Abstract
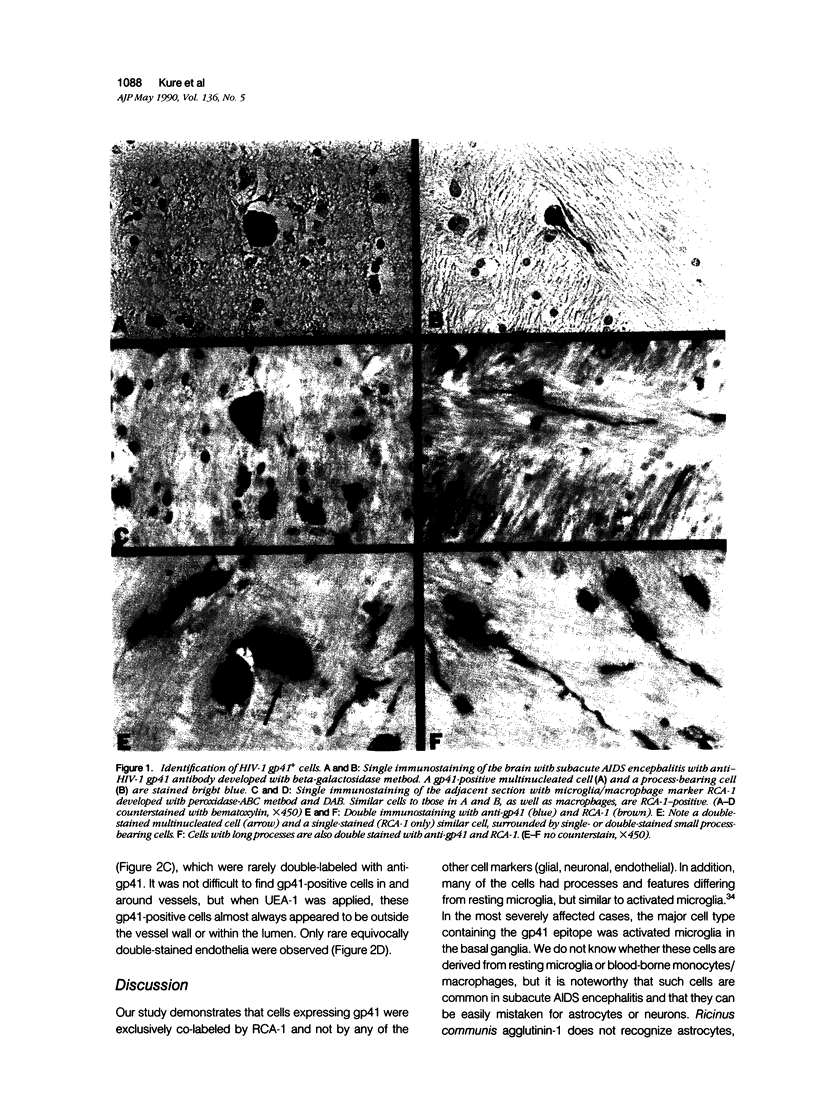
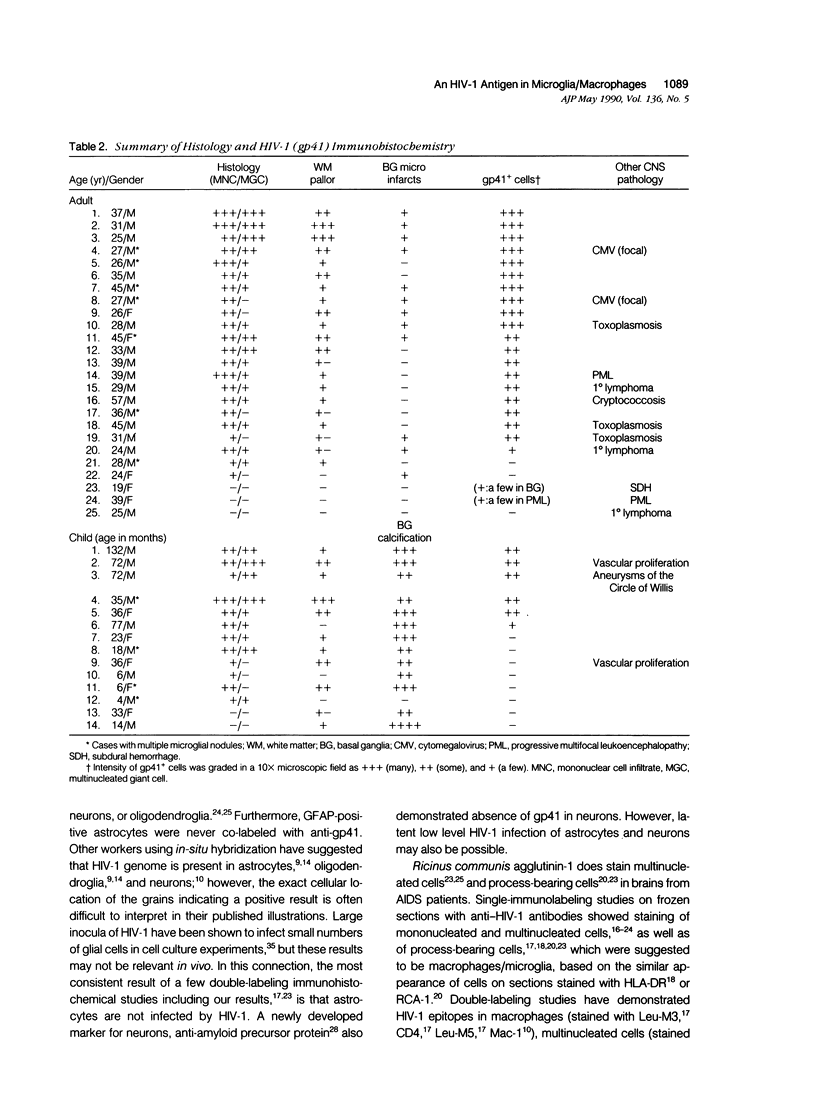
Among 102 brains obtained from patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS), 34 cases with subacute AIDS encephalitis were characterized by immunohistochemistry using an antibody that binds to a human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) envelope glycoprotein, gp41. This glycoprotein was detected in mononucleated and/or multinucleated cells in 90% of adult and 50% of pediatric brains with subacute AIDS encephalitis. In addition, many gp41-positive cells with bipolar or multipolar processes were found in 10 cases, and these cells occurred most frequently in the basal ganglia and internal capsule. The phenotype of the gp41-positive cells was determined using an improved double-labeling immunohistochemical technique that employed beta-galactosidase and peroxidase conjugated reagents. Cell-type specific markers for double-labeling included: Ricinus communis agglutinin-1 (RCA-1) for macrophages and microglia; Ulex europaeus agglutinin-1 for endothelium; anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) for astrocytes; anti-amyloid precursor protein for neurons; and anti-leukocyte common antigen for leukocytes. Results of double-immunostaining revealed that gp41-positive cells of all morphologic types, including cells with bipolar or multipolar processes, were double-labeled with RCA-1, but not with markers for astrocytes, neurons, or endothelia. These findings support the contention that HIV-1 infection of the CNS is predominantly restricted to cells of the macrophage/microglia lineage.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belman A. L., Lantos G., Horoupian D., Novick B. E., Ultmann M. H., Dickson D. W., Rubinstein A. AIDS: calcification of the basal ganglia in infants and children. Neurology. 1986 Sep;36(9):1192–1199. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.9.1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budka H., Costanzi G., Cristina S., Lechi A., Parravicini C., Trabattoni R., Vago L. Brain pathology induced by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). A histological, immunocytochemical, and electron microscopical study of 100 autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol. 1987;75(2):185–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00687080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budka H. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-induced disease of the central nervous system: pathology and implications for pathogenesis. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;77(3):225–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00687573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Rutka J. T., Rosenblum M. L., McHugh T., Stites D. P., Levy J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus can productively infect cultured human glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. W., Belman A. L., Park Y. D., Wiley C., Horoupian D. S., Llena J., Kure K., Lyman W. D., Morecki R., Mitsudo S. Central nervous system pathology in pediatric AIDS: an autopsy study. APMIS Suppl. 1989;8:40–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. W., Mattiace L. A. Astrocytes and microglia in human brain share an epitope recognized by a B-lymphocyte-specific monoclonal antibody (LN-1). Am J Pathol. 1989 Jul;135(1):135–147. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. W. Multinucleated giant cells in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome encephalopathy. Origin from endogenous microglia? Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986 Oct;110(10):967–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabuzda D. H., Ho D. D., de la Monte S. M., Hirsch M. S., Rota T. R., Sobel R. A. Immunohistochemical identification of HTLV-III antigen in brains of patients with AIDS. Ann Neurol. 1986 Sep;20(3):289–295. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyorkey F., Melnick J. L., Gyorkey P. Human immunodeficiency virus in brain biopsies of patients with AIDS and progressive encephalopathy. J Infect Dis. 1987 May;155(5):870–876. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.5.870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kure K., Park Y. D., Kim T. S., Lyman W. D., Lantos G., Lee S., Cho S., Belman A. L., Weidenheim K. M., Dickson D. W. Immunohistochemical localization of an HIV epitope in cerebral aneurysmal arteriopathy in pediatric acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Pediatr Pathol. 1989;9(6):655–667. doi: 10.3109/15513818909022373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang W., Miklossy J., Deruaz J. P., Pizzolato G. P., Probst A., Schaffner T., Gessaga E., Kleihues P. Neuropathology of the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS): a report of 135 consecutive autopsy cases from Switzerland. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;77(4):379–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00687372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannoji H., Yeger H., Becker L. E. A specific histochemical marker (lectin Ricinus communis agglutinin-1) for normal human microglia, and application to routine histopathology. Acta Neuropathol. 1986;71(3-4):341–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00688060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattiace L. A., Davies P., Dickson D. W. Detection of HLA-DR on microglia in the human brain is a function of both clinical and technical factors. Am J Pathol. 1990 May;136(5):1101–1114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., Itagaki S., Boyes B. E., McGeer E. G. Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease brains. Neurology. 1988 Aug;38(8):1285–1291. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.8.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels J., Price R. W., Rosenblum M. K. Microglia in the giant cell encephalitis of acquired immune deficiency syndrome: proliferation, infection and fusion. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;76(4):373–379. doi: 10.1007/BF00686974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J. M., Chou S. M. A new immunoperoxidase marker for microglia in paraffin section. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1988 Nov;47(6):579–587. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198811000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgello S., Cho E. S., Nielsen S., Devinsky O., Petito C. K. Cytomegalovirus encephalitis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: an autopsy study of 30 cases and a review of the literature. Hum Pathol. 1987 Mar;18(3):289–297. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(87)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K. Simultaneous localization of multiple tissue antigens using the peroxidase-labeled antibody method: a study on pituitary glands of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 Sep;16(9):557–560. doi: 10.1177/16.9.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peluso R., Haase A., Stowring L., Edwards M., Ventura P. A Trojan Horse mechanism for the spread of visna virus in monocytes. Virology. 1985 Nov;147(1):231–236. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petito C. K., Cho E. S., Lemann W., Navia B. A., Price R. W. Neuropathology of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS): an autopsy review. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1986 Nov;45(6):635–646. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198611000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Brew B., Sidtis J., Rosenblum M., Scheck A. C., Cleary P. The brain in AIDS: central nervous system HIV-1 infection and AIDS dementia complex. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):586–592. doi: 10.1126/science.3277272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumarola-Sune T., Navia B. A., Cordon-Cardo C., Cho E. S., Price R. W. HIV antigen in the brains of patients with the AIDS dementia complex. Ann Neurol. 1987 May;21(5):490–496. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes R. H. Histopathology of the central nervous system in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Hum Pathol. 1987 Jun;18(6):636–643. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(87)80365-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostad S. W., Sumi S. M., Shaw C. M., Olson K., McDougall J. K. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection in brains with AIDS-related leukoencephalopathy. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987;3(4):363–373. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. M., Harper M. E., Hahn B. H., Epstein L. G., Gajdusek D. C., Price R. W., Navia B. A., Petito C. K., O'Hara C. J., Groopman J. E. HTLV-III infection in brains of children and adults with AIDS encephalopathy. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.2981429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoler M. H., Eskin T. A., Benn S., Angerer R. C., Angerer L. M. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III infection of the central nervous system. A preliminary in situ analysis. JAMA. 1986 Nov 7;256(17):2360–2364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazeux R., Brousse N., Jarry A., Henin D., Marche C., Vedrenne C., Mikol J., Wolff M., Michon C., Rozenbaum W. AIDS subacute encephalitis. Identification of HIV-infected cells. Am J Pathol. 1987 Mar;126(3):403–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. G., Itagaki S., Berry K., McGeer P. L. Examination of brains of AIDS cases for human immunodeficiency virus and human cytomegalovirus nucleic acids. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989 May;52(5):583–590. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.52.5.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Grafe M., Kennedy C., Nelson J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and JC virus in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;76(4):338–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00686970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Nelson J. A. Role of human immunodeficiency virus and cytomegalovirus in AIDS encephalitis. Am J Pathol. 1988 Oct;133(1):73–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Schrier R. D., Nelson J. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Cellular localization of human immunodeficiency virus infection within the brains of acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7089–7093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Crowe A., Dickson D. W. Monoclonal antibodies to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. 1. Identification of polypeptides. Am J Pathol. 1985 Aug;120(2):282–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Monte S. M., Ho D. D., Schooley R. T., Hirsch M. S., Richardson E. P., Jr Subacute encephalomyelitis of AIDS and its relation to HTLV-III infection. Neurology. 1987 Apr;37(4):562–569. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.4.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]