Abstract
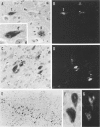
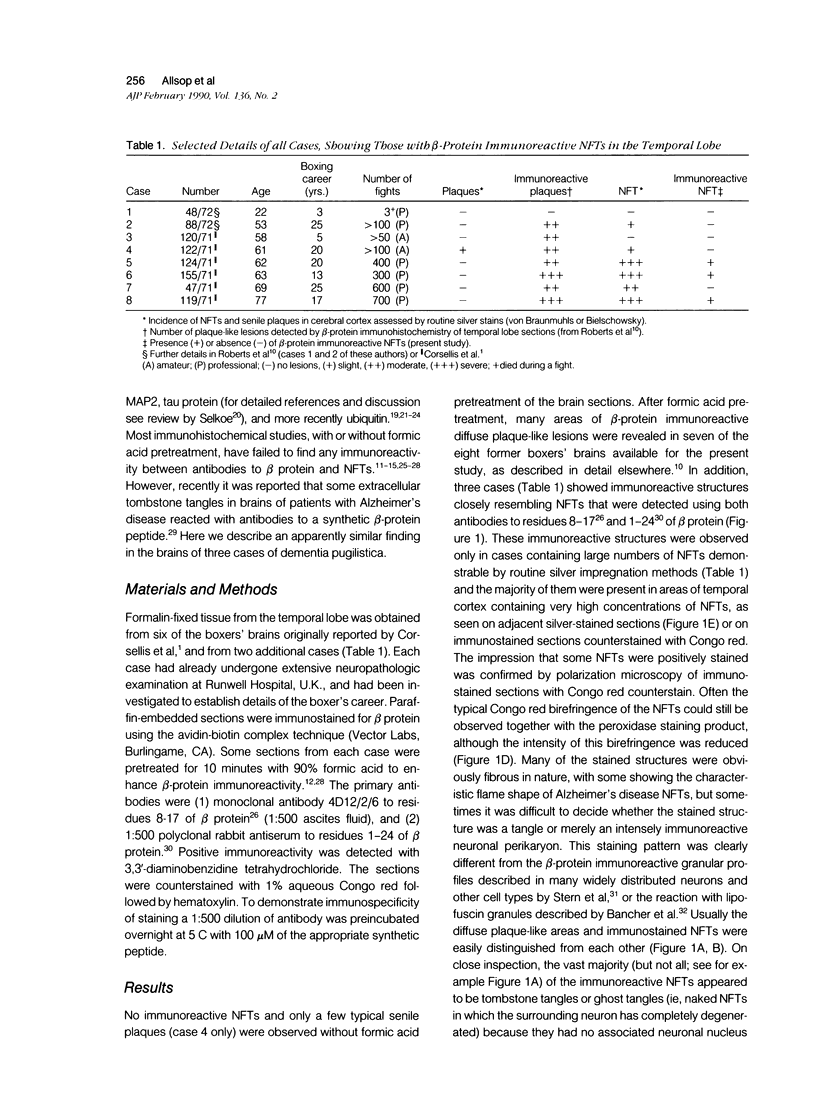
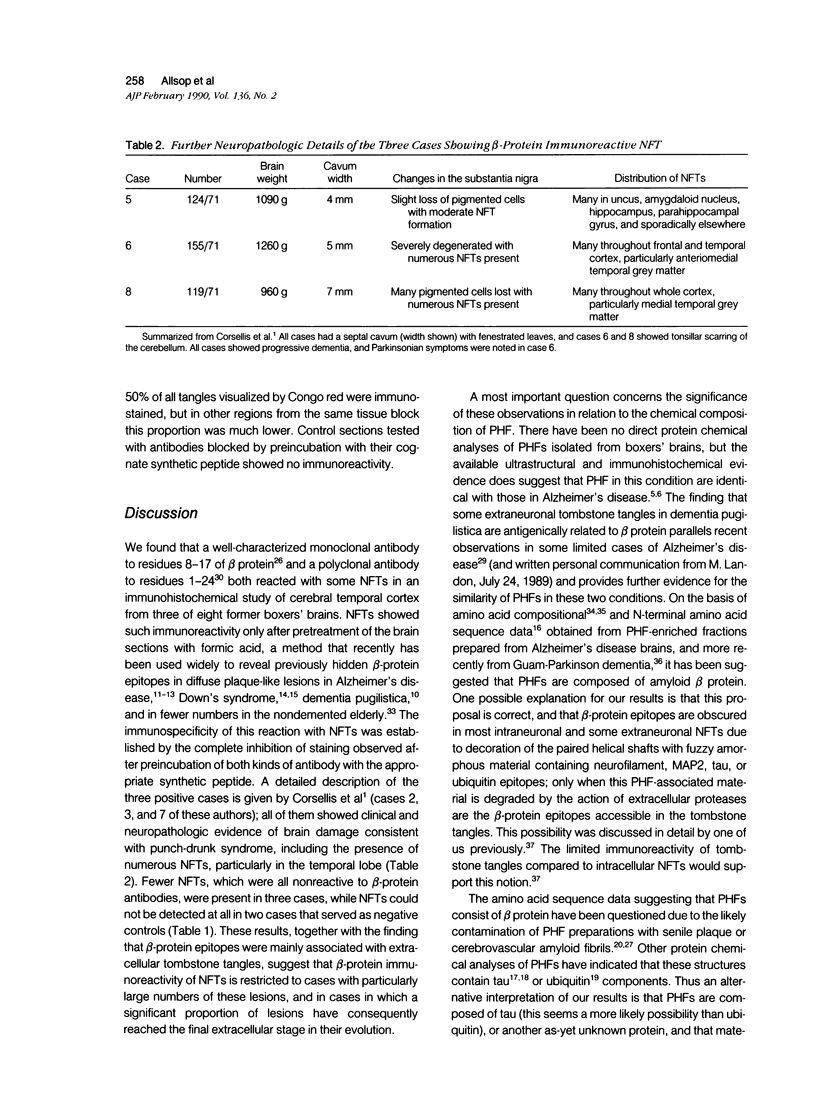
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded temporal lobe sections from eight former boxers' brains were examined using an immunohistochemical method with antibodies to amyloid beta protein. In accord with recent observations in Alzheimer's disease, significant numbers of beta-protein immunoreactive neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) were observed in three cases. Most of these immunoreactive NFTs appeared to be tombstone tangles, although not all such tangles were stained. This immunoreaction was completely abolished by preincubation of antibodies with synthetic beta-protein peptides, and the identity of the immunostained NFTs was confirmed by polarization microscopy of sections counterstained with Congo red. However, it is not yet clear if the beta-protein antigens are, in fact, an integral part of paired helical filaments. These observations, together with our recent finding of beta-immunoreactive plaque-like lesions in dementia pugilistica, also emphasize the many similarities in pathology between this condition and Alzheimer's disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams C. W., Bruton C. J. The cerebral vasculature in dementia pugilistica. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989 May;52(5):600–604. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.52.5.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allsop D., Landon M., Kidd M., Lowe J. S., Reynolds G. P., Gardner A. Monoclonal antibodies raised against a subsequence of senile plaque core protein react with plaque cores, plaque periphery and cerebrovascular amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jul 24;68(2):252–256. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancher C., Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Kim K. S., Wisniewski H. M. Immunoreactivity of neuronal lipofuscin with monoclonal antibodies to the amyloid beta-protein. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Mar-Apr;10(2):125–132. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. M., Timiras P. S. Ubiquitin-protein conjugates in Alzheimer's lesions. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Aug 18;79(1-2):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90698-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsellis J. A., Bruton C. J., Freeman-Browne D. The aftermath of boxing. Psychol Med. 1973 Aug;3(3):270–303. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700049588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentleman S. M., Bruton C., Allsop D., Lewis S. J., Polak J. M., Roberts G. W. A demonstration of the advantages of immunostaining in the quantification of amyloid plaque deposits. Histochemistry. 1989;92(4):355–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00500553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaccone G., Tagliavini F., Linoli G., Bouras C., Frigerio L., Frangione B., Bugiani O. Down patients: extracellular preamyloid deposits precede neuritic degeneration and senile plaques. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Feb 13;97(1-2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiroy D. C., Miyazaki M., Multhaup G., Fischer P., Garruto R. M., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L., Simms G., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Amyloid of neurofibrillary tangles of Guamanian parkinsonism-dementia and Alzheimer disease share identical amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):2073–2077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.2073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., Van Hoesen G. W., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L. A4 amyloid protein immunoreactivity is present in Alzheimer's disease neurofibrillary tangles. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Jul 3;101(3):352–355. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S., Allsop D., Glenner G. G. Morphology and distribution of plaque and related deposits in the brains of Alzheimer's disease and control cases. An immunohistochemical study using amyloid beta-protein antibody. Lab Invest. 1989 Jan;60(1):113–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S., Yanagisawa N., Allsop D., Glenner G. G. Evidence of amyloid beta-protein immunoreactive early plaque lesions in Down's syndrome brains. Lab Invest. 1989 Jul;61(1):133–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii T., Kametani F., Haga S., Sato M. The immunohistochemical demonstration of subsequences of the precursor of the amyloid A4 protein in senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1989 Mar-Apr;15(2):135–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1989.tb01216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIDD M. Paired helical filaments in electron microscopy of Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1963 Jan 12;197:192–193. doi: 10.1038/197192b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd M., Allsop D., Landon M. Senile plaque amyloid, paired helical filaments, and cerebrovascular amyloid in Alzheimer's disease are all deposits of the same protein. Lancet. 1985 Feb 2;1(8423):278–278. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Ogomori K., Tateishi J., Prusiner S. B. Formic acid pretreatment enhances immunostaining of cerebral and systemic amyloids. Lab Invest. 1987 Aug;57(2):230–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo J., Honda T., Mori H., Hamada Y., Miura R., Ogawara M., Ihara Y. The carboxyl third of tau is tightly bound to paired helical filaments. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):827–834. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennox G., Lowe J., Morrell K., Landon M., Mayer R. J. Ubiquitin is a component of neurofibrillary tangles in a variety of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Nov 22;94(1-2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90297-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Multhaup G., Simms G., Pottgiesser J., Martins R. N., Beyreuther K. Neuronal origin of a cerebral amyloid: neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease contain the same protein as the amyloid of plaque cores and blood vessels. