Abstract
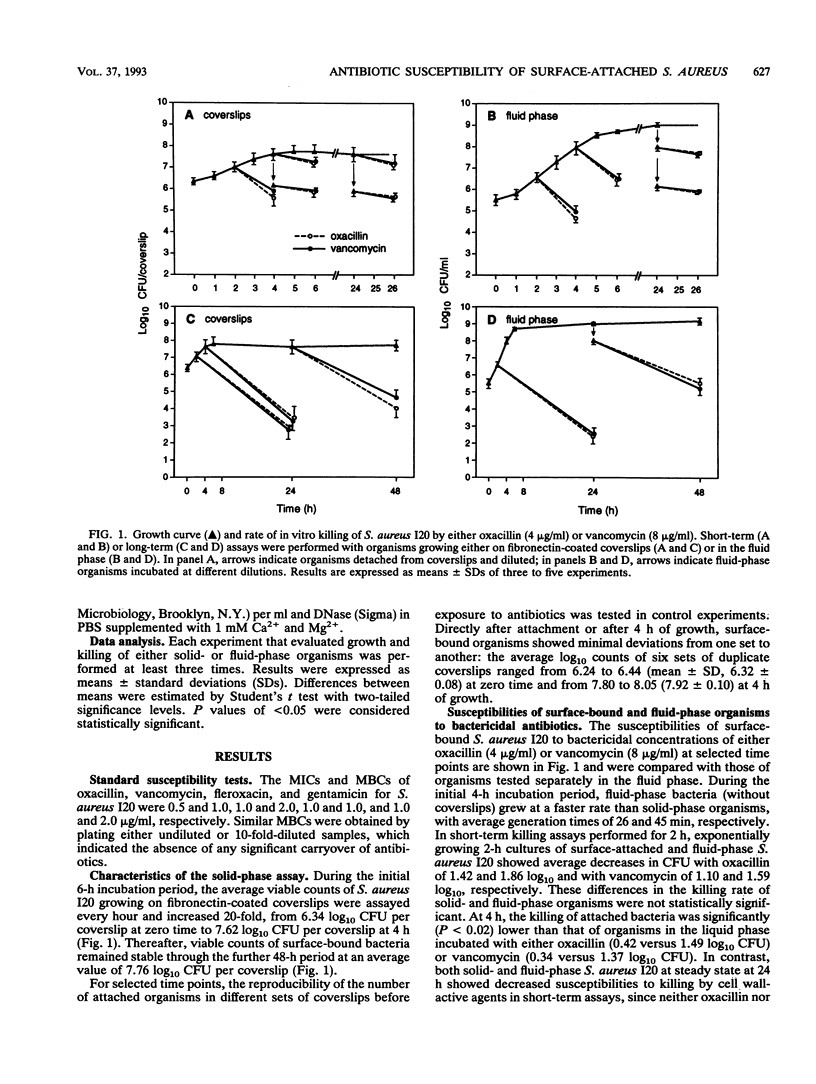
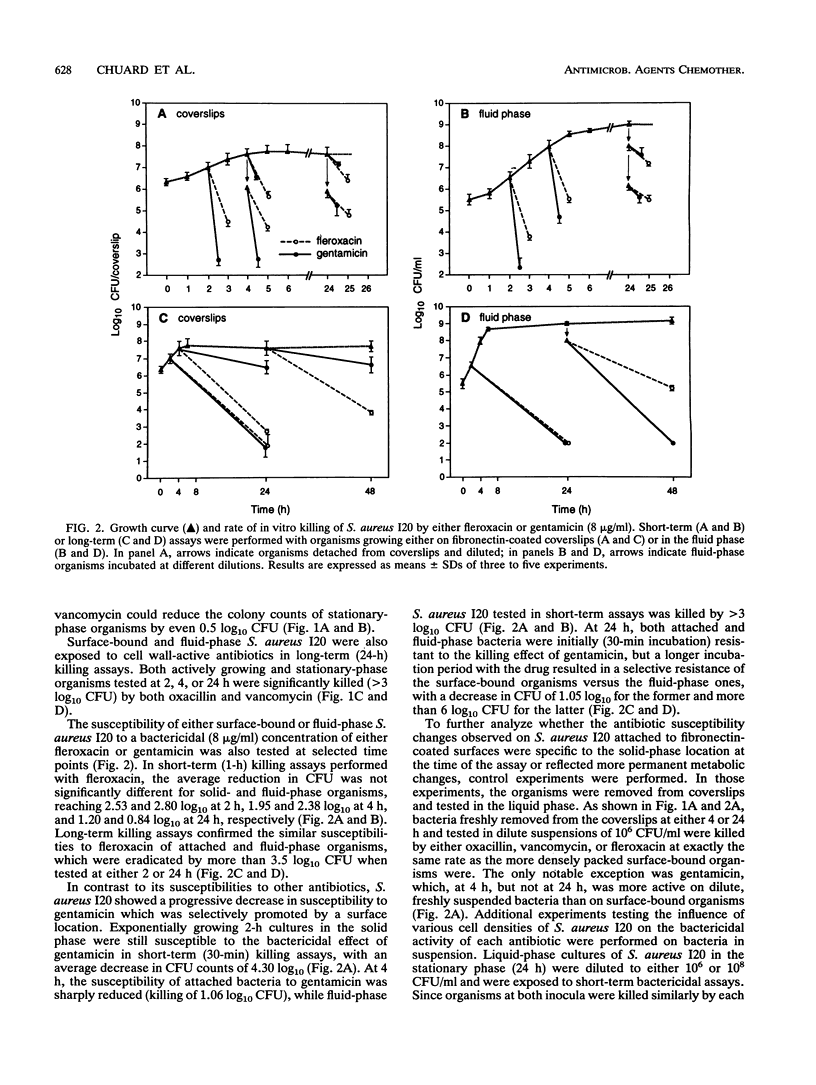
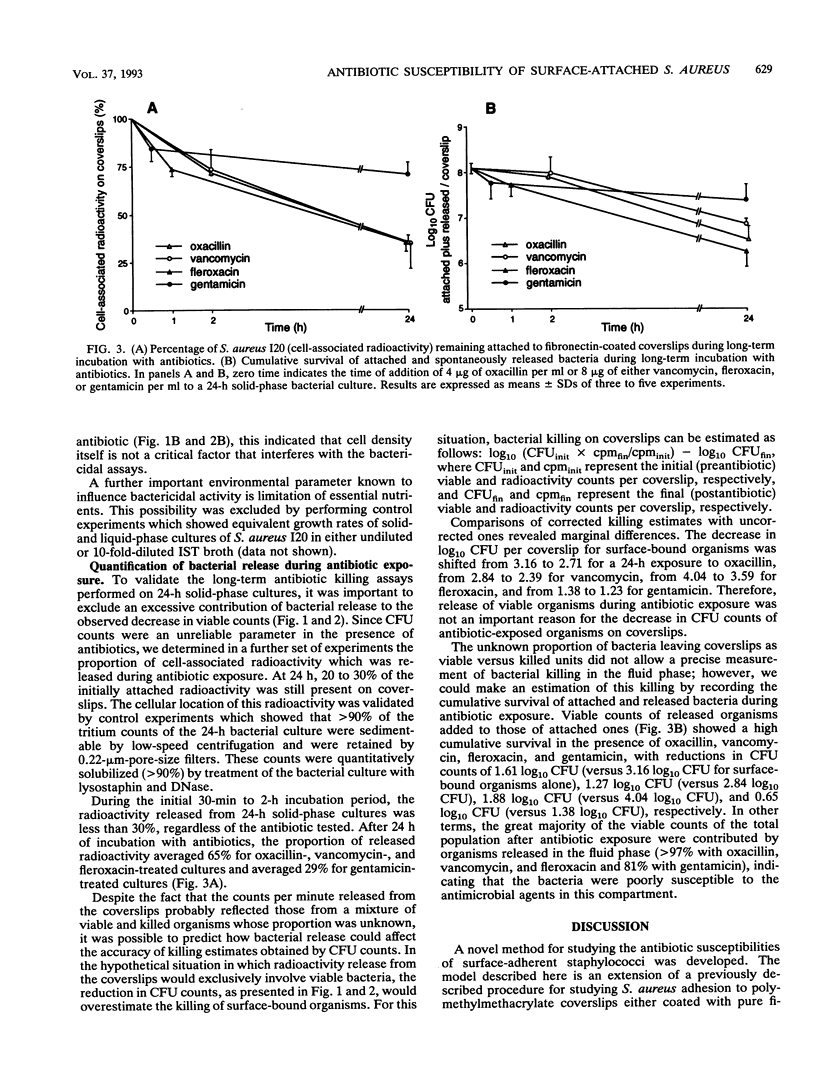
Several recent studies have shown that bacteria either grown in vitro as adherent biofilms or recovered from infected prosthetic devices have decreased susceptibilities to antimicrobial killing. To further study the microbial and environmental factors responsible for this decreased antibiotic susceptibility, we developed an in vitro model of surface-adherent Staphylococcus aureus growing on polymethylmethacrylate coverslips coated with pure fibronectin. After exponential growth for 4 h, the population of fibronectin-attached S. aureus remained constant for a further 48-h period, as evaluated by CFU counts of organisms quantitatively removed from the coverslips. At selected time points, surface-bound organisms were exposed to bactericidal concentrations of either oxacillin, vancomycin, fleroxacin, or gentamicin in short-term (0.5 to 2 h) or long-term (24 h) killing assays. Whereas at 2 h surface-growing organisms were still optimally killed by all antimicrobial agents, at 4 and 24 h attached bacteria expressed markedly altered susceptibilities to these agents. The decrease in susceptibility was moderate for fleroxacin, more important for oxacillin and vancomycin, and extensive for gentamicin. When surface-attached S. aureus was compared with bacteria grown in a fluid phase, both populations showed a parallel time-dependent decrease in their susceptibilities to either oxacillin, vancomycin, or fleroxacin. In contrast, attached organisms became considerably more resistance to gentamicin than suspended bacteria did. Subpopulations of organisms spontaneously released from coverslips during antibiotic exposure also showed markedly reduced susceptibilities to antimicrobial killing. This simple model of S. aureus colonization of in vitro fibronectin-coated surfaces might represent a useful approach to the study of the physiological and biochemical changes that underlie the decreased antibiotic susceptibilities of biomaterial-attached organisms.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anwar H., Dasgupta M. K., Costerton J. W. Testing the susceptibility of bacteria in biofilms to antibacterial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2043–2046. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwar H., van Biesen T., Dasgupta M., Lam K., Costerton J. W. Interaction of biofilm bacteria with antibiotics in a novel in vitro chemostat system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Oct;33(10):1824–1826. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.10.1824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Allison D. G., Gilbert P. Resistance of bacterial biofilms to antibiotics: a growth-rate related effect? J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Dec;22(6):777–780. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.6.