Abstract
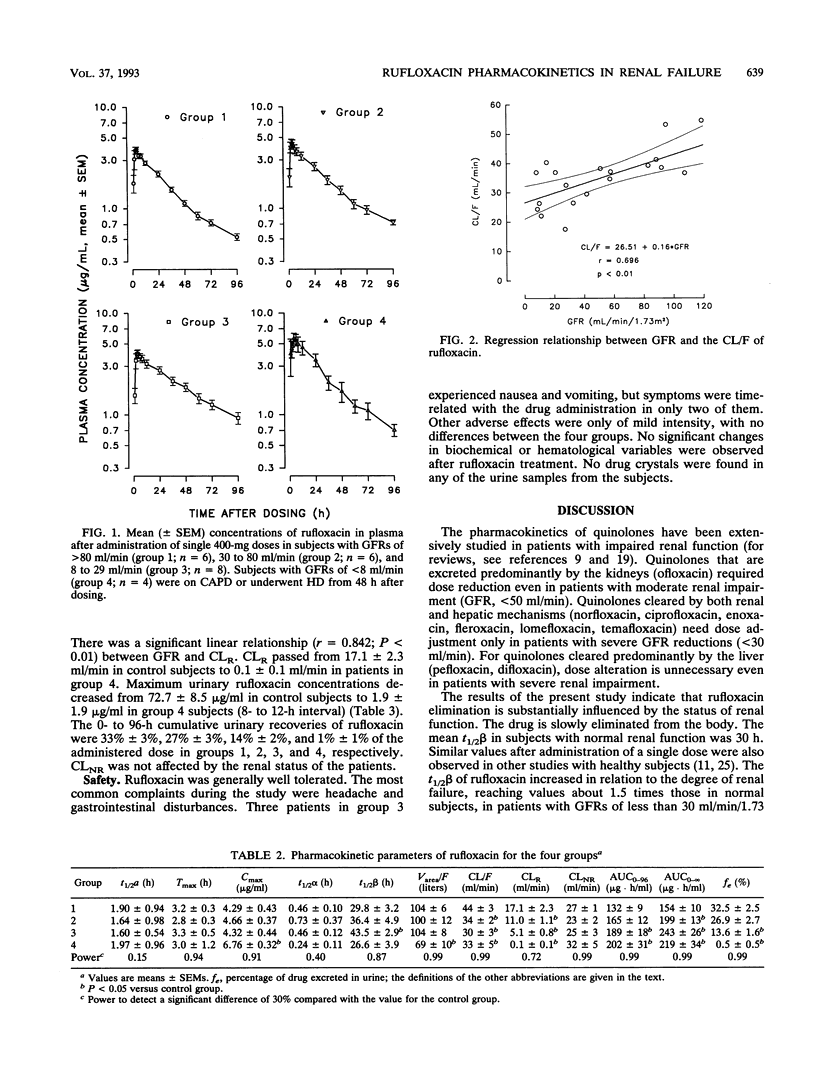
The pharmacokinetics of rufloxacin were investigated in normal subjects and in patients with various degrees of renal failure after the administration of a single oral 400-mg dose. Twenty-four subjects were classified by glomerular filtration rate (GFR) normalized for body surface area. Group 1 subjects had GFRs of > 80 ml/min, group 2 subjects had GFRs from 30 to 80 ml/min, group 3 subjects had GFRs from 8 to 29 ml/min, and group 4 subjects had GFRs of < 8 ml/min. The patients in group 4 were on continuous peritoneal dialysis or underwent hemodialysis 48 h after dosing. Plasma and urinary rufloxacin concentrations were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. A two-compartment model was used to calculate rufloxacin pharmacokinetic parameters. Apparent total body clearance of the drug was linearly related to GFR (r = 0.696; P < 0.01). The elimination half-life increased proportionally with the severity of renal impairment, with values of 30 +/- 3, 36 +/- 5, and 44 +/- 3 h in groups 1, 2, and 3, respectively. In patients with moderate renal failure, dosage adjustment of rufloxacin is not needed. The rufloxacin dose interval should be prolonged to 48 h as the GFR falls below 30 ml/min/1.73 m2.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boerema J. B., Bach D., Jol C., Pahlmann W. Penetration of rufloxacin into human prostatic tissue and fluid. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Oct;28(4):547–554. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecchetti V., Fravolini A., Fringuelli R., Mascellani G., Pagella P., Palmioli M., Segre G., Terni P. Quinolonecarboxylic acids. 2. Synthesis and antibacterial evaluation of 7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7H-pyrido[1,2,3-de][1,4]benzothiazine-6-carboxylic acids. J Med Chem. 1987 Mar;30(3):465–473. doi: 10.1021/jm00386a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantler C., Garnett E. S., Parsons V., Veall N. Glomerular filtration rate measurement in man by the single injection methods using 51Cr-EDTA. Clin Sci. 1969 Aug;37(1):169–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Gault M. H. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 1976;16(1):31–41. doi: 10.1159/000180580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogo R., Rimoldi R., Mattina R., Imbimbo B. P. Steady-state pharmacokinetics of rufloxacin in elderly patients with lower respiratory tract infections. Ther Drug Monit. 1992 Feb;14(1):36–41. doi: 10.1097/00007691-199202000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirksen M., Focht J., Boerema J. Rufloxacin once daily in acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis. Infection. 1991 Jul-Aug;19(4):297–300. doi: 10.1007/BF01644971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbimbo B. P., Broccali G., Cesana M., Crema F., Attardo-Parrinello G. Inter- and intrasubject variabilities in the pharmacokinetics of rufloxacin after single oral administration to healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):390–393. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbimbo B. P., Imbimbo E., Daniotti S., Verotta D., Bassotti G. A new criterion for selection of pharmacokinetic multiexponential equations. J Pharm Sci. 1988 Sep;77(9):784–789. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600770914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisicki J. C., Griess R. S., Ott C. L., Cohen G. M., McCormack R. J., Troetel W. M., Imbimbo B. P. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics and safety of rufloxacin in normal volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jun;36(6):1296–1301. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.6.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattina R., Bonfiglio G., Cocuzza C. E., Gulisano G., Cesana M., Imbimbo B. P. Pharmacokinetics of rufloxacin in healthy volunteers after repeated oral doses. Chemotherapy. 1991;37(6):389–397. doi: 10.1159/000238885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattina R., Cocuzza C. E., Cesana M., Bonfiglio G. In vitro activity of a new quinolone, rufloxacin, against nosocomial isolates. Chemotherapy. 1991;37(4):260–269. doi: 10.1159/000238865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuman M. Clinical pharmacokinetics of the newer antibacterial 4-quinolones. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1988 Feb;14(2):96–121. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198814020-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimoldi R., Fioretti M., Albrici A., Imbimbo B. P. Pharmacokinetics of rufloxacin once daily in patients with lower respiratory tract infections. Infection. 1992 Mar-Apr;20(2):89–93. doi: 10.1007/BF01711071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segre G., Cerretani D., Cerri D., Moltoni L. A new tricyclic fluoroquinolone, rufloxacin (MF-934), with interesting antibacterial and pharmacokinetic characteristics. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1988;14(12):747–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Matthews R., Wolstenholme M. The in-vitro activity of two new quinolones: rufloxacin and MF 961. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Jun;29(6):649–660. doi: 10.1093/jac/29.6.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Johnson J., O'Sullivan N., Andrews J. M., Imbimbo B. P. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of rufloxacin, a long acting quinolone antimicrobial agent. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Dec;28(6):905–909. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.6.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


