/- 2.9% [n = 2]) were the most susceptible to killing by PMP, while Candida guillermondii and Candida parapsilosis were relatively resistant to PMP-induced killing. Compared with C. albicans, C. neoformans was relatively resistant to the fungicidal activity of PMP, with a mean survival among the isolates studied of 77.4% +/- 12.4% (n = 6). Against C. albicans, PMP-induced fungicidal activity was time dependent (range, 0 to 180 min), PMP concentration dependent (range, 10 to 150 U/ml), and inversely related to the fungal inoculum (range, 5 x 10(3) to 1 x 10(5) CFU/ml). Scanning electron microscopy of PMP-exposed C. albicans and C. neoformans cells revealed extensive surface damage and collapse, suggesting that the site of PMP fungicidal action may directly or indirectly involve the fungal cell envelope.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer A. S., Speert D. P., Park S., Tu J., Witt M., Nast C. C., Norman D. C. Functional role of mucoid exopolysaccharide (alginate) in antibiotic-induced and polymorphonuclear leukocyte-mediated killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):302–308. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.302-308.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee A. K., Bennett J. E., Glaudemans C. P. Capsular polysaccharides of Cryptococcus neoformans. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;6(5):619–624. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.5.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R. A., Rotondo M. F., Sande M. A. Candida albicans endocarditis: ultrastructural studies of vegetation formation. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):279–289. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.279-289.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson D. M., Tew J. G. beta-Lysin of platelet origin. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):501–513. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.501-513.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. Defensins. Eur J Haematol. 1990 Jan;44(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1990.tb00339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghannoum M. A., Elteen K. A., Ellabib M., Whittaker P. A. Antimycotic effects of octenidine and pirtenidine. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Feb;25(2):237–245. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan B. L., Selsted M. E., Ganz T., Lehrer R. I. Antimicrobial defensin peptides form voltage-dependent ion-permeable channels in planar lipid bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):210–214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Barton A., Daher K. A., Harwig S. S., Ganz T., Selsted M. E. Interaction of human defensins with Escherichia coli. Mechanism of bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):553–561. doi: 10.1172/JCI114198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein A. K., Ganz T., Nguyen T. M., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. Mechanism of target cytolysis by peptide defensins. Target cell metabolic activities, possibly involving endocytosis, are crucial for expression of cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2686–2694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisch P. A., Calderone R. A. Adherence of Candida albicans to a fibrin-platelet matrix formed in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):650–656. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.650-656.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisch P. A., Calderone R. A. Role of surface mannan in the adherence of Candida albicans to fibrin-platelet clots formed in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):92–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.92-97.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. W., Evans M. J., Slack M. P., Walmsley H. L. The penetration of antibiotics into aggregates of mucoid and non-mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 May;135(5):1291–1303. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-5-1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Rinaldi M. G., Galgiani J. N., Bartlett M. S., Body B. A., Espinel-Ingroff A., Fromtling R. A., Hall G. S., Hughes C. E., Odds F. C. Collaborative investigation of variables in susceptibility testing of yeasts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1648–1654. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad R. Nutrient transport in Candida albicans, a pathogenic yeast. Yeast. 1987 Dec;3(4):209–221. doi: 10.1002/yea.320030402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Harwig S. S. Purification, primary structure, and antimicrobial activities of a guinea pig neutrophil defensin. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2281–2286. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2281-2286.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein R. L., Nachman R. L. Thrombospondin binds to monocytes-macrophages and mediates platelet-monocyte adhesion. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):867–874. doi: 10.1172/JCI112896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler B. B., Nachman R. L. Rabbit platelet bactericidal protein. J Exp Med. 1971 Nov 1;134(5):1114–1130. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.5.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman M. R., Norman D. C., Bayer A. S. Staphylococcus aureus susceptibility to thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein is independent of platelet adherence and aggregation in vitro. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2368–2374. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2368-2374.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman M. R., Puentes S. M., Norman D. C., Bayer A. S. Partial characterization and staphylocidal activity of thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1202–1209. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1202-1209.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman M. R., Sullam P. M., Dazin P. F., Norman D. C., Bayer A. S. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus-platelet binding by quantitative flow cytometric analysis. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jul;166(1):65–73. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]