Abstract
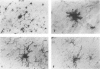
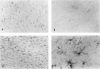
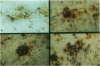
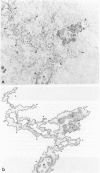
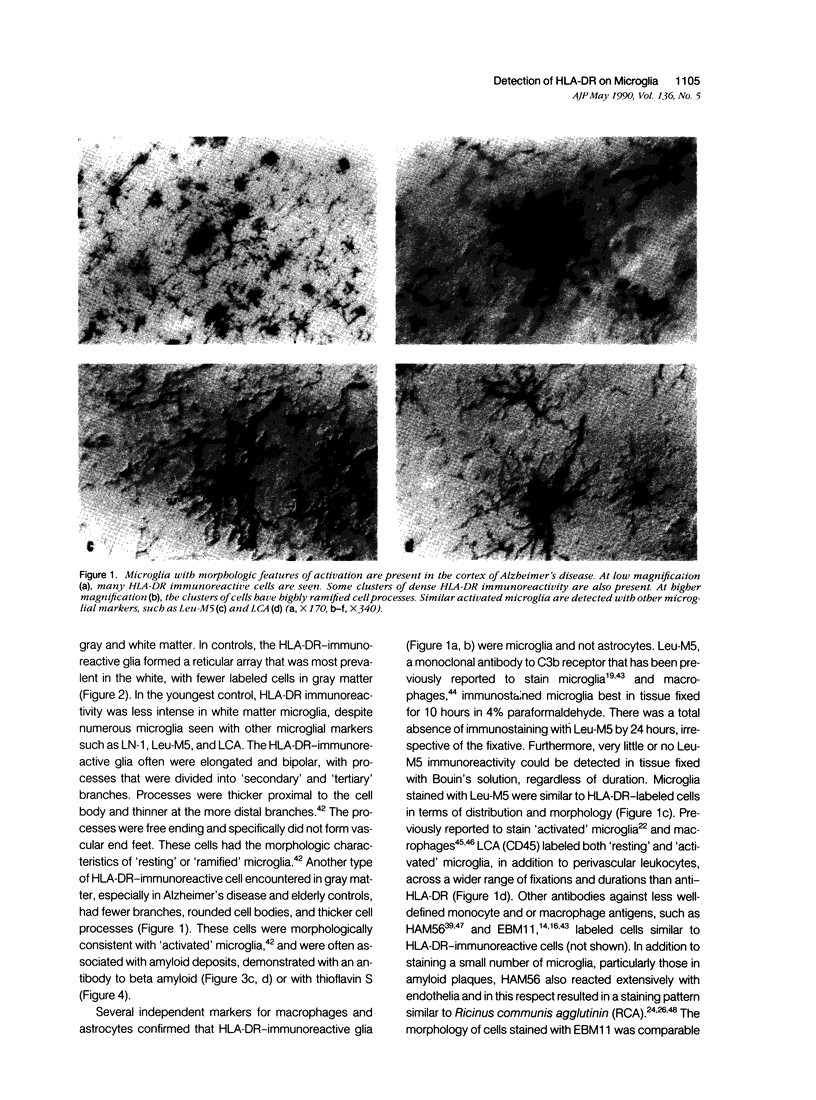
Detection of HLA-DR, a class II major histocompatibility antigen, on glial cells is dependent not only on duration and type of tissue fixation and processing, but also on clinical factors. Glial cells labeled by anti-HLA-DR were consistent with microglia by light microscopic and ultrastructural criteria, and were colabeled with other microglial markers, including LN-1, Leu-M5, and leukocyte common antigen (LCA). In young and elderly subjects who died suddenly, anti-HLA-DR labeled microglia in the white matter, but far fewer cells in the gray matter. In subjects who died of chronic debilitating illness, such as Alzheimer's disease and carcinomatosis, anti-HLA-DR labeled numerous microglia throughout both the gray and white matter. In Alzheimer's disease, microglia were aggregated in compact senile plaques, but loosely associated with diffuse amyloid deposits. These results suggest that HLA-DR may be constitutively expressed in white matter, but induced in gray matter microglia in chronic disease states or in association with amyloid deposits.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bottazzo G. F., Pujol-Borrell R., Hanafusa T., Feldmann M. Role of aberrant HLA-DR expression and antigen presentation in induction of endocrine autoimmunity. Lancet. 1983 Nov 12;2(8359):1115–1119. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90629-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer D. V., Gill T. J., 3rd Genetic aspects of cellular interactions in the immune response. Lab Invest. 1986 Aug;55(2):126–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar A. S., Fuggle S. V., Fabre J. W., Ting A., Morris P. J. The detailed distribution of MHC Class II antigens in normal human organs. Transplantation. 1984 Sep;38(3):293–298. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198409000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Tribolet N., Hamou M. F., Mach J. P., Carrel S., Schreyer M. Demonstration of HLA-DR antigens in normal human brain. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 Apr;47(4):417–418. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.4.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. W., Crystal H., Mattiace L. A., Kress Y., Schwagerl A., Ksiezak-Reding H., Davies P., Yen S. H. Diffuse Lewy body disease: light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry of senile plaques. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;78(6):572–584. doi: 10.1007/BF00691284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. W., Farlo J., Davies P., Crystal H., Fuld P., Yen S. H. Alzheimer's disease. A double-labeling immunohistochemical study of senile plaques. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jul;132(1):86–101. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. W., Mattiace L. A. Astrocytes and microglia in human brain share an epitope recognized by a B-lymphocyte-specific monoclonal antibody (LN-1). Am J Pathol. 1989 Jul;135(1):135–147. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esiri M. M., McGee J. O. Monoclonal antibody to macrophages (EMB/11) labels macrophages and microglial cells in human brain. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jun;39(6):615–621. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.6.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsum U., Claesson K., Hjelm E., Karlsson-Parra A., Klareskog L., Scheynius A., Tjernlund U. Class II transplantation antigens: distribution in tissues and involvement in disease. Scand J Immunol. 1985 May;21(5):389–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank E., Pulver M., de Tribolet N. Expression of class II major histocompatibility antigens on reactive astrocytes and endothelial cells within the gliosis surrounding metastases and abscesses. J Neuroimmunol. 1986 Jul;12(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(86)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin W. A., Mason D. Y., Pulford K., Falini B., Bliss E., Gatter K. C., Stein H., Clarke L. C., McGee J. O. Immunohistological analysis of human mononuclear phagocytes and dendritic cells by using monoclonal antibodies. Lab Invest. 1986 Mar;54(3):322–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gown A. M., Tsukada T., Ross R. Human atherosclerosis. II. Immunocytochemical analysis of the cellular composition of human atherosclerotic lesions. Am J Pathol. 1986 Oct;125(1):191–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga S., Akai K., Ishii T. Demonstration of microglial cells in and around senile (neuritic) plaques in the Alzheimer brain. An immunohistochemical study using a novel monoclonal antibody. