Abstract
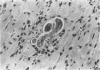
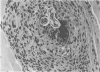
In humans, chronic eosinophilia has been associated clinically with endomyocardial fibrosis and myocardial damage. Mice infected with Toxocara canis have a marked eosinophilia, and develop eosinophil-rich granulomatous lesions in the soft tissues of the body, especially the lungs, liver, brain, and skeletal muscle. Few reports have described myocardial lesions associated with T. canis infections in mice. We examined the hearts of CBA/J mice killed at weekly intervals over an 8-week period for evidence of myocardial damage that might be attributable to eosinophils. Total white blood cell counts and eosinophil counts were obtained during this period, and revealed a peak white blood cell count of approximately 28,000 cells/mm3 at day 7 after infection and a peak eosinophil count of approximately 4,000 cells/mm3 at day 14 after infection. Myocardial lesions in the ventricular wall began as focal infiltrates of eosinophils and histiocytes, then progressed into granulomata containing necrotic debris. Collagen deposition was noted by day 21 after infection. By day 42 after infection, the lesions had contracted greatly because of a loss of cellularity, and consisted mainly of fibroblasts and hemosiderin-laden macrophages. Myocyte damage, characterized by increased eosinophilia and necrosis, was observed. T. canis-infected CBA/J mice thus offer a useful model to study eosinophil-dependent myocardial damage.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEAVER P. C., SNYDER C. H., CARRERA G. M., DENT J. H., LAFFERTY J. W. Chronic eosinophilia due to visceral larva migrans; report of three cases. Pediatrics. 1952 Jan;9(1):7–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRILL R., CHURG J., BEAVER P. C. Allergic granulomatosis associated with visceral larva migrans; case report with autopsy findings on Toxocara infection in a child. Am J Clin Pathol. 1953 Dec;23(12):1208–1215. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/23.12.1208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman D. D., Mika-Grieve M., Grieve R. B. Circulating excretory-secretory antigen levels and specific antibody responses in mice infected with Toxocara canis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Jan;36(1):75–82. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burren C. H. Experimental toxocariasis. I. Some observations on the histopathology of the migration of Toxocara canis larvae in the mouse. Z Parasitenkd. 1968;30(2):152–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00259724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Bazin H., Joseph M., Capron A. Evidence for IgE-dependent cytotoxicity by rat eosinophils. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1764–1768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chusid M. J., Dale D. C., West B. C., Wolff S. M. The hypereosinophilic syndrome: analysis of fourteen cases with review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1975 Jan;54(1):1–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENT J. H., NICHOLS R. L., BEAVER P. C., CARRERA G. M., STAGGERS R. J. Visceral larva migrans; with a case report. Am J Pathol. 1956 Jul-Aug;32(4):777–803. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunsmore J. D., Thompson R. C., Bates I. A. The accumulation of Toxocara canis larvae in the brains of mice. Int J Parasitol. 1983 Oct;13(5):517–521. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(83)80017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN S., HERVADA A. R. Severe myocarditis with recovery in a child with visceral larva migrans. J Pediatr. 1960 Jan;56:91–96. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(60)80292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A. Immunobiology of eosinophils. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:429–459. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman L. T., Schantz P. M. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of zoonotic toxocariasis. Epidemiol Rev. 1981;3:230–250. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayes S. G., Jones R. E., Omholt P. E. Use of bronchoalveolar lavage to compare local pulmonary immunity with the systemic immune response of Toxocara canis-infected mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2132–2136. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2132-2136.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayes S. G., Oaks J. A. Development of the granulomatous response in murine toxocariasis. Initial events. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):277–294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayes S. G., Oaks J. A. Toxocara canis: T lymphocyte function in murine visceral larva migrans and eosinophilia onset. Exp Parasitol. 1980 Feb;49(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(80)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayes S. G., Omholt P. E., Grieve R. B. Immune responses of CBA/J mice to graded infections with Toxocara canis. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):697–703. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.697-703.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayes S. G. Spleen cell responses in experimental murine toxocariasis. J Parasitol. 1984 Aug;70(4):522–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSON L. J. Organ disturbution of Toxocara canis larvae in normal mice and in mice previously infected with Toxocara, Ascaris or Trichinella. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1962;20:651–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrillo J. E., Borer J. S., Henry W. L., Wolff S. M., Fauci A. S. The cardiovascular manifestations of the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Prospective study of 26 patients, with review of the literature. Am J Med. 1979 Oct;67(4):572–582. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90227-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRENT J. F. A. On the migratory behavior of the larvae of various Ascaris species in white mice. I. Distribution of larvae in tissues. J Infect Dis. 1952 Mar-Apr;90(2):165–176. doi: 10.1093/infdis/90.2.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz P. M., Glickman L. T. Toxocaral visceral larva migrans. N Engl J Med. 1978 Feb 23;298(8):436–439. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197802232980806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Ackerman S. J., Spry C. J., Dunnette S., Olsen E. G., Gleich G. J. Deposits of eosinophil granule proteins in cardiac tissues of patients with eosinophilic endomyocardial disease. Lancet. 1987 Mar 21;1(8534):643–647. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90412-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Hayes D. J., Clark J. B., Spry C. J. Toxic effects of human eosinophil products on isolated rat heart cells in vitro. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):75–80. doi: 10.1042/bj2040075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargo T. A., Singer D. B., Gillatte P. C., Fernbach D. J. Myocarditis due to visceral larva migrans. J Pediatr. 1977 Feb;90(2):322–323. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80666-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]