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Collier P. J., Gilbert P. Influence of growth rate on susceptibility to antimicrobial agents: modification of the cell envelope and batch and continuous culture studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1623–1628. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):318–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.318-326.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuard C., Herrmann M., Vaudaux P., Waldvogel F. A., Lew D. P. Successful therapy of experimental chronic foreign-body infection due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by antimicrobial combinations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Dec;35(12):2611–2616. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.12.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuard C., Lucet J. C., Rohner P., Herrmann M., Auckenthaler R., Waldvogel F. A., Lew D. P. Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus recovered from infected foreign body in vivo to killing by antimicrobials. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1369–1373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Cheng K. J., Geesey G. G., Ladd T. I., Nickel J. C., Dasgupta M., Marrie T. J. Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:435–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin R., Modin G., Kunz S., Rich R., Zak O., Sande M. Comparative efficacies of ciprofloxacin, pefloxacin, and vancomycin in combination with rifampin in a rat model of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus chronic osteomyelitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1014–1016. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Allison D. G., Brown M. R., Gilbert P. Susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli biofilms towards ciprofloxacin: effect of specific growth rate. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Feb;27(2):177–184. doi: 10.1093/jac/27.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Brown M. R., Allison D. G., Gilbert P. Susceptibility of bacterial biofilms to tobramycin: role of specific growth rate and phase in the division cycle. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Apr;25(4):585–591. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.4.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. C., Holmes C. J. Effect of vancomycin hydrochloride on Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm associated with silicone elastomer. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jun;31(6):889–894. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.6.889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert P., Allison D. G., Evans D. J., Handley P. S., Brown M. R. Growth rate control of adherent bacterial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1308–1311. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1308-1311.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert P., Brown M. R., Costerton J. W. Inocula for antimicrobial sensitivity testing: a critical review. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Aug;20(2):147–154. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert P., Collier P. J., Brown M. R. Influence of growth rate on susceptibility to antimicrobial agents: biofilms, cell cycle, dormancy, and stringent response. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Oct;34(10):1865–1868. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.10.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gristina A. G., Hobgood C. D., Webb L. X., Myrvik Q. N. Adhesive colonization of biomaterials and antibiotic resistance. Biomaterials. 1987 Nov;8(6):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0142-9612(87)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gristina A. G., Jennings R. A., Naylor P. T., Myrvik Q. N., Webb L. X. Comparative in vitro antibiotic resistance of surface-colonizing coagulase-negative staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jun;33(6):813–816. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.6.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry N. K., Rouse M. S., Whitesell A. L., McConnell M. E., Wilson W. R. Treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus experimental osteomyelitis with ciprofloxacin or vancomycin alone or in combination with rifampin. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):73–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle B. D., Jass J., Costerton J. W. The biofilm glycocalyx as a resistance factor. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Jul;26(1):1–5. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucet J. C., Herrmann M., Rohner P., Auckenthaler R., Waldvogel F. A., Lew D. P. Treatment of experimental foreign body infection caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Dec;34(12):2312–2317. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.12.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. H., Edberg S. C., Mandel L. J., Behar C. F., Steigbigel N. H. Gentamicin uptake in wild-type and aminoglycoside-resistant small-colony mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):722–729. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. H., Wexler M. A., Steigbigel N. H. Single and combination antibiotic therapy of Staphylococcus aureus experimental endocarditis: emergence of gentamicin-resistant mutants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):336–343. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Baughn R. E., Templeton G. B., Minuth J. N. Emergence of variant forms of Staphylococcus aureus after exposure to gentamicin and infectivity of the variants in experimental animals. J Infect Dis. 1977 Sep;136(3):360–369. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.3.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. W., Evans M. J., Slack M. P., Walmsley H. L. The penetration of antibiotics into aggregates of mucoid and non-mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 May;135(5):1291–1303. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-5-1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel J. C., Ruseska I., Wright J. B., Costerton J. W. Tobramycin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells growing as a biofilm on urinary catheter material. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):619–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier L. L., Jr, Richardson M., Feist M. Virulent gentamicin-induced small colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Aug;94(2):324–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser B. L., Taylor D., Dix B. A., Cleeland R. Method of evaluating effects of antibiotics on bacterial biofilm. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1502–1506. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheth N. K., Franson T. R., Sohnle P. G. Influence of bacterial adherence to intravascular catheters on in-vitro antibiotic susceptibility. Lancet. 1985 Dec 7;2(8467):1266–1268. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91552-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudaux P. E., Waldvogel F. A., Morgenthaler J. J., Nydegger U. E. Adsorption of fibronectin onto polymethylmethacrylate and promotion of Staphylococcus aureus adherence. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):768–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.768-774.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudaux P., Suzuki R., Waldvogel F. A., Morgenthaler J. J., Nydegger U. E. Foreign body infection: role of fibronectin as a ligand for the adherence of Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):546–553. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer A. F., Frei R., Rajacic Z., Zimmerli W. Correlation between in vivo and in vitro efficacy of antimicrobial agents against foreign body infections. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):96–102. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer A. F., Wiestner A., Frei R., Zimmerli W. Killing of nongrowing and adherent Escherichia coli determines drug efficacy in device-related infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Apr;35(4):741–746. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younger J. J., Christensen G. D., Bartley D. L., Simmons J. C., Barrett F. F. Coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from cerebrospinal fluid shunts: importance of slime production, species identification, and shunt removal to clinical outcome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):548–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Lew P. D., Waldvogel F. A. Pathogenesis of foreign body infection. Evidence for a local granulocyte defect. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1191–1200. doi: 10.1172/JCI111305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Waldvogel F. A., Vaudaux P., Nydegger U. E. Pathogenesis of foreign body infection: description and characteristics of an animal model. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):487–497. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