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;77(6):569–575. doi: 10.1007/BF00687883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser S. L., Bhan A. K., Gilles F. H., Hoban C. J., Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F., Weiner H. L. Immunohistochemical staining of human brain with monoclonal antibodies that identify lymphocytes, monocytes, and the Ia antigen. J Neuroimmunol. 1983 Oct;5(2):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(83)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi T., Morimoto C., Burks J. S., Kerr C., Hauser S. L. Dual-label immunocytochemistry of the active multiple sclerosis lesion: major histocompatibility complex and activation antigens. Ann Neurol. 1988 Oct;24(4):523–531. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes G. M., Woodroofe M. N., Cuzner M. L. Microglia are the major cell type expressing MHC class II in human white matter. J Neurol Sci. 1987 Aug;80(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(87)90218-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg H., Braathen L. R., Thorsby E. Antigen presentation by vascular endothelial cells and epidermal Langerhans cells: the role of HLA-DR. Immunol Rev. 1982;66:57–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itagaki S., McGeer P. L., Akiyama H. Presence of T-cytotoxic suppressor and leucocyte common antigen positive cells in Alzheimer's disease brain tissue. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Sep 12;91(3):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90690-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ksiezak-Reding H., Dickson D. W., Davies P., Yen S. H. Recognition of tau epitopes by anti-neurofilament antibodies that bind to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3410–3414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtin P. J., Pinkus G. S. Leukocyte common antigen--a diagnostic discriminant between hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic neoplasms in paraffin sections using monoclonal antibodies: correlation with immunologic studies and ultrastructural localization. Hum Pathol. 1985 Apr;16(4):353–365. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(85)80229-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Hickey W. F. Monoclonal antibody analysis of MHC expression in human brain biopsies: tissue ranging from "histologically normal" to that showing different levels of glial tumor involvement. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4054–4062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Arnaout M. A., Schwarting R., Warner N. L., Ross G. D. p150/95, Third member of the LFA-1/CR3 polypeptide family identified by anti-Leu M5 monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jul;15(7):713–718. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luber-Narod J., Rogers J. Immune system associated antigens expressed by cells of the human central nervous system. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Nov 22;94(1-2):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannoji H., Yeger H., Becker L. E. A specific histochemical marker (lectin Ricinus communis agglutinin-1) for normal human microglia, and application to routine histopathology. Acta Neuropathol. 1986;71(3-4):341–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00688060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. Y., Sammons R. E. The labeled antigen method of immunoenzymatic staining. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Apr;27(4):832–840. doi: 10.1177/27.4.109496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., Itagaki S., Boyes B. E., McGeer E. G. Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease brains. Neurology. 1988 Aug;38(8):1285–1291. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.8.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., Itagaki S., McGeer E. G. Expression of the histocompatibility glycoprotein HLA-DR in neurological disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;76(6):550–557. doi: 10.1007/BF00689592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., Itagaki S., Tago H., McGeer E. G. Reactive microglia in patients with senile dementia of the Alzheimer type are positive for the histocompatibility glycoprotein HLA-DR. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Aug 18;79(1-2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E. G., Itagaki S., Mizukawa K. Anatomy and pathology of the basal ganglia. Can J Neurol Sci. 1987 Aug;14(3 Suppl):363–372. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100037756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicol A. M. Class II MHC antigen expression in adrenal cortex. Lancet. 1986 Nov 29;2(8518):1282–1282. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92711-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J. M., Chou S. M. A new immunoperoxidase marker for microglia in paraffin section. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1988 Nov;47(6):579–587. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198811000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natali P. G., De Martino C., Quaranta V., Nicotra M. R., Frezza F., Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S. Expression of Ia-like antigens in normal human nonlymphoid tissues. Transplantation. 1981 Jan;31(1):75–78. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198101000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perentes E., Rubinstein L. J. Immunohistochemical recognition of human neuroepithelial tumors by anti-Leu 7 (HNK-1) monoclonal antibody. Acta Neuropathol. 1986;69(3-4):227–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00688298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Luber-Narod J., Styren S. D., Civin W. H. Expression of immune system-associated antigens by cells of the human central nervous system: relationship to the pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(4):339–349. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(88)80079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi M. L., Cruz-Sanchez F., Hughes J. T., Esiri M. M., Coakham H. B., Moss T. H. Mononuclear cell infiltrate and HLA-DR expression in low grade astrocytomas. An immunohistological study of 23 cases. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;76(3):281–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00687776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Mukai K., Watanabe S., Goto M., Shimosato Y. The AMeX method. A simplified technique of tissue processing and paraffin embedding with improved preservation of antigens for immunostaining. Am J Pathol. 1986 Dec;125(3):431–435. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snary D., Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Goodfellow P. N., Crumpton M. J. Cellular distrubtion, purification, and molecular nature of human Ia antigens. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(5):439–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb02101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel R. A., Ames M. B. Major histocompatibility complex molecule expression in the human central nervous system: immunohistochemical analysis of 40 patients. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1988 Jan;47(1):19–28. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198801000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Franz H., Yamamoto T., Iwasaki Y., Konno H. Identification of the normal microglial population in human and rodent nervous tissue using lectin-histochemistry. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1988 May-Jun;14(3):221–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1988.tb00883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzumura A., Mezitis S. G., Gonatas N. K., Silberberg D. H. MHC antigen expression on bulk isolated macrophage-microglia from newborn mouse brain: induction of Ia antigen expression by gamma-interferon. J Neuroimmunol. 1987 Jul-Aug;15(3):263–278. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(87)90121-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugott U., Lebon P. Interferon-gamma and Ia antigen are present on astrocytes in active chronic multiple sclerosis lesions. J Neurol Sci. 1988 Apr;84(2-3):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(88)90130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugott U. Multiple sclerosis: relevance of class I and class II MHC-expressing cells to lesion development. J Neuroimmunol. 1987 Oct;16(2):283–302. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(87)90082-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnke R. A., Gatter K. C., Falini B., Hildreth P., Woolston R. E., Pulford K., Cordell J. L., Cohen B., De Wolf-Peeters C., Mason D. Y. Diagnosis of human lymphoma with monoclonal antileukocyte antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1983 Nov 24;309(21):1275–1281. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198311243092102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolozin B. L., Pruchnicki A., Dickson D. W., Davies P. A neuronal antigen in the brains of Alzheimer patients. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):648–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3083509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Bartlett P. F., Clark-Lewis I., McKimm-Breschkin J. L., Schrader J. W. Interferon-gamma induces the expression of H-2 and Ia antigens on brain cells. J Neuroimmunol. 1985 Feb-Mar;7(5-6):255–278. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(84)80026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Crowe A., Dickson D. W. Monoclonal antibodies to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. 1. Identification of polypeptides. Am J Pathol. 1985 Aug;120(2):282–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]