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2757–2763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Kondo J., Ihara Y. Ubiquitin is a component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1641–1644. doi: 10.1126/science.3029875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Friedman R., Shaw G., Chau V. Ubiquitin is detected in neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaque neurites of Alzheimer disease brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):3033–3036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.3033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. W. Immunocytochemistry of neurofibrillary tangles in dementia pugilistica and Alzheimer's disease: evidence for common genesis. Lancet. 1988 Dec 24;2(8626-8627):1456–1458. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90934-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. L., Gur R. E., Gur R. C., Trojanowski J. Q. Intraneuronal and extracellular neurofibrillary tangles exhibit mutually exclusive cytoskeletal antigens. Ann Neurol. 1988 Feb;23(2):184–189. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Abraham C. R., Podlisny M. B., Duffy L. K. Isolation of low-molecular-weight proteins from amyloid plaque fibers in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 1986 Jun;46(6):1820–1834. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb08501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J. Biochemistry of altered brain proteins in Alzheimer's disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:463–490. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern R. A., Otvos L., Jr, Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M. Monoclonal antibodies to a synthetic peptide homologous with the first 28 amino acids of Alzheimer's disease beta-protein recognize amyloid and diverse glial and neuronal cell types in the central nervous system. Am J Pathol. 1989 May;134(5):973–978. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini F., Giaccone G., Frangione B., Bugiani O. Preamyloid deposits in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease and nondemented individuals. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Nov 11;93(2-3):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wischik C. M., Novak M., Thøgersen H. C., Edwards P. C., Runswick M. J., Jakes R., Walker J. E., Milstein C., Roth M., Klug A. Isolation of a fragment of tau derived from the core of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4506–4510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. W., Quaranta V., Glenner G. G. Neuritic plaques and cerebrovascular amyloid in Alzheimer disease are antigenically related. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8729–8732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Hirai S., Morimatsu M., Shoji M., Ihara Y. A variety of cerebral amyloid deposits in the brains of the Alzheimer-type dementia demonstrated by beta protein immunostaining. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;76(6):541–549. doi: 10.1007/BF00689591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Morimatsu M., Hirai S., Takahashi K. Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles are penetrated by astroglial processes and appear eosinophilic in their final stages. Acta Neuropathol. 1987;72(3):214–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00691092